The African Black-Bellied Pangolin: A Critically Endangered Species
The African black-bellied pangolin ( Phataginus tetradactyla ) is a fascinating creature and one of the eight pangolin species found in Africa. These solitary, nocturnal mammals are known for their unique features, including their scaly armor, long prehensile tails, and powerful claws. Despite their intriguing characteristics, they are facing severe threats, leading to a critical decline in their populations. This article will delve into the world of the African black-bellied pangolin, exploring its biology, habitat, behavior, and conservation efforts.
Unveiling the Mysteries of the African Black-Bellied Pangolin
The African black-bellied pangolin is a medium-sized pangolin, typically weighing between 4 and 8 kg. It has a distinctive black or dark brown body covered in overlapping scales, which are actually modified hair. Its head is small and elongated, with a long, sticky tongue used to catch ants and termites, its primary food source. The pangolin’s tail is incredibly strong, serving as a counterbalance while climbing and a defense mechanism when threatened. The African black-bellied pangolin is found in various regions of Central and West Africa, spanning countries like Nigeria, Cameroon, Ghana, and Gabon.
A Solitary Existence in the Rainforest
The African black-bellied pangolin prefers humid, dense rainforests as its habitat. These forests provide ample opportunities for foraging and offer protection from predators. They are primarily nocturnal, spending their days sleeping in tree cavities or underground burrows. Their solitary nature, coupled with their excellent camouflage, makes them difficult to spot in the wild.
Foraging for Ants and Termites
The African black-bellied pangolin’s diet consists almost entirely of ants and termites. Its long, sticky tongue, which can extend up to 25 cm, is a marvel of nature. Equipped with tiny backward-pointing barbs, it allows the pangolin to efficiently lick up its prey. Powerful claws help the pangolin dig into termite mounds and ant nests, gaining access to its food source.
The Importance of Pangolins to the Ecosystem
The African black-bellied pangolin plays a crucial role in maintaining the health of the rainforest ecosystem. Their diet of ants and termites helps control their populations, preventing overgrazing and ensuring the balance of the forest floor. Pangolins also contribute to soil aeration and nutrient cycling through their digging activities, promoting healthy growth of vegetation.
Threats to Pangolin Survival
The African black-bellied pangolin faces a multitude of threats, leading to its status as critically endangered.
- Habitat Loss and Degradation: Deforestation and agricultural expansion continue to encroach upon their natural habitat, forcing them to compete for limited resources.
- Hunting and Trafficking: Pangolins are highly sought after in traditional medicine markets, particularly in Asia. The demand for their scales, flesh, and other body parts has fuelled illegal hunting and trafficking, decimating their populations.
- Disease and Parasites: Pangolins can be susceptible to diseases and parasites that can weaken their immune systems, making them more vulnerable to predators and further accelerating their decline.
Conservation Efforts: A Race Against Time
The conservation of the African black-bellied pangolin requires immediate action. Numerous conservation efforts are underway to protect this species from extinction.
- Protected Areas: Establishing and managing protected areas within their range provides safe havens for pangolins.
- Anti-Poaching Initiatives: Combating poaching activities through stricter enforcement of wildlife laws, public awareness campaigns, and community engagement is essential.
- Research and Monitoring: Research on pangolin biology, ecology, and conservation strategies is crucial to inform effective conservation measures.
- Community Engagement: Involving local communities in conservation efforts, particularly those living near pangolin habitats, is crucial for ensuring long-term success.
Expert Insight
“The African black-bellied pangolin is a charismatic and unique creature that plays a vital role in the rainforest ecosystem. Their decline is a stark reminder of the dire consequences of habitat loss, unsustainable hunting practices, and the illegal wildlife trade.” – Dr. Jane Ngugi, Conservation Biologist
“Protecting this remarkable species requires a multi-pronged approach, involving strong legislation, collaborative conservation efforts, and public awareness campaigns. We must act now to prevent the extinction of this fascinating creature.” – Professor David Thompson, Wildlife Ecologist
Conclusion
The African black-bellied pangolin is a magnificent animal that deserves our protection. Its future depends on our collective efforts to address the threats it faces. Conservationists, policymakers, and individuals must work together to protect its habitat, combat poaching, and raise awareness about its plight. By taking action today, we can ensure that future generations have the opportunity to witness the wonder of this truly remarkable creature.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the African black-bellied pangolin’s lifespan in the wild? The average lifespan of an African black-bellied pangolin in the wild is estimated to be around 10-15 years.
- Why are pangolins considered “living fossils”? Pangolins are often referred to as “living fossils” due to their ancient lineage and their unique physical characteristics, which have changed relatively little over millions of years.
- Are pangolins venomous? No, pangolins are not venomous. They do not possess any venom glands or fangs.
- How can I help in pangolin conservation? You can support pangolin conservation by donating to reputable organizations, advocating for their protection, and avoiding products made from pangolin parts.
- What is the best way to report suspected pangolin poaching or trafficking? Contact your local wildlife authorities or conservation organizations.
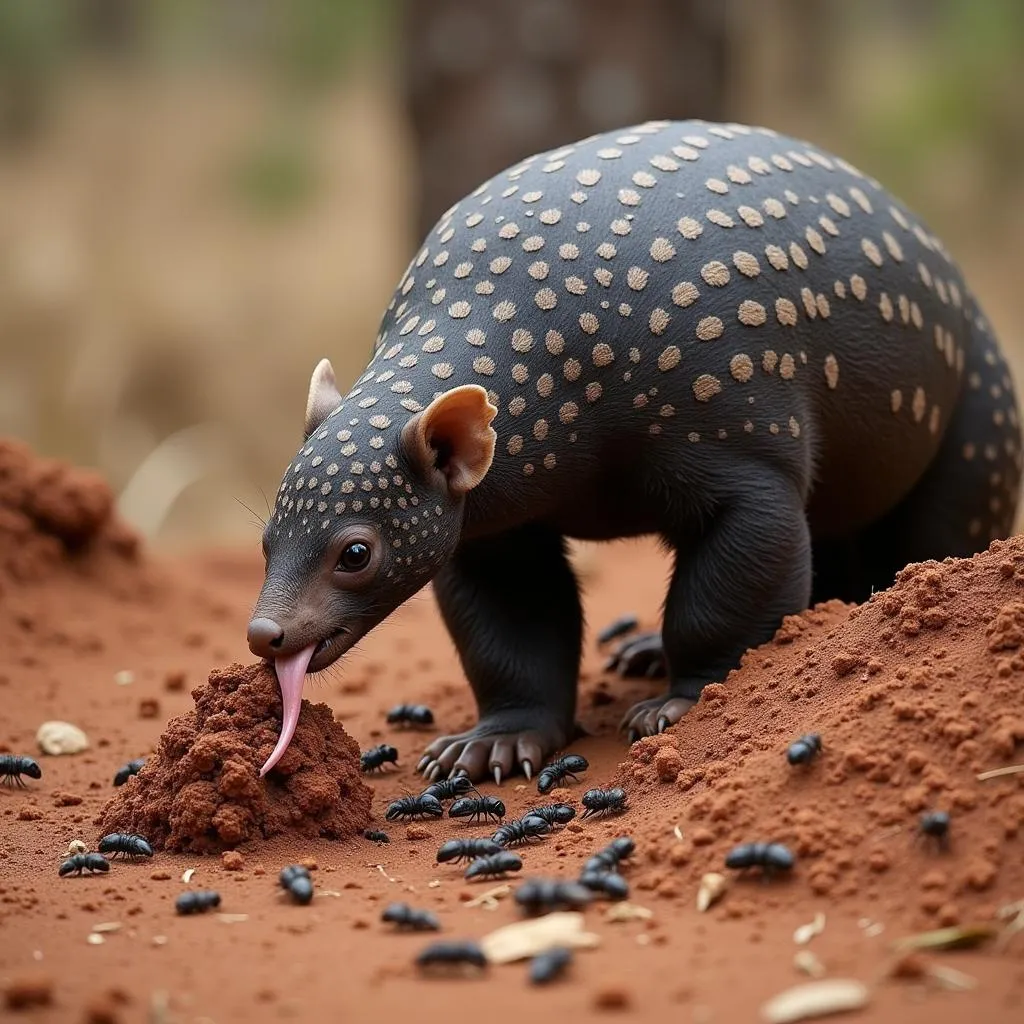 African Black-Bellied Pangolin Eating Ants
African Black-Bellied Pangolin Eating Ants
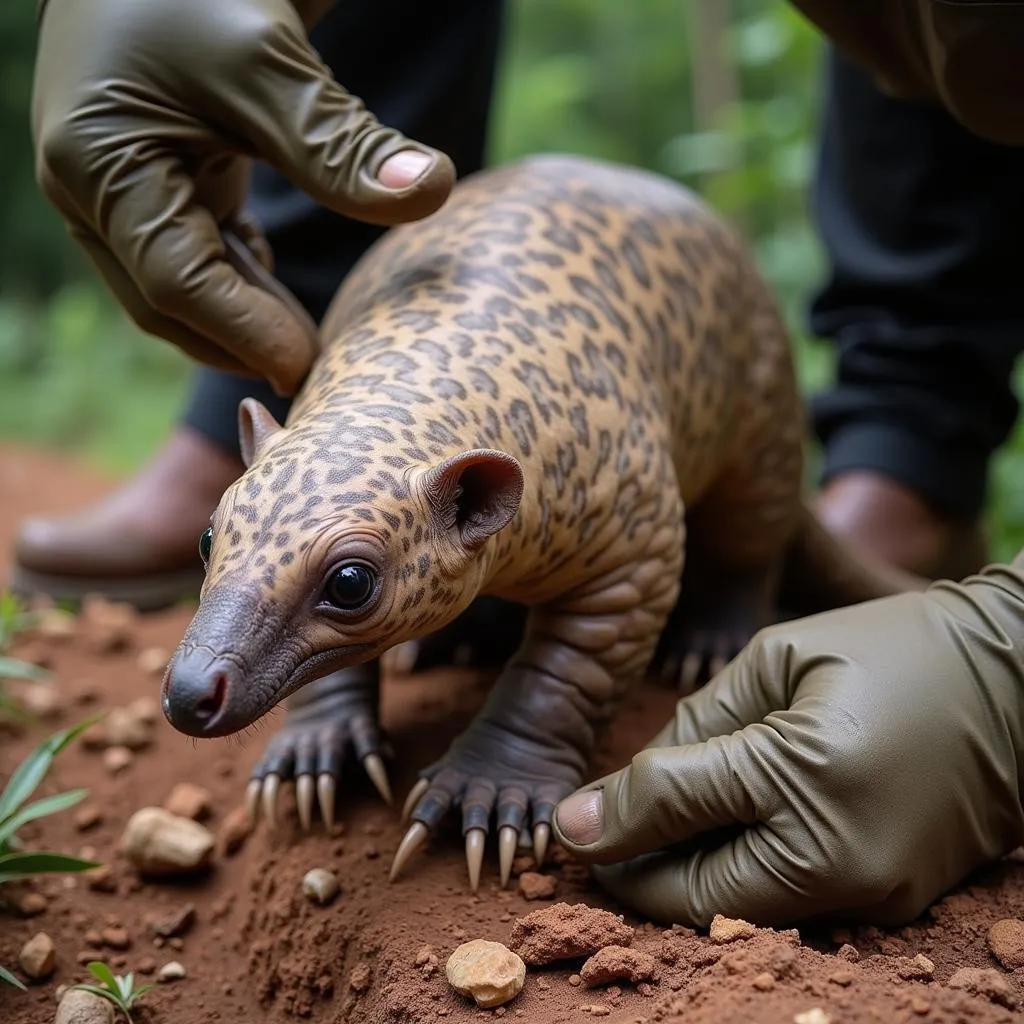 African Black-Bellied Pangolin Being Rescued from Trafficking
African Black-Bellied Pangolin Being Rescued from Trafficking
For more information on African black-bellied pangolins and how to help, please contact us at +255768904061, kaka.mag@gmail.com, or visit us at Mbarali DC Mawindi, Kangaga, Tanzania. We have a 24/7 customer service team available to assist you.