The Ultimate Guide to the African Animal Migration Map
Africa is renowned for its incredible wildlife, and one of the most spectacular natural phenomena is the annual migration of millions of animals across the continent. The African Animal Migration Map is a fascinating tool for understanding these incredible journeys. It reveals the paths taken by various species, the ecological factors influencing their movements, and the conservation efforts protecting this natural wonder.
This article delves into the heart of the African animal migration map, exploring the key migration routes, the reasons behind these movements, the species involved, and the challenges faced by these animals.
Unveiling the Grand Migration Routes
The African animal migration map is not a single, static map; it’s a complex tapestry of movements woven across diverse landscapes. The most famous migration route is the Great Migration in East Africa, where over 1.5 million wildebeest, hundreds of thousands of zebra, and countless other animals embark on a circular journey across the Serengeti National Park in Tanzania and the Masai Mara National Reserve in Kenya.
 African Animal Migration Map: Unveiling the Great Migration
African Animal Migration Map: Unveiling the Great Migration
However, the Great Migration is just one part of the vast picture. Other significant migration routes include:
- The Southern Migration: This route involves a large herd of wildebeest, zebra, and other herbivores moving from the Selous Game Reserve in Tanzania to the Ruaha National Park.
- The Western Migration: This migration takes place in the Okavango Delta in Botswana, where a diverse array of animals, including zebras, wildebeest, and elephants, move with the changing seasons.
- The Eastern Migration: This movement involves populations of zebras, wildebeest, and other herbivores across the Tsavo East National Park in Kenya.
The Driving Forces of Migration
The African animal migration map reveals that these movements are driven by a delicate interplay of environmental factors, primarily:
- Seasonal Rainfall and Grassland Availability: The changing seasons influence the availability of fresh grasslands, a crucial resource for herbivores. Animals follow the rains to areas where nutritious pastures are plentiful.
- Water Availability: The search for water sources is another primary driver of migration. During dry seasons, animals often congregate near permanent water bodies, like lakes and rivers, ensuring their survival.
- Predator-Prey Dynamics: The migration pattern is also influenced by predator-prey dynamics. Predators, like lions, leopards, and hyenas, follow the movements of their prey, creating a dynamic balance in the ecosystem.
The Species on the Move
The African animal migration map paints a vivid picture of a vast and diverse cast of characters. From iconic species like wildebeest and zebra to less-known herbivores like hartebeest and eland, the map highlights the interconnectedness of the ecosystem:
- Wildebeest: The iconic wildebeest is the most abundant participant in the Great Migration, forming vast herds that move across the landscape.
- Zebra: Zebras accompany the wildebeest, contributing to the massive movement of herbivores.
- Elephants: Elephants are also known to migrate, searching for food and water.
- Gazelle: Gazelles, like Grant’s and Thomson’s, are agile and swift herbivores, often seen alongside the larger herds.
- Giraffe: These graceful giants are also migratory, driven by the availability of fresh foliage.
Challenges Faced During Migration
While the African animal migration map showcases a magnificent spectacle of nature, it also sheds light on the challenges faced by migrating animals. These include:
- Habitat Loss and Fragmentation: Human encroachment and agricultural expansion threaten the natural habitats used by migrating animals, disrupting their movement.
- Poaching and Illegal Wildlife Trade: The illegal hunting of animals and the demand for wildlife products pose a serious threat to the entire migration system.
- Climate Change: Shifting rainfall patterns and increasing droughts due to climate change are making migration routes unpredictable and challenging.
- Disease Outbreaks: Disease outbreaks can impact entire herds, affecting their ability to complete their migration successfully.
Conservation Efforts: Protecting the Migratory Journey
The African animal migration map serves as a vital tool for conservationists. It provides crucial information for:
- Habitat Protection: By understanding the migratory routes, conservationists can prioritize the protection of key habitats.
- Predator Management: Balancing predator populations is crucial for maintaining the health of the ecosystem and protecting migrating animals.
- Anti-Poaching Efforts: The map helps focus anti-poaching efforts on areas heavily used by migrating animals.
- Education and Awareness: Raising public awareness about the importance of migration and the threats it faces is crucial for long-term conservation.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: How long does the Great Migration take?
A: The Great Migration is a continuous journey that takes about a year to complete.
Q: What is the most dangerous part of the migration?
A: The Mara River crossing is often considered the most dangerous part of the Great Migration, as wildebeest face predation from crocodiles and lions.
Q: How can I contribute to protecting the African animal migration?
A: You can support conservation organizations working to protect migratory animals and their habitats. You can also choose sustainable travel options and learn more about the challenges facing migration to spread awareness.
The African Animal Migration: A Symphony of Life
The African animal migration map unveils a mesmerizing spectacle of life on Earth. It showcases the remarkable adaptations of animals, the delicate balance of ecosystems, and the interconnectedness of all living things. By understanding and protecting these magnificent migrations, we can ensure that future generations can witness this natural wonder for years to come.
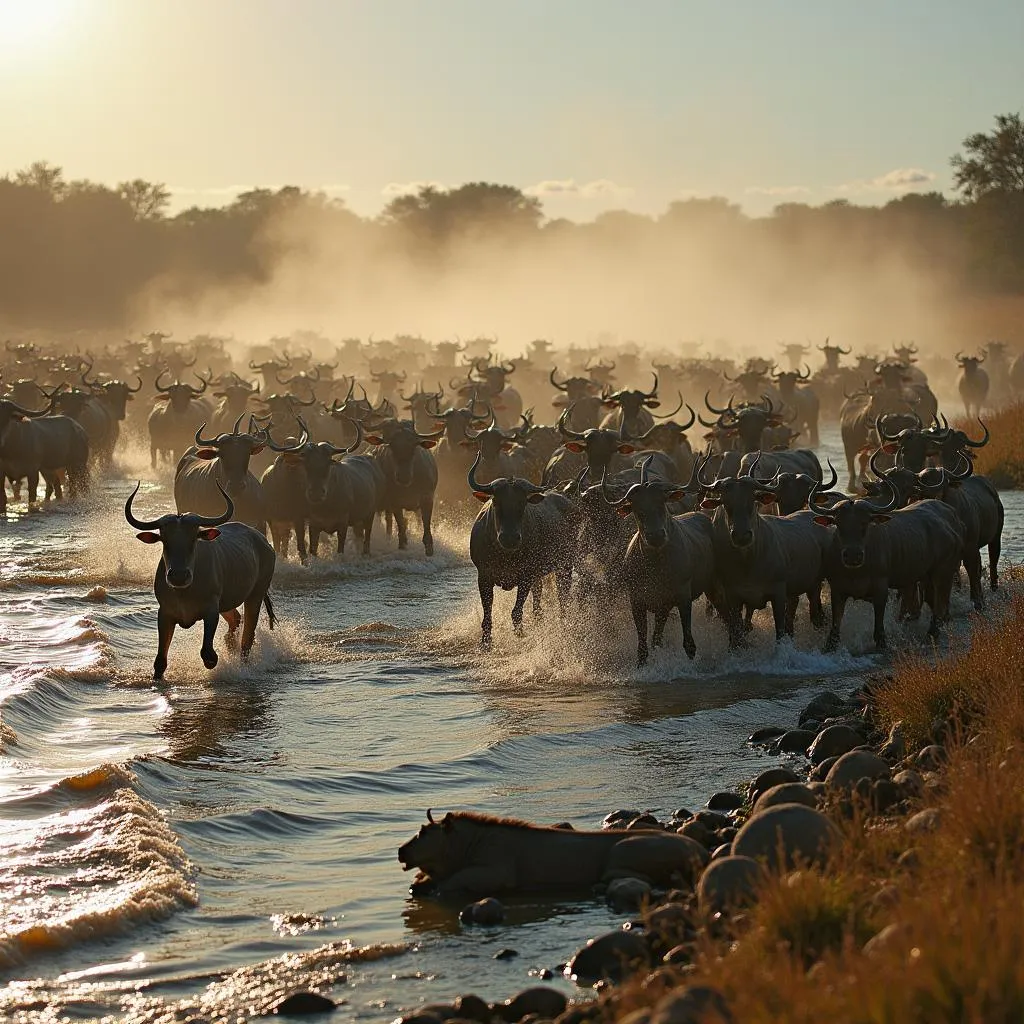 Wildebeest Crossing the Mara River: A Moment of High Drama
Wildebeest Crossing the Mara River: A Moment of High Drama
For more information or to contribute to conservation efforts, please contact us:
+255768904061 | kaka.mag@gmail.com | Mbarali DC Mawindi, Kangaga, Tanzania.
We are here to answer your questions and help you engage with the African animal migration in a meaningful way.
