African Franc vs. Indian Rupee: A Currency Comparison
The African franc and the Indian rupee are two distinct currencies used in different parts of the world, representing different economic realities. Understanding the relationship between the African franc vs. Indian rupee involves examining the historical, economic, and political factors influencing their respective values and usage.
The CFA franc, often referred to as the African franc, is used in 14 African countries, mostly former French colonies. These countries are divided into two monetary zones: the West African CFA franc and the Central African CFA franc. The Indian rupee, on the other hand, is the official currency of India and is also used in neighboring countries like Nepal and Bhutan. Comparing these currencies offers insights into the contrasting economic landscapes of the regions they represent. The exchange rate between the two fluctuates based on market forces, reflecting the economic performance and stability of the respective regions. It’s important to note that the “African franc” isn’t a single unified currency, further complicating a direct comparison with the Indian rupee.
Understanding the African Franc
The African franc’s history is intricately linked to France’s colonial past. Its value is pegged to the Euro, providing a degree of stability but also raising questions about monetary sovereignty. The CFA franc’s peg to the Euro has its advantages and disadvantages for the African nations that use it. It can help to control inflation and facilitate trade with the Eurozone. However, it also limits the ability of these countries to independently manage their monetary policy.
The Two Zones of the CFA Franc
The two zones, West African CFA franc and Central African CFA franc, operate under separate central banks but share the common peg to the Euro. This dual system reflects the diverse economies within Africa and the need for tailored monetary policies. Within each zone, the individual economies vary significantly, influenced by factors like natural resources, political stability, and infrastructure development.
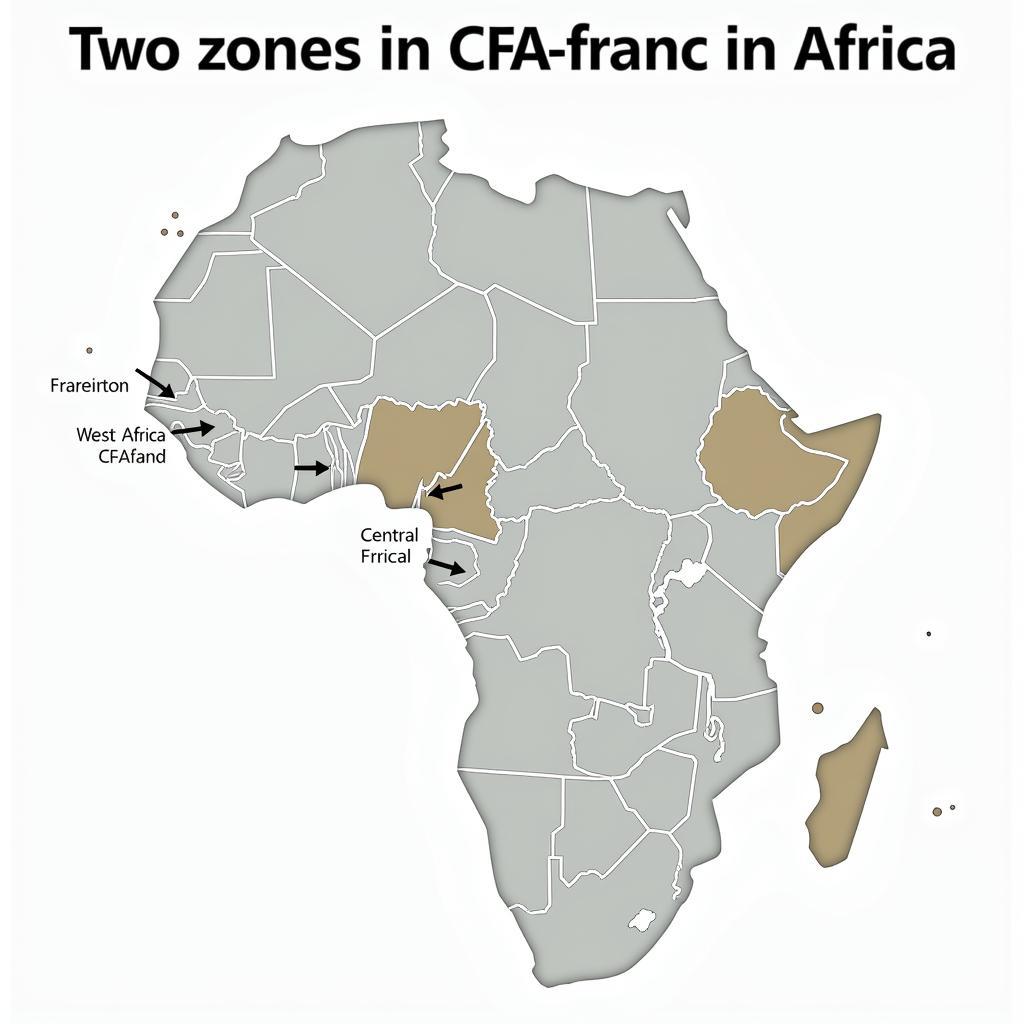 Map of African Franc Zones
Map of African Franc Zones
Understanding these differences is key to analyzing the African franc’s value against other currencies, including the Indian rupee. The varying economic performance within these zones impacts the overall perception and value of the CFA franc in the global market. For instance, a strong economic performance in one zone can positively influence the franc’s value, while economic struggles in another zone could have the opposite effect.
The Indian Rupee: A History and Current Status
The Indian rupee has a long and complex history, reflecting India’s economic evolution. It’s a freely floating currency, meaning its value is determined by market forces. This makes it susceptible to global economic fluctuations but also allows for greater flexibility in monetary policy. 100 francs wedtern african indian rupees.
Factors Influencing the Rupee’s Value
Several factors influence the rupee’s value, including India’s economic growth, inflation rates, and global market sentiment. The Indian economy’s reliance on specific sectors, like IT and manufacturing, can also impact the rupee’s performance in the forex market. 1 west african franc aqwal to how many indian rupees.
“India’s economic growth and increasing global influence have positioned the rupee as a significant player in international trade,” says Dr. Anya Sharma, Professor of Economics at the University of Delhi. “Its performance is intricately tied to global market dynamics.”
Comparing the African Franc and Indian Rupee
Directly comparing the African franc and the Indian rupee is complex due to the CFA franc’s peg to the Euro and the rupee’s free-floating nature. However, examining their relative performance against other major currencies like the US dollar can offer valuable insights. 1 west african franc equal to how many indian rupees.
Economic Implications of the Currency Differences
The different monetary systems influence how these regions interact with the global economy. The CFA franc’s stability offers predictability for trade with the Eurozone. The rupee’s flexibility, while potentially volatile, allows India to respond more dynamically to changing market conditions. african continent using rupee currency.
 Comparison Chart of CFA Franc and Indian Rupee
Comparison Chart of CFA Franc and Indian Rupee
“The contrasting currency systems highlight the diverse approaches to economic management in Africa and India,” states Mr. Jean-Pierre Dubois, a financial analyst specializing in African markets. “Each system presents unique challenges and opportunities for economic growth and stability.”
Conclusion
The African franc vs. Indian rupee comparison offers a fascinating glimpse into the complex interplay of history, politics, and economics in shaping currency values and international trade. While a direct comparison is complicated, understanding the individual characteristics of each currency, including their respective monetary systems and influencing factors, allows for a deeper appreciation of the diverse economic landscapes they represent. The continuing evolution of these currencies will undoubtedly play a crucial role in the future economic development of their respective regions.
FAQ
- What is the CFA franc pegged to? (The Euro)
- Is the Indian rupee a freely floating currency? (Yes)
- What are the two zones of the CFA franc? (West African CFA franc and Central African CFA franc)
- What factors influence the Indian rupee’s value? (Economic growth, inflation, global market sentiment)
- Why is it difficult to directly compare the African franc and Indian rupee? (Due to different monetary systems)
- What are the advantages of the CFA franc’s peg to the Euro? (Stability, controlled inflation, easier trade with Eurozone)
- What are the disadvantages of the CFA franc’s peg to the Euro? (Limited monetary policy independence)
Need help? Contact us 24/7: Phone: +255768904061, Email: kaka.mag@gmail.com, Address: Mbarali DC Mawindi, Kangaga, Tanzania.

