Exploring the African Amphibian and Reptile Family
The African continent pulsates with life, and among its most fascinating inhabitants are the members of the African Amphibian And Reptile Family. From the slithering snakes of the Sahara to the vibrant frogs of the Congo rainforest, these cold-blooded creatures represent an incredibly diverse and crucial part of Africa’s ecosystems. This exploration will delve into the remarkable world of these animals, highlighting their unique adaptations, ecological roles, and the challenges they face.
Diversity within the African Amphibian and Reptile Family
Africa boasts an astonishing array of amphibian and reptile species. The continent is home to over 1,000 species of frogs, toads, salamanders, caecilians (limbless amphibians), as well as lizards, snakes, turtles, tortoises, and crocodiles. This incredible diversity is attributed to the continent’s varied landscapes, ranging from arid deserts to lush rainforests, and encompassing vast savannas and towering mountains. Each environment has fostered the evolution of unique adaptations in its amphibian and reptile inhabitants. For instance, the desert-dwelling reptiles have developed remarkable strategies for water conservation, while the rainforest amphibians showcase a vibrant array of colors and patterns.
The Sahara Desert, though seemingly barren, harbors reptiles like the desert horned viper, which has evolved a sidewinding locomotion to navigate the shifting sands. These adaptations are not merely fascinating but are also essential for their survival. Consider the Gaboon viper, one of the largest vipers in the world, found in the rainforests of Central and West Africa. Its camouflage is so effective that it can lie in wait for unsuspecting prey, blending seamlessly into the leaf litter.
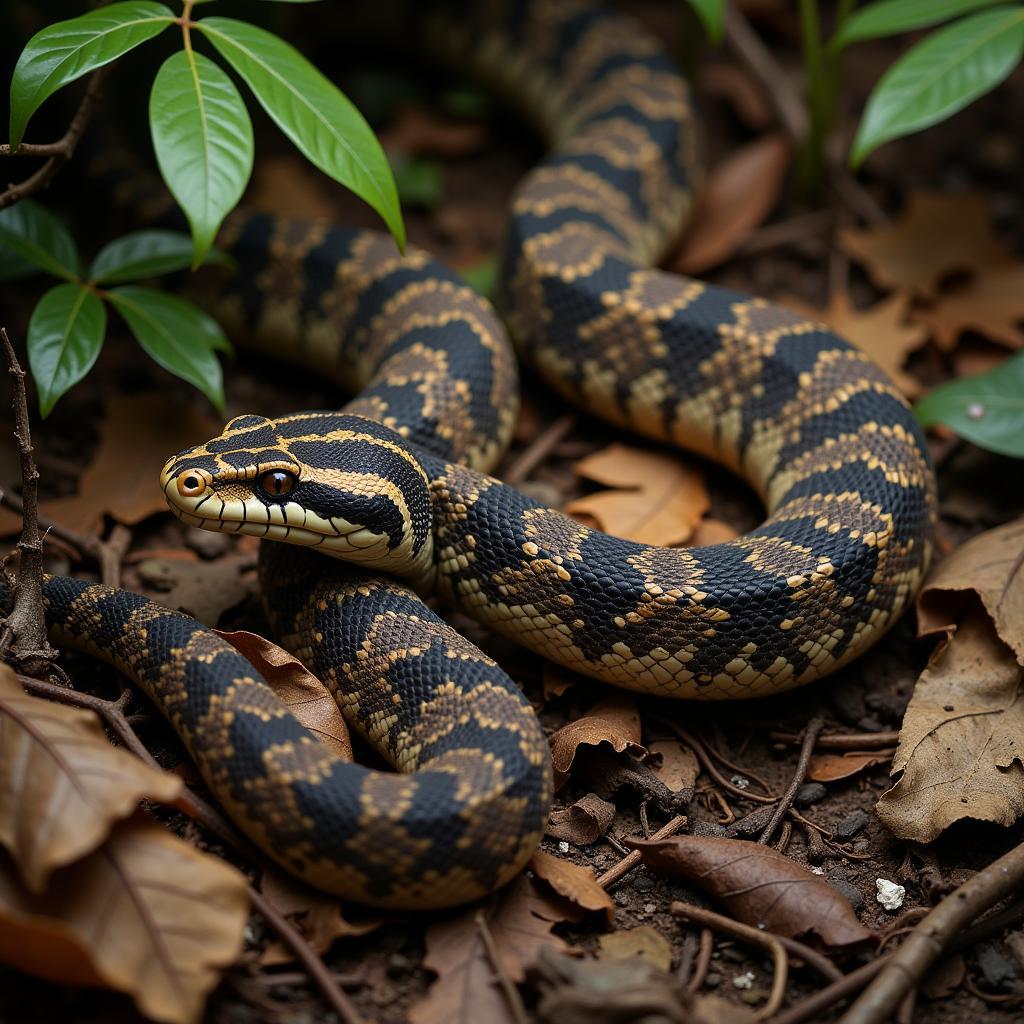 Gaboon Viper Camouflaged in Leaf Litter
Gaboon Viper Camouflaged in Leaf Litter
The Ecological Significance of African Amphibians and Reptiles
African amphibians and reptiles play vital roles in their respective ecosystems. Many species act as both predator and prey, maintaining a delicate balance within the food web. Amphibians, especially frogs and toads, are crucial indicators of environmental health. Their sensitivity to changes in water quality and habitat makes them valuable barometers of ecosystem integrity. Reptiles, such as crocodiles and monitor lizards, help control populations of rodents and other small animals. Let’s not forget the crucial role that these creatures play in nutrient cycling and seed dispersal.
Consider the Nile crocodile, apex predator of the Nile River. Its presence regulates fish populations and contributes to the overall health of the river ecosystem. These animals are not just fascinating specimens; they are integral threads in the complex tapestry of African Life. Check out some interesting facts about another iconic African predator: African fish eagle facts.
Threats and Conservation Efforts for the African Amphibian and Reptile Family
Unfortunately, many African amphibian and reptile species are facing numerous threats, primarily due to habitat loss, climate change, pollution, and the illegal wildlife trade. The continued destruction of rainforests and wetlands, driven by human activities, is pushing many species towards the brink of extinction. Climate change further exacerbates these pressures, leading to altered rainfall patterns and increased temperatures, which can severely impact amphibian breeding cycles and reptile survival.
Numerous conservation organizations are working tirelessly to protect these incredible creatures and their habitats. These initiatives range from establishing protected areas to raising awareness about the importance of amphibian and reptile conservation. Learn more about the diversity of African wildlife here: African animals images and names. Protecting these remarkable animals is not just about preserving biodiversity; it’s about ensuring the health and resilience of the entire African ecosystem. Many of these species are also highlighted on the African animals page.
What are some common African reptiles?
Some common African reptiles include the Nile crocodile, the African rock python, the black mamba, and various species of monitor lizards and chameleons.
How are African amphibians adapted to dry climates?
Many African amphibians, particularly those in arid or semi-arid regions, have developed adaptations such as burrowing behavior, aestivation (a period of dormancy similar to hibernation), and the ability to absorb water through their skin.
Why are African amphibians important?
African amphibians are vital for maintaining ecological balance, serving as both predators and prey. They are also important indicators of environmental health, as they are highly sensitive to changes in water quality and habitat.
In conclusion, the African amphibian and reptile family represents a crucial component of the continent’s biodiversity. These fascinating creatures, with their unique adaptations and ecological roles, are facing increasing threats. Understanding their importance and supporting conservation efforts are crucial for ensuring their survival and the health of the African ecosystems they inhabit. You can even find information about the African crocodile size and the African drongo on our website.
Dr. Khadija Mosi, a renowned herpetologist specializing in African amphibians and reptiles, shares her insights: “The diversity of amphibians and reptiles in Africa is breathtaking. Each species plays a crucial role, and their conservation is paramount for the overall health of the continent’s ecosystems.”
Dr. Adebayo Olalekan, a conservation biologist working in East Africa, adds, “Protecting these animals is not just about saving individual species, it’s about preserving the intricate web of life that sustains us all.”
Professor Fatima El-Amin, an expert in African ecology, notes: “The threats facing African amphibians and reptiles are real and urgent. We must act now to mitigate these threats and ensure the survival of these magnificent creatures for future generations.”
FAQ
-
What is the largest reptile in Africa? The Nile crocodile is the largest reptile in Africa.
-
What is the most venomous snake in Africa? The black mamba is considered the most venomous snake in Africa.
-
Are there poisonous frogs in Africa? Yes, there are several species of poisonous frogs in Africa, including the brightly colored Mantella frogs of Madagascar.
-
How many species of amphibians are found in Africa? Africa is home to over 1,000 species of amphibians.
-
What are the main threats to African amphibians and reptiles? The main threats include habitat loss, climate change, pollution, and the illegal wildlife trade.
-
How can I help with amphibian and reptile conservation in Africa? You can support conservation organizations working in Africa, educate yourself and others about these animals, and advocate for sustainable practices that protect their habitats.
-
What are some examples of African amphibians and reptiles adapting to their environment? Examples include the sidewinding locomotion of the desert horned viper, the camouflage of the Gaboon viper, and the aestivation of some amphibian species in dry climates.
Need more information? Explore our other articles on African wildlife. Are you curious about the intriguing calls of the African Grey Parrot? Or perhaps the migratory patterns of the wildebeest? We have a wealth of information waiting to be discovered.
For further assistance, contact us:
Phone: +255768904061
Email: kaka.mag@gmail.com
Address: Mbarali DC Mawindi, Kangaga, Tanzania.
Our customer service team is available 24/7.