Unveiling the Giants: African Elephant Physical Characteristics
The African elephant, an iconic symbol of Africa, commands attention with its sheer size and magnificent features. Understanding the African Elephant Physical Characteristics unveils a fascinating world of adaptations that allow these gentle giants to thrive in diverse habitats. From their towering height to their surprisingly agile trunks, every aspect of their physique plays a crucial role in their survival.
Size and Weight: True Titans of the Savanna
African elephants are the largest land mammals on Earth. Their colossal size is one of the most distinguishing African elephant physical characteristics. Males, known as bulls, are larger than females, or cows. An adult bull can reach a shoulder height of up to 4 meters (13 feet), while cows average around 2.7 meters (8.9 feet). This difference in size is also reflected in their weight. Bulls can weigh up to 6,000 kilograms (13,200 pounds), almost twice as much as cows, which typically weigh around 3,000 kilograms (6,600 pounds).
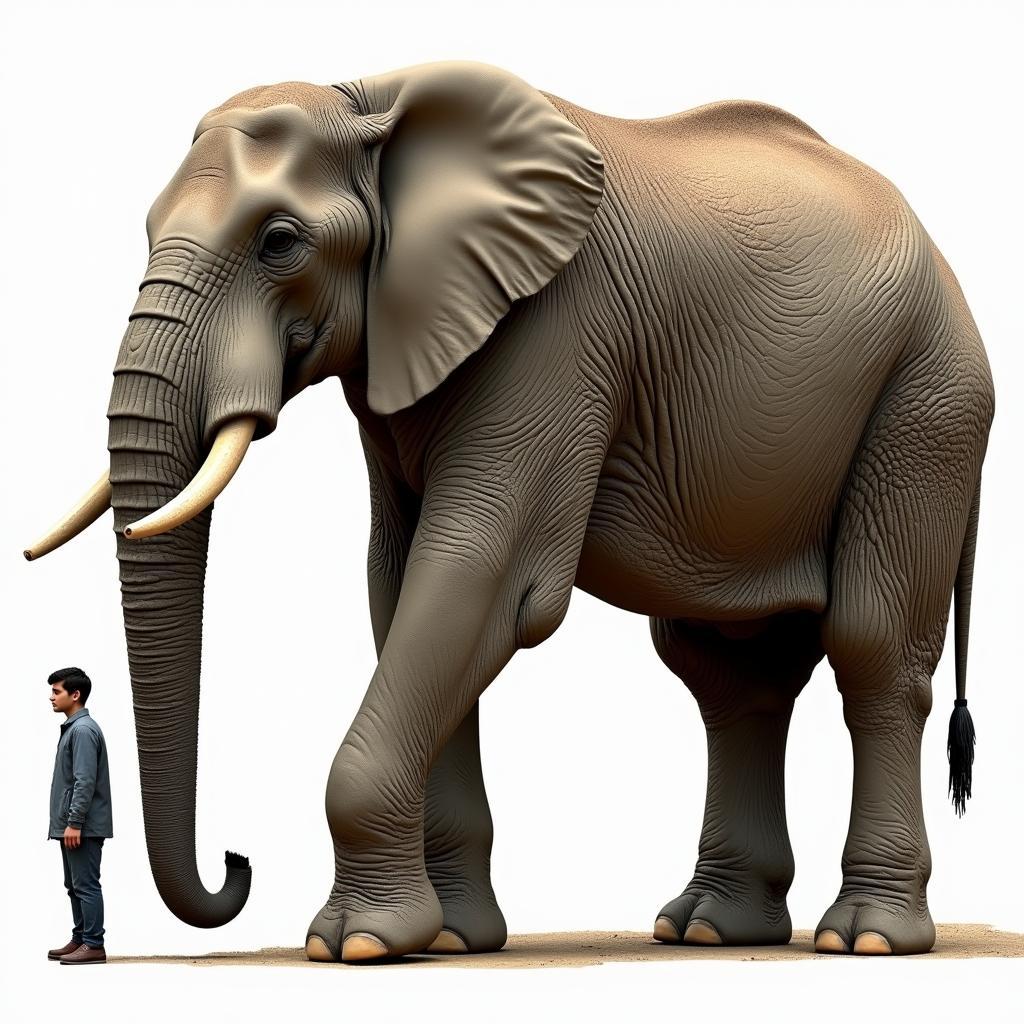 African Elephant Size Comparison
African Elephant Size Comparison
The Trunk: A Multi-Purpose Marvel
The trunk is arguably the most remarkable of all African elephant physical characteristics. This fusion of nose and upper lip is a highly sensitive and muscular organ with over 40,000 muscles. It’s used for a wide array of tasks, from breathing and smelling to trumpeting and touching. Elephants use their trunks to pluck leaves and grasses, dig for water and minerals, and even to communicate with each other through a complex language of rumbles, trumpets, and snorts.
Tusks: More Than Just Ivory
Both male and female African elephants possess tusks, which are elongated incisor teeth. These ivory tusks are another prominent African elephant physical characteristics, growing throughout their lifetime. Elephants use their tusks for a variety of purposes, including digging for water and minerals, stripping bark from trees, and defense against predators or rivals. Sadly, these magnificent tusks have also made them a target for poachers, leading to a decline in elephant populations.
Ears: Hearing Giants
African elephants are renowned for their large, fan-shaped ears, another distinctive African elephant physical characteristics. These ears are not just for show; they play a vital role in thermoregulation. The extensive network of blood vessels in their ears helps them to radiate heat, keeping them cool in the scorching African sun. Elephants can also flap their ears to create air currents and further enhance cooling.
Skin and Color: A Rugged Exterior
African elephants have thick, gray skin that is covered in wrinkles and creases. This rugged hide protects them from the sun, insects, and even minor injuries. While their skin appears gray, it can also have a reddish or brownish tinge depending on the soil in their habitat.
Feet: Designed for Stability
Despite their massive size, African elephants are surprisingly agile and can move almost silently through the bush. This is due in part to their large, padded feet. The soles of their feet are composed of a thick layer of fibrous tissue and fat, which acts as a shock absorber and allows them to distribute their weight evenly.
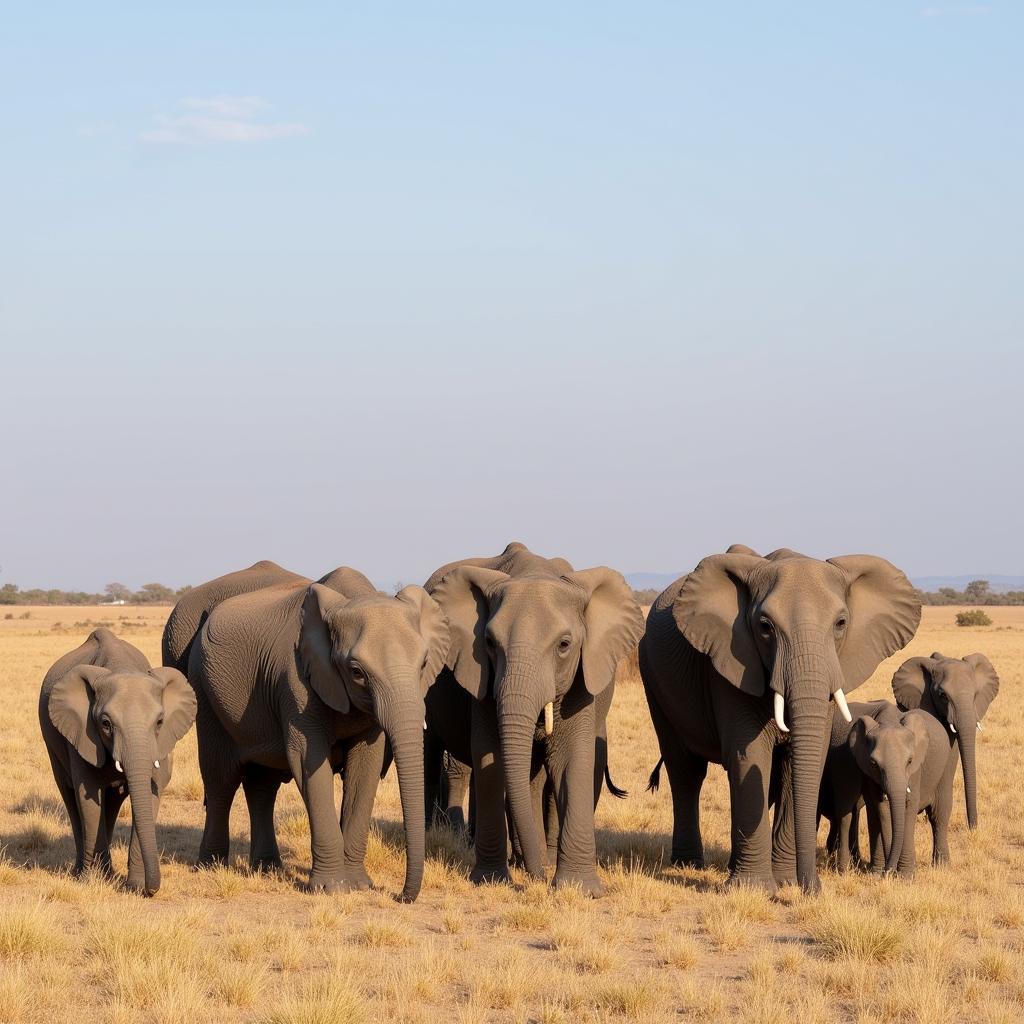 African Elephant Family Group
African Elephant Family Group
Understanding African Elephant Physical Characteristics: A Window into Their World
By exploring the African elephant physical characteristics, we gain a deeper appreciation for these magnificent creatures and their remarkable adaptations. Their size, trunk, tusks, ears, skin, and feet all play a crucial role in their survival, enabling them to thrive in diverse habitats across Africa. As we continue to learn more about these gentle giants, it is our responsibility to protect them and ensure their survival for generations to come.
FAQs: African Elephant Physical Characteristics
1. What is the most unique physical characteristic of an African elephant?
While all features are important, the trunk stands out as the most unique. Its versatility and dexterity are unmatched in the animal kingdom.
2. Do all African elephants have tusks?
Yes, both male and female African elephants have tusks. However, there are some populations where tusks are less common due to poaching pressure.
3. Why are African elephant ears so big?
Their large ears are primarily for thermoregulation, helping them to radiate heat and stay cool in hot climates.
4. How can you tell the difference between an African elephant and an Asian elephant?
African elephants are generally larger and have larger ears than Asian elephants. They also have concave backs, while Asian elephants have convex backs. Additionally, their tusks and trunk shapes differ.
5. How do African elephant feet support their weight?
Their large, padded feet have a thick layer of fibrous tissue and fat that acts as a shock absorber, distributing their weight evenly.
Need further assistance? Contact us at Phone Number: +255768904061, Email: [email protected] Or visit us at: Mbarali DC Mawindi, Kangaga, Tanzania. Our customer service team is available 24/7.


