Majestic African Animal with Long Horns: A Closer Look
Africa, a land of diverse wildlife, is home to some of the most fascinating creatures on earth. Among them are several magnificent African Animal With Long Horns, each with unique characteristics and adaptations. These impressive horns serve various purposes, from defense against predators to establishing dominance within their social hierarchies. Let’s delve into the world of these horned wonders.
The most iconic african animal with long horns are undoubtedly the various antelope species. From the majestic kudu with its spiraling horns to the nimble impala with its lyre-shaped appendages, these animals have captivated wildlife enthusiasts for centuries. The horns, primarily found in males, play a crucial role in their social dynamics, particularly during mating season. african deer springbok offers an insight to the springbok.
Unveiling the Secrets of African Horned Animals
Horns are not just ornamental; they are essential tools for survival in the harsh African landscape. For example, the strong, sharp horns of the oryx are effective weapons against lions and other predators. Similarly, the robust horns of the african baffalow, while not particularly long, are formidable defensive tools. african baffalow further explains their significance.
The Role of Horns in Social Hierarchy
Within herds of african jungle animals in herds, horns often determine dominance. Males with larger, more impressive horns are more likely to attract mates and establish their position within the herd. This competition can lead to dramatic displays of strength and agility as males lock horns in fierce battles for supremacy. african jungle animals in herds showcases the dynamic of these herds.
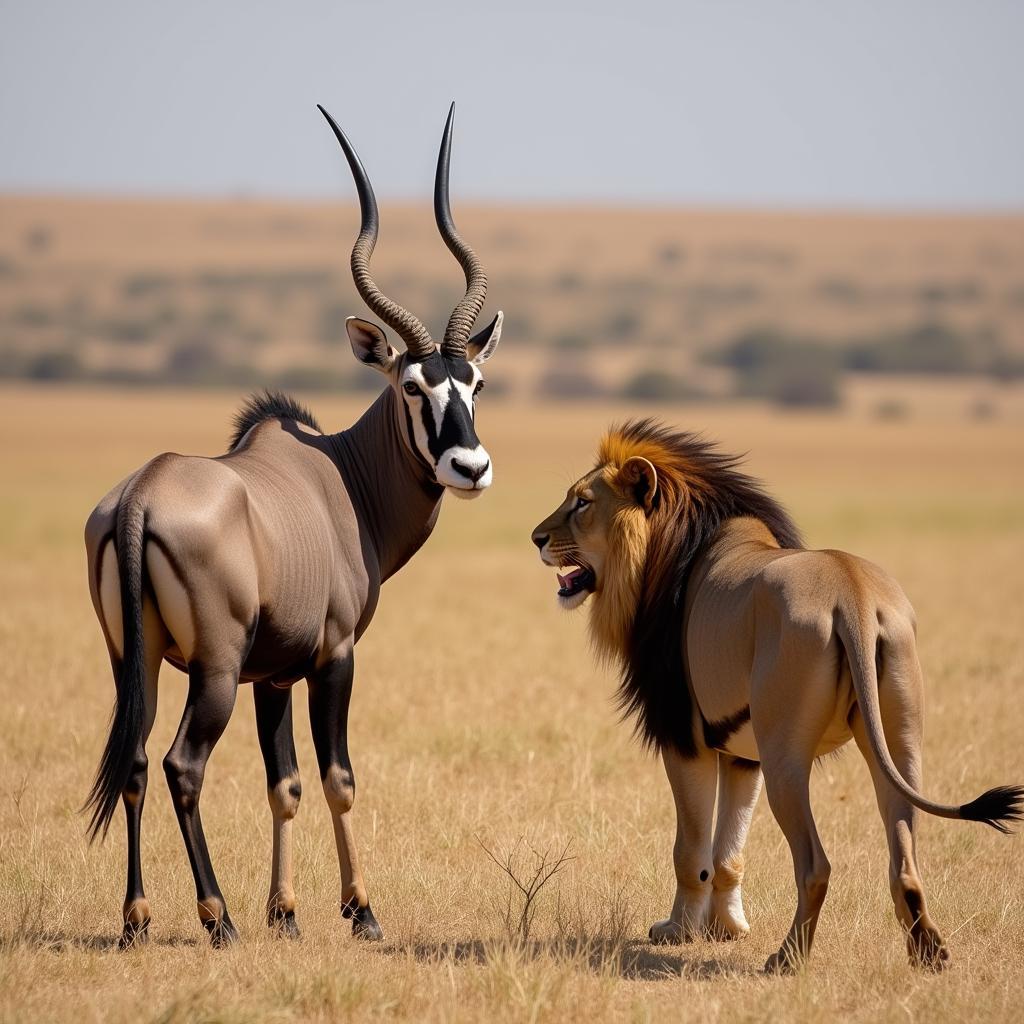 Oryx Defending Against Lion
Oryx Defending Against Lion
Why Do Some African Animals Have Long Horns?
The development of long horns in African animals is a result of millions of years of evolution. Natural selection favors individuals with traits that enhance their survival and reproductive success. Long horns provide a distinct advantage in both defense and competition, making them a valuable asset in the struggle for survival.
How Do These Horns Grow?
Unlike antlers, which are shed annually, horns are permanent structures made of keratin, the same material that makes up human fingernails. They grow continuously throughout an animal’s life, gradually increasing in size and impressive stature. Interestingly, the african elephant body parts, though lacking horns, exhibit a similar keratinous structure in their tusks. More information regarding this can be found in african elephant body parts.
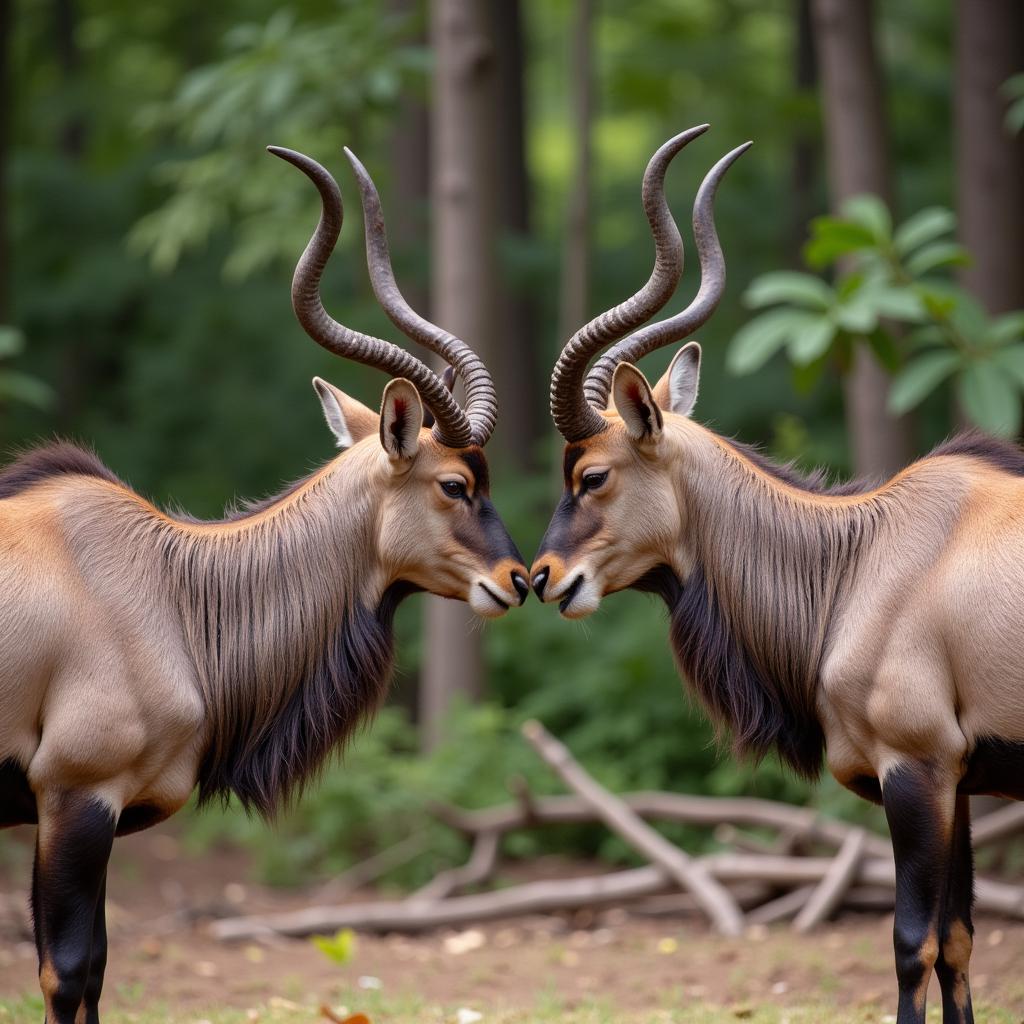 Kudu Bulls Locking Horns in Mating Display
Kudu Bulls Locking Horns in Mating Display
Conservation Efforts for African Horned Animals
Sadly, many african animal with long horns are facing threats to their survival, primarily due to habitat loss and poaching. Conservation efforts are crucial to protect these magnificent creatures and ensure their continued existence for future generations. Organizations are working tirelessly to combat these threats and preserve the biodiversity of the African continent.
The Impact of Poaching
Poaching poses a significant threat to animals with valuable horns, such as rhinos. The illegal wildlife trade fuels this devastating practice, driving some species to the brink of extinction. Increased anti-poaching patrols and stricter regulations are vital to curb this illegal activity. You might be interested in the cultural practices highlighted in the african ear stretching article.
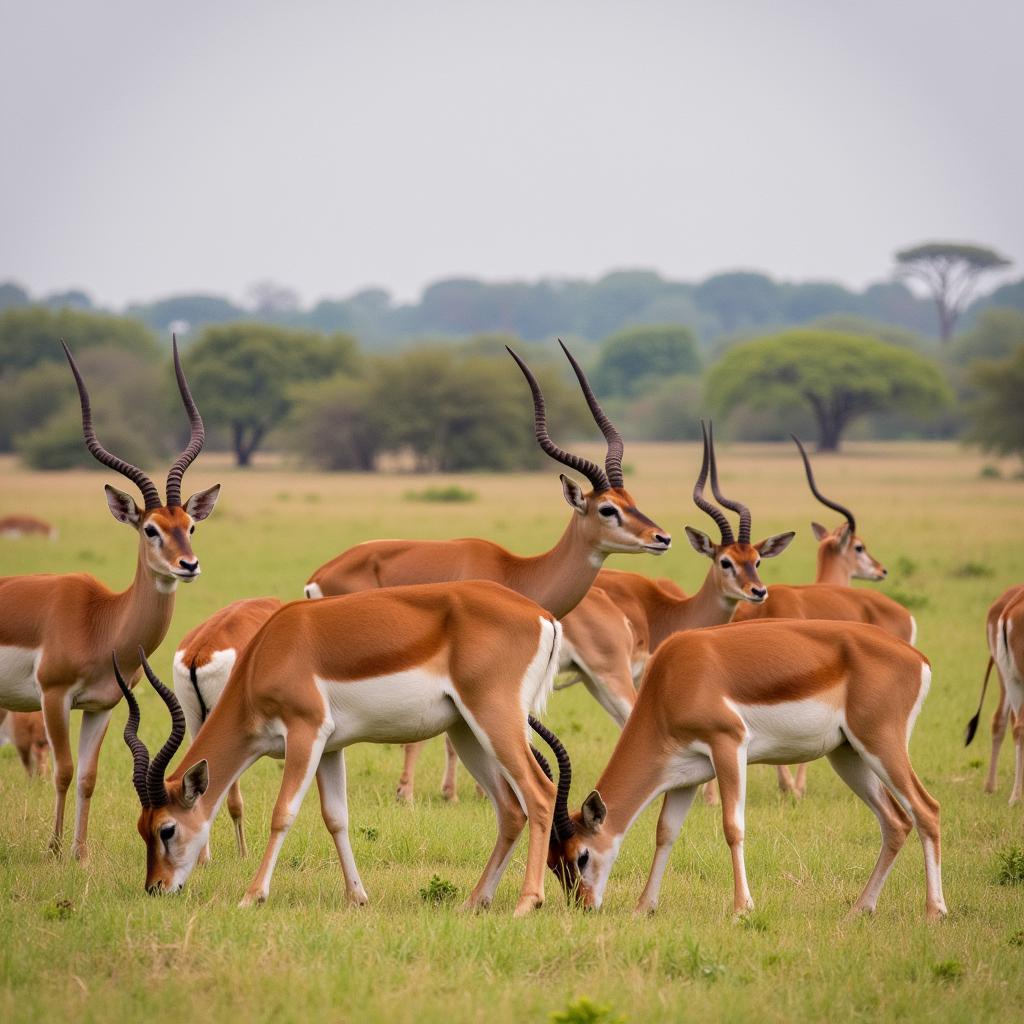 Impala Herd Grazing on the Savanna
Impala Herd Grazing on the Savanna
Dr. Anika Moti, a renowned wildlife biologist specializing in African mammals, states, “The long horns of these animals are not just beautiful; they are a testament to the power of natural selection and the intricate balance of the African ecosystem.” Another expert, Dr. Jabari Olufemi, adds, “Protecting these animals is not just about preserving biodiversity; it’s about safeguarding a crucial part of Africa’s natural heritage.”
In conclusion, the african animal with long horns are a testament to the remarkable biodiversity of the African continent. Their majestic horns, a product of millions of years of evolution, play a vital role in their survival and social interactions. Let us strive to protect these magnificent creatures and their unique habitats for generations to come.
FAQs
- What is the purpose of long horns in African animals? Primarily for defense against predators and establishing dominance within their social hierarchies.
- Are horns made of bone? No, they are made of keratin, the same material as human fingernails.
- What are some threats to African horned animals? Habitat loss and poaching are the primary threats.
- What is being done to protect these animals? Conservation organizations are working to combat poaching and protect their habitats.
- Are all African horned animals antelope? No, other animals like rhinos and buffalo also have horns, although not always long.
- How do horns differ from antlers? Horns are permanent, while antlers are shed annually.
- Why are some horns spiraled? The spiral shape likely provides additional strength and defensive capabilities.
For further assistance, please contact us at Phone: +255768904061, Email: kaka.mag@gmail.com or visit us at Mbarali DC Mawindi, Kangaga, Tanzania. We have a 24/7 customer service team.