The African Concept of Conflict Resolution
Conflict is an inevitable part of human existence, and African societies are no strangers to it. However, the African approach to conflict resolution stands out for its emphasis on harmony, reconciliation, and restoring balance within the community. Unlike Western models that often prioritize individualism and legalistic solutions, African conflict resolution draws upon a rich tapestry of cultural values, spiritual beliefs, and traditional practices that prioritize consensus-building and healing.
One of the core tenets of the African Concept Of Conflict Resolution is the understanding that conflict is not solely a negative occurrence. Instead, it is seen as an opportunity for growth, transformation, and strengthening community bonds. This perspective encourages parties in conflict to approach the situation with a spirit of understanding and a willingness to find common ground.
The Role of Ubuntu in African Conflict Resolution
Central to the African worldview is the concept of “Ubuntu,” a Nguni Bantu term that roughly translates to “humanity towards others.” It encapsulates the interconnectedness of individuals within a community and emphasizes the importance of empathy, compassion, and respect in all interactions. In the context of conflict resolution, Ubuntu encourages parties to recognize their shared humanity and seek solutions that benefit all involved. It fosters a sense of collective responsibility for resolving disputes and emphasizes the restoration of harmonious relationships over individual victory.
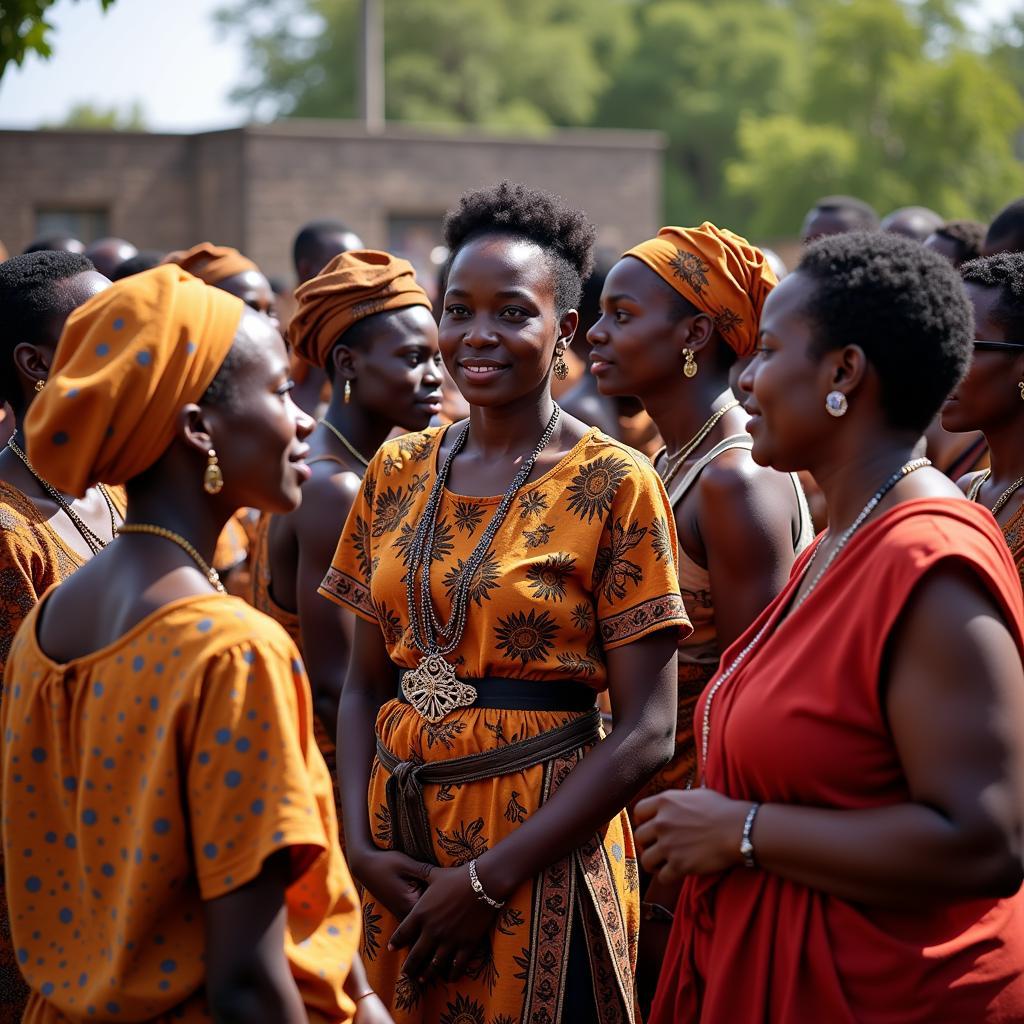 A large gathering of people from an African community, possibly for a celebration or an important event Ubuntu also underpins the significance of community involvement in African conflict resolution. Rather than relying solely on external mediators or formal legal systems, traditional African societies often turn to respected elders, community leaders, or family members to facilitate dialogue and guide parties towards reconciliation.
A large gathering of people from an African community, possibly for a celebration or an important event Ubuntu also underpins the significance of community involvement in African conflict resolution. Rather than relying solely on external mediators or formal legal systems, traditional African societies often turn to respected elders, community leaders, or family members to facilitate dialogue and guide parties towards reconciliation.
Traditional Methods of Conflict Resolution in Africa
African cultures boast a diverse array of traditional conflict resolution methods, each tailored to the specific cultural context. Some common approaches include:
- Palaver: A widely practiced method involving a facilitated dialogue between disputing parties, often led by elders or chiefs. The emphasis is on open communication, active listening, and finding a mutually agreeable solution.
- Mediation: Similar to palaver, mediation involves a neutral third party who assists in facilitating communication and finding a compromise. Mediators are often respected figures within the community known for their wisdom and impartiality.
- Rituals and Ceremonies: Some cultures employ rituals or ceremonies to address conflict and restore harmony. These practices can involve symbolic actions, offerings, or prayers aimed at appeasing ancestors or seeking spiritual guidance.
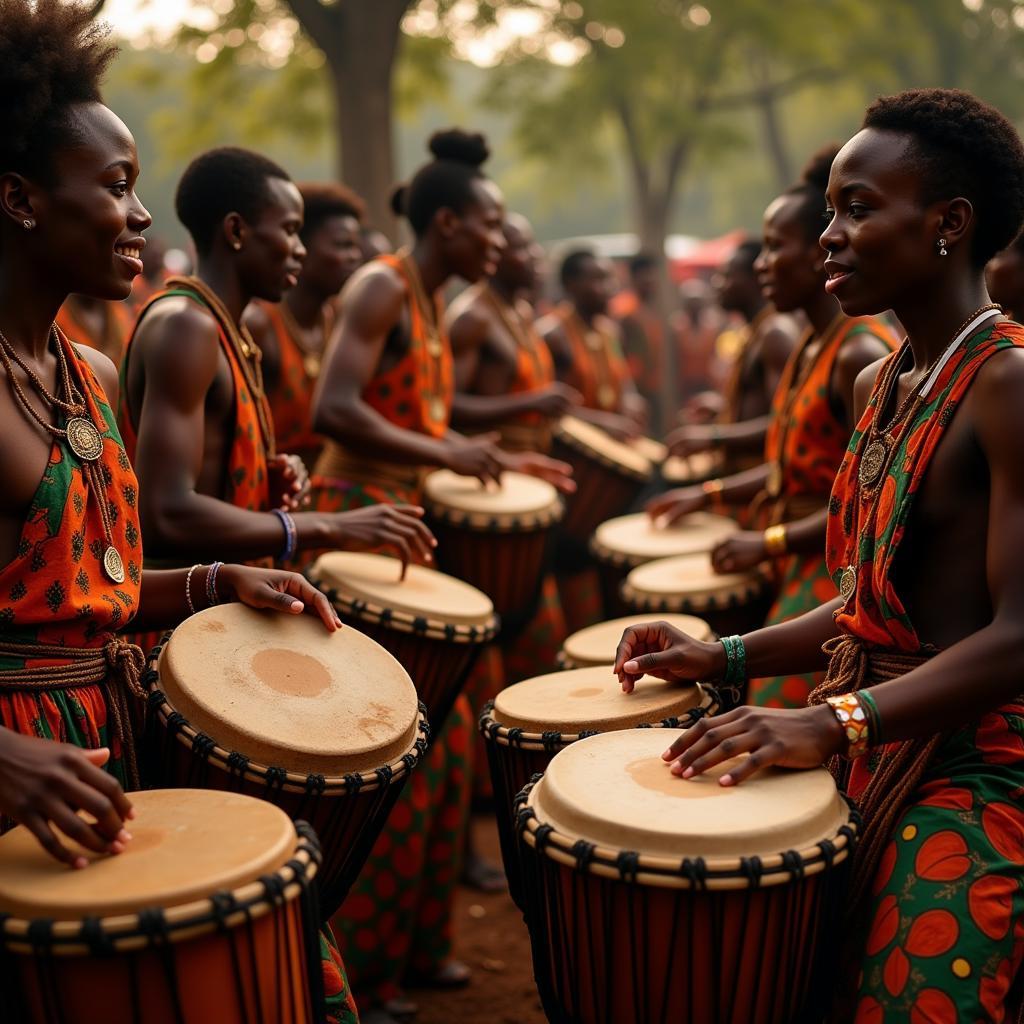 A group of people playing drums in a rhythmic pattern, possibly as part of a traditional African ceremony These methods, often passed down through generations, highlight the value placed on collective wisdom, community involvement, and the restoration of balance and harmony.
A group of people playing drums in a rhythmic pattern, possibly as part of a traditional African ceremony These methods, often passed down through generations, highlight the value placed on collective wisdom, community involvement, and the restoration of balance and harmony.
The Enduring Relevance of African Conflict Resolution
In an increasingly globalized world grappling with complex conflicts, the African concept of conflict resolution offers valuable insights. Its emphasis on dialogue, consensus-building, and community healing provides a refreshing alternative to adversarial approaches that often exacerbate divisions. The principles of Ubuntu, with its focus on interconnectedness and empathy, hold particular relevance in addressing contemporary challenges that transcend national borders and cultural differences.
By embracing the values of empathy, understanding, and community involvement, we can draw inspiration from African traditions to foster a more peaceful and harmonious world.
FAQ
- What is the core principle behind African conflict resolution?
- The core principle is Ubuntu, emphasizing interconnectedness, empathy, and community harmony.
- How is conflict perceived in African cultures?
- Conflict is seen as an opportunity for growth, transformation, and strengthening community bonds.
- Who typically mediates conflicts in African societies?
- Respected elders, community leaders, or family members often facilitate dialogue and guide parties towards reconciliation.
- What are some traditional methods of conflict resolution in Africa?
- Common methods include palaver, mediation, and rituals or ceremonies.
- Why is the African concept of conflict resolution relevant today?
- It offers valuable insights for addressing complex conflicts in an increasingly globalized world, emphasizing dialogue, consensus-building, and community healing.
Do you have other questions about African culture?
For more information on this topic and other aspects of African Life, explore these articles:
Need help understanding African cultural concepts or practices?
Get in touch with us!
Contact us:
- Phone: +255768904061
- Email: [email protected]
- Address: Mbarali DC Mawindi, Kangaga, Tanzania
We have a 24/7 customer support team ready to assist you.




