Understanding the Complexities of the African Exodus in 2014
The term “African Exodus 2014” encompasses a complex reality, referring not to a single, mass migration, but rather to a confluence of various migration flows within and from the African continent during that year. These movements were driven by a multitude of factors, ranging from political instability and armed conflict to economic hardship and environmental disasters. Understanding this multifaceted phenomenon requires examining the diverse push and pull factors influencing migration patterns across different regions of Africa.
Unpacking the Drivers of the African Exodus in 2014
Several key factors contributed to the diverse migration patterns observed across Africa in 2014. Conflict and political instability, particularly in countries like South Sudan and the Central African Republic, forced countless individuals to flee their homes in search of safety. Economic hardship, exacerbated by unemployment and lack of opportunities, also played a significant role, compelling many to migrate within their own countries or across borders in pursuit of better livelihoods. Furthermore, environmental factors, such as droughts and desertification, particularly in the Sahel region, displaced communities and added to the complexity of the migration landscape.
The “African exodus 2014” is often misunderstood as a singular event. However, it represents the intersection of numerous, often intertwined, migration streams. These migrations varied in scale, duration, and destination, reflecting the specific circumstances of each region and the diverse motivations of those who chose to migrate.
 African Migration Routes in 2014
African Migration Routes in 2014
Examining the Impact of the 2014 Migration Flows
The 2014 migration flows across Africa had profound impacts on both sending and receiving communities. In countries experiencing conflict, mass displacement strained already limited resources and created humanitarian crises. Host countries, often facing their own challenges, struggled to absorb the influx of refugees and migrants, leading to increased competition for jobs and resources. The strain on infrastructure and social services also presented significant challenges.
Furthermore, the 2014 migrations highlighted the complex relationship between migration and development. While remittances sent home by migrants could provide a vital source of income for families and communities, the loss of skilled labor and human capital could hinder development prospects in sending countries. Understanding these intricate dynamics is crucial for developing effective policies and interventions to address the root causes of migration and mitigate its negative consequences.
What Were the Main Causes of the African Exodus in 2014?
The primary drivers of the “African exodus 2014” included armed conflict, political instability, economic hardship, and environmental disasters. These factors often interacted and reinforced each other, creating complex and challenging situations for individuals and communities across the continent.
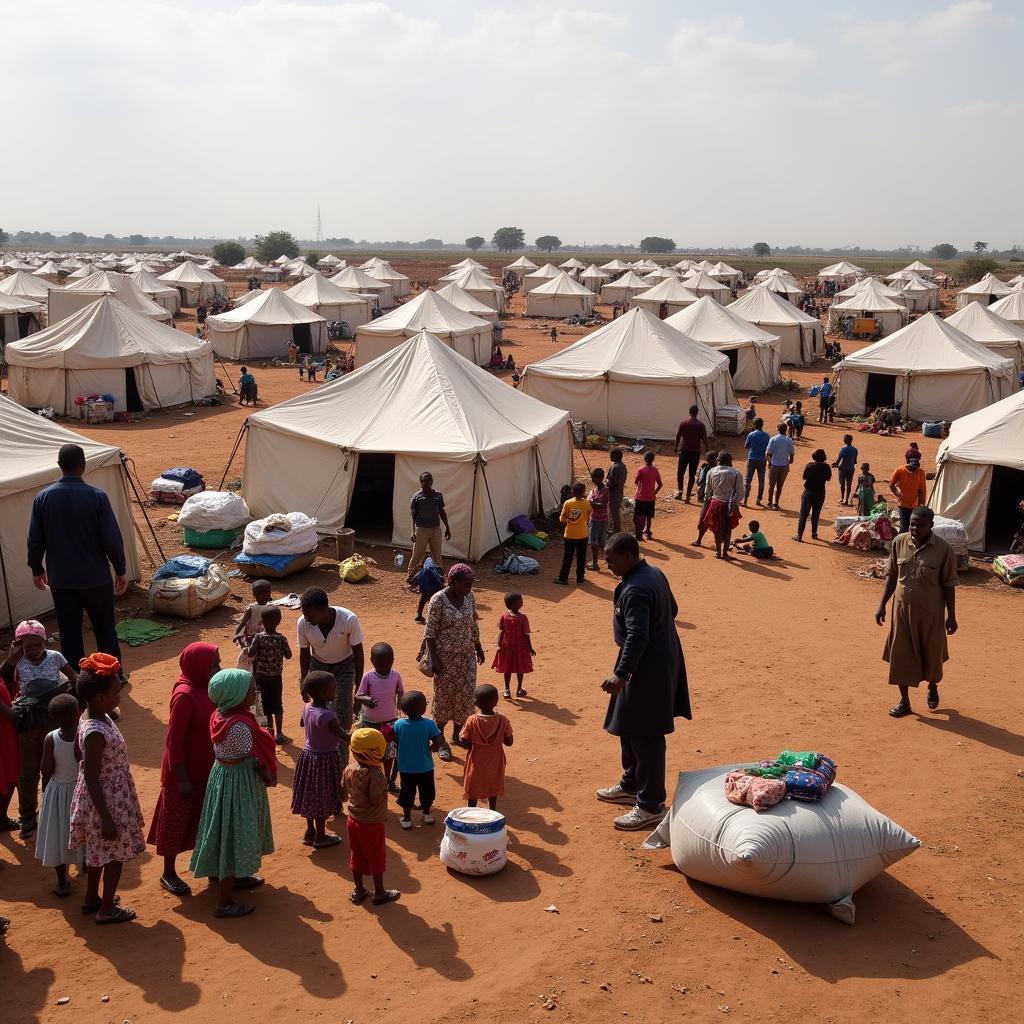 Refugee Camp in Africa, 2014
Refugee Camp in Africa, 2014
The Role of Conflict and Political Instability
Conflict and political instability were significant drivers of migration in 2014, particularly in countries like South Sudan and the Central African Republic. Civil wars and armed conflicts forced people to flee their homes, seeking safety and refuge in neighboring countries or other regions within their own countries.
“The 2014 migrations underscore the devastating impact of conflict on human lives and livelihoods,” says Dr. Abena Oduro, a leading expert on African migration at the University of Ghana. “Forced displacement not only creates immediate humanitarian crises but also has long-term consequences for individuals, families, and communities.”
Addressing the Challenges of African Migration
The complexities of the “African exodus 2014” highlight the need for comprehensive and multi-faceted approaches to address the challenges of migration. This includes promoting peace and stability, fostering economic development, and strengthening resilience to environmental challenges. International cooperation and collaboration are also essential for providing humanitarian assistance, managing migration flows, and protecting the rights of migrants and refugees.
Promoting Sustainable Solutions
Addressing the root causes of migration requires a long-term perspective and a commitment to sustainable solutions. This involves investing in education, creating job opportunities, promoting good governance, and strengthening social safety nets. Empowering communities to build resilience to environmental challenges is also crucial for reducing displacement and fostering sustainable development.
“Migration is a complex issue with no easy answers,” explains Professor Kwame Asante, a renowned sociologist at the University of Nairobi. “However, by addressing the underlying drivers of migration, we can create a more stable and prosperous future for all Africans.”
In conclusion, the “African exodus 2014” represents a complex tapestry of migration flows driven by a multitude of factors. Understanding the drivers, impacts, and challenges of this phenomenon is crucial for developing effective strategies to manage migration and promote sustainable development across the African continent. Addressing the root causes of migration, fostering regional cooperation, and protecting the rights of migrants are essential for building a more stable and prosperous future for all.
FAQ
- What does “African exodus 2014” refer to? It refers to the various migration flows within and from Africa during 2014.
- What were the main causes of the 2014 migrations? Conflict, political instability, economic hardship, and environmental disasters.
- What were the impacts of the 2014 migrations? Humanitarian crises, strain on resources, and complex development challenges.
- How can the challenges of African migration be addressed? Through comprehensive approaches that address root causes, promote peace and development, and foster international cooperation.
- What is the significance of understanding the “African exodus 2014”? It helps in developing effective strategies to manage migration and promote sustainable development in Africa.
- What were some of the major destinations for African migrants in 2014? Neighboring countries, Europe, and other regions within Africa.
- How did the 2014 migrations impact the development of sending countries? Loss of skilled labor and human capital, but also potential gains from remittances.
Common Scenarios and Questions
- Scenario: A family fleeing conflict in South Sudan. Question: What resources are available to support refugees and asylum seekers?
- Scenario: A young person migrating from rural to urban areas in search of work. Question: What are the challenges and opportunities faced by internal migrants?
- Scenario: A community displaced by drought in the Sahel region. Question: What strategies can be implemented to build resilience to environmental challenges?
Further Exploration
Explore other articles on our website related to African migration, development, and humanitarian aid. Learn more about the specific challenges and opportunities in different regions of Africa.
For support, contact us 24/7: Phone: +255768904061, Email: [email protected], or visit us at Mbarali DC Mawindi, Kangaga, Tanzania.