African and Asian Elephants: A Comparison of Gentle Giants
African and Asian elephants, the largest land mammals on Earth, captivate us with their size, intelligence, and complex social structures. While both share the title “elephant,” there are key distinctions between these two magnificent creatures. This article delves into the fascinating world of African and Asian elephants, exploring their unique characteristics, habitats, and the challenges they face.
African elephants are generally larger than their Asian counterparts, with larger ears shaped like the African continent. They also have more wrinkled skin and two finger-like projections on the tip of their trunk, as opposed to the single projection found on Asian elephants. Both male and female African elephants can grow tusks, while in Asian elephants, primarily only the males have prominent tusks. Habitat-wise, African elephants roam the savannas and forests of sub-Saharan Africa, while Asian elephants inhabit the grasslands and rainforests of South and Southeast Asia. You can learn more about African elephant tusks on this site about African elephant tusk weight.
Distinguishing Features: Size, Tusks, and Ears
One of the most noticeable differences between African and Asian elephants lies in their size and physical characteristics. African elephants are the largest land animals, with males reaching heights of up to 13 feet and weighing over six tons. Asian elephants are slightly smaller, with males typically reaching heights of up to 10 feet and weighing around five tons. Their ears are also distinctly different, with African elephants sporting large, fan-shaped ears resembling the shape of Africa, while Asian elephants have smaller, rounded ears. Another key difference lies in their tusks: both male and female African elephants develop tusks, but among Asian elephants, tusks are primarily found in males, and even then, not all possess them.
 African and Asian Elephant Ear Comparison
African and Asian Elephant Ear Comparison
Habitat and Diet: From Savannas to Rainforests
The two species also differ in their habitats and diets. African elephants thrive in diverse environments, from the vast savannas of East Africa to the dense forests of Central Africa. They are primarily grazers, feeding on grasses, leaves, bark, and fruits. Asian elephants, on the other hand, inhabit the grasslands and rainforests of India, Sri Lanka, and Southeast Asia. Their diet consists mainly of grasses, bamboo, fruits, and bark. The differences in their habitats and diets contribute to their distinct evolutionary paths.
Social Structures: Matriarchal Herds and Solitary Bulls
Both African and Asian elephants exhibit complex social structures, albeit with some key variations. African elephants live in large, matriarchal herds led by the oldest female, while male African elephants tend to live solitary lives or in small bachelor groups. You can find more details about African elephants on African elephant facts wikipedia. Asian elephant herds are generally smaller than African herds, and adult males often leave the herd to live alone.
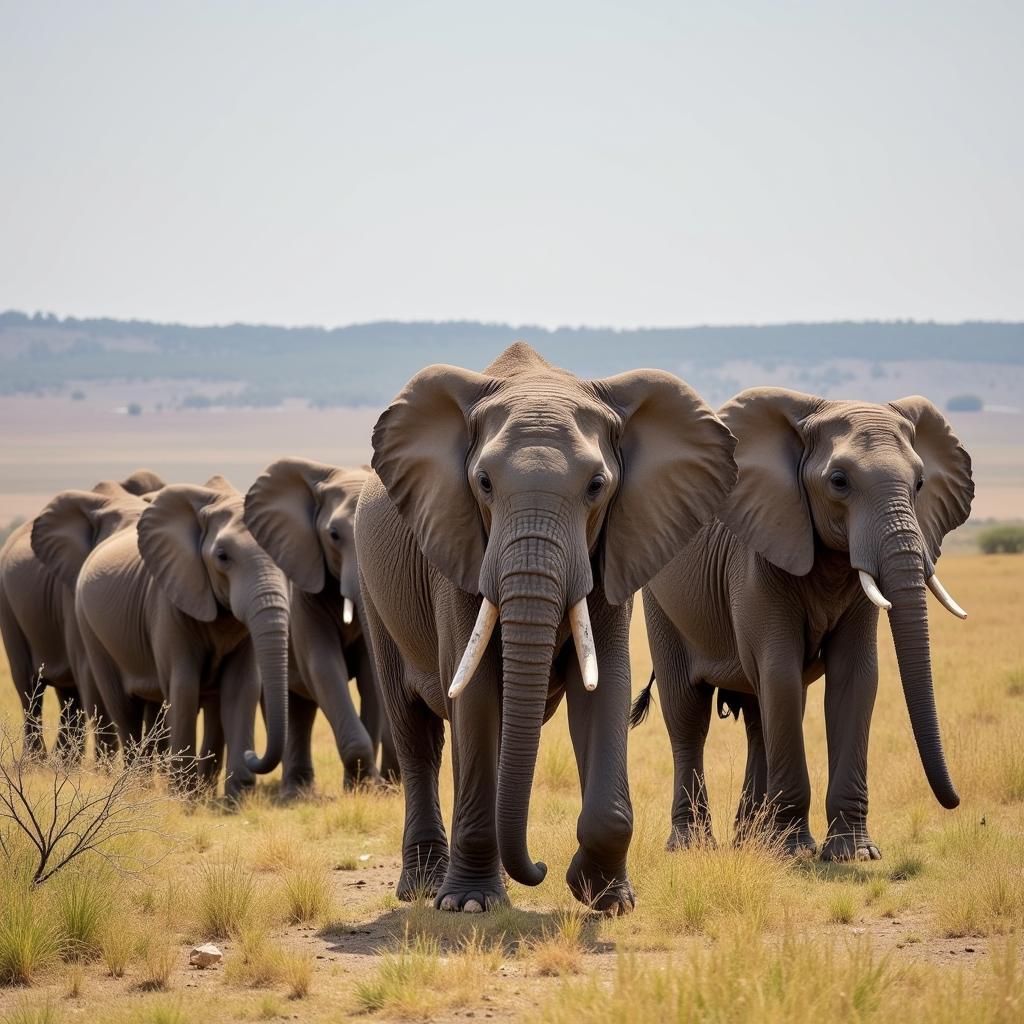 African Elephant Herd in Savanna
African Elephant Herd in Savanna
Conservation Concerns: Poaching and Habitat Loss
Both African and Asian elephants face significant conservation challenges, primarily due to habitat loss and poaching for their ivory tusks. The demand for ivory has led to a devastating decline in elephant populations, pushing both species towards endangerment. Learn more about the endangerment of African elephants at african elephant how did it get endangered. Conservation efforts are underway to protect these magnificent creatures and their habitats, but the fight to save them is far from over. Understanding the specific threats facing each species is crucial to developing effective conservation strategies. Learn about their unique dental structure at African elephant teeth facts.
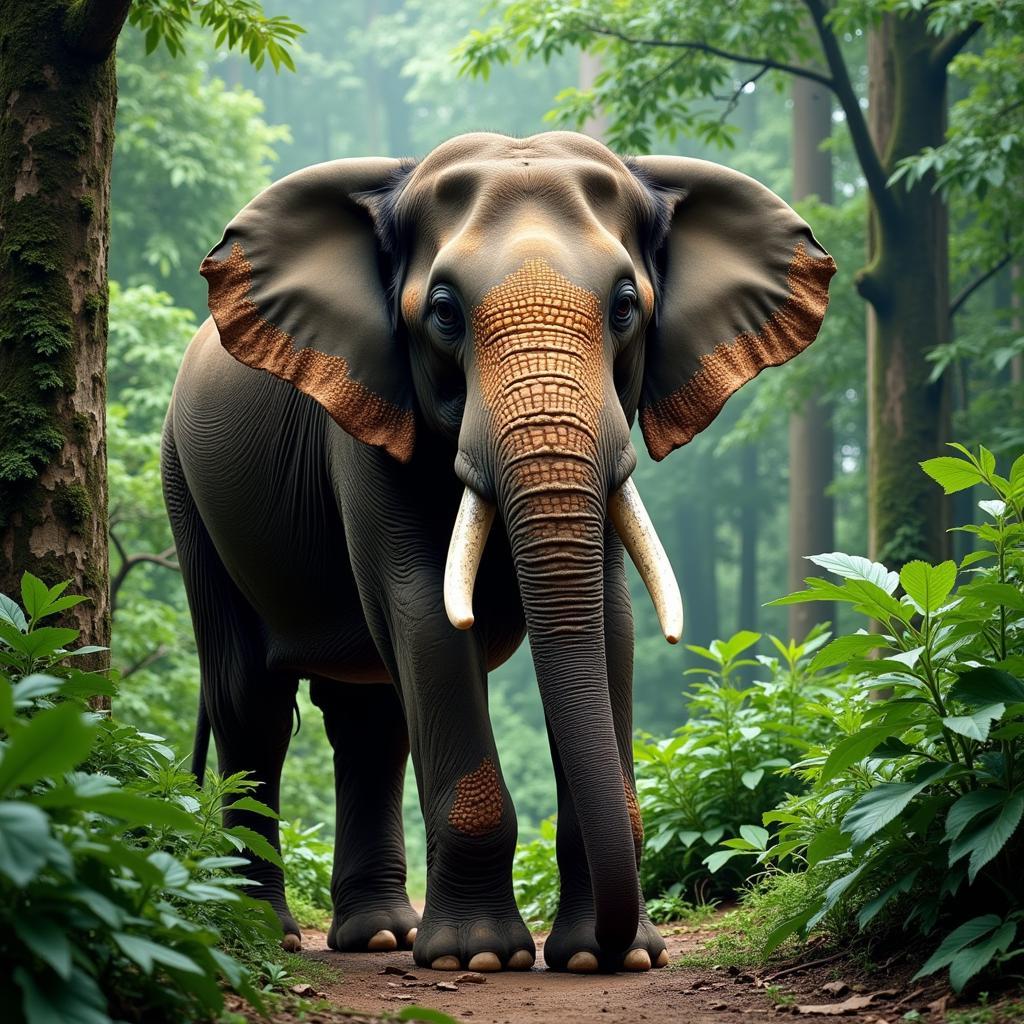 Asian Elephant in Rainforest
Asian Elephant in Rainforest
Conclusion: Protecting the Giants of Africa and Asia
African and Asian elephants, though distinct in their features and habitats, share a common plight: the threat of extinction. Understanding the differences and unique challenges faced by each species is paramount to ensuring their survival. Continued conservation efforts, focused on combating poaching and preserving their natural habitats, are crucial for protecting these gentle giants for generations to come.
FAQ
- What is the main difference between African and Asian elephant ears? African elephants have large, fan-shaped ears, while Asian elephants have smaller, rounded ears.
- Which elephant species is larger? African elephants are generally larger than Asian elephants.
- Do all elephants have tusks? No, only some male Asian elephants have tusks, and both male and female African elephants can grow tusks.
- Where do African elephants live? African elephants live in the savannas and forests of sub-Saharan Africa.
- What do Asian elephants eat? Asian elephants primarily eat grasses, bamboo, fruits, and bark.
- Why are elephants endangered? Elephants are endangered due to habitat loss and poaching for their ivory.
- What can be done to help protect elephants? Supporting conservation organizations, raising awareness about the threats they face, and advocating for stronger anti-poaching measures can all contribute to elephant conservation.
Need help with African human head reference for your art? Check out this link: african human head reference art.
For further assistance, please contact us: Phone: +255768904061, Email: kaka.mag@gmail.com or visit us at: Mbarali DC Mawindi, Kangaga, Tanzania. We have a 24/7 customer service team.