Unveiling the Secrets of the African Hunting Dog
African hunting dogs, also known as painted wolves or Cape hunting dogs, are fascinating and often misunderstood creatures. These highly social animals roam the open plains and woodlands of sub-Saharan Africa, showcasing a unique blend of intelligence, cooperation, and hunting prowess. Let’s delve into the captivating world of these remarkable canids and uncover some intriguing African Hunting Dog Facts.
African hunting dogs possess a striking coat pattern of irregular patches of black, brown, yellow, and white, giving them their “painted” moniker. No two dogs have the same markings, making each individual easily identifiable. Their long legs, slender bodies, and large, rounded ears are perfectly adapted for their active lifestyle. Unlike most canids, they have only four toes on each foot, further enhancing their running efficiency. Did you know they can reach speeds of up to 44 miles per hour during pursuits? These impressive athletes work together in packs, employing sophisticated communication and coordinated strategies to bring down prey much larger than themselves.
The Cooperative Hunters of the African Savanna
African hunting dogs are renowned for their exceptional hunting success rate, often exceeding that of lions and other large predators. Their cooperative hunting style is a marvel of nature. Packs typically consist of 6 to 20 individuals, led by a dominant alpha pair. They communicate through a variety of vocalizations, including whistles, barks, and chattering calls, allowing them to coordinate their movements and strategize during hunts. Their prey primarily includes antelopes, zebras, and wildebeests.
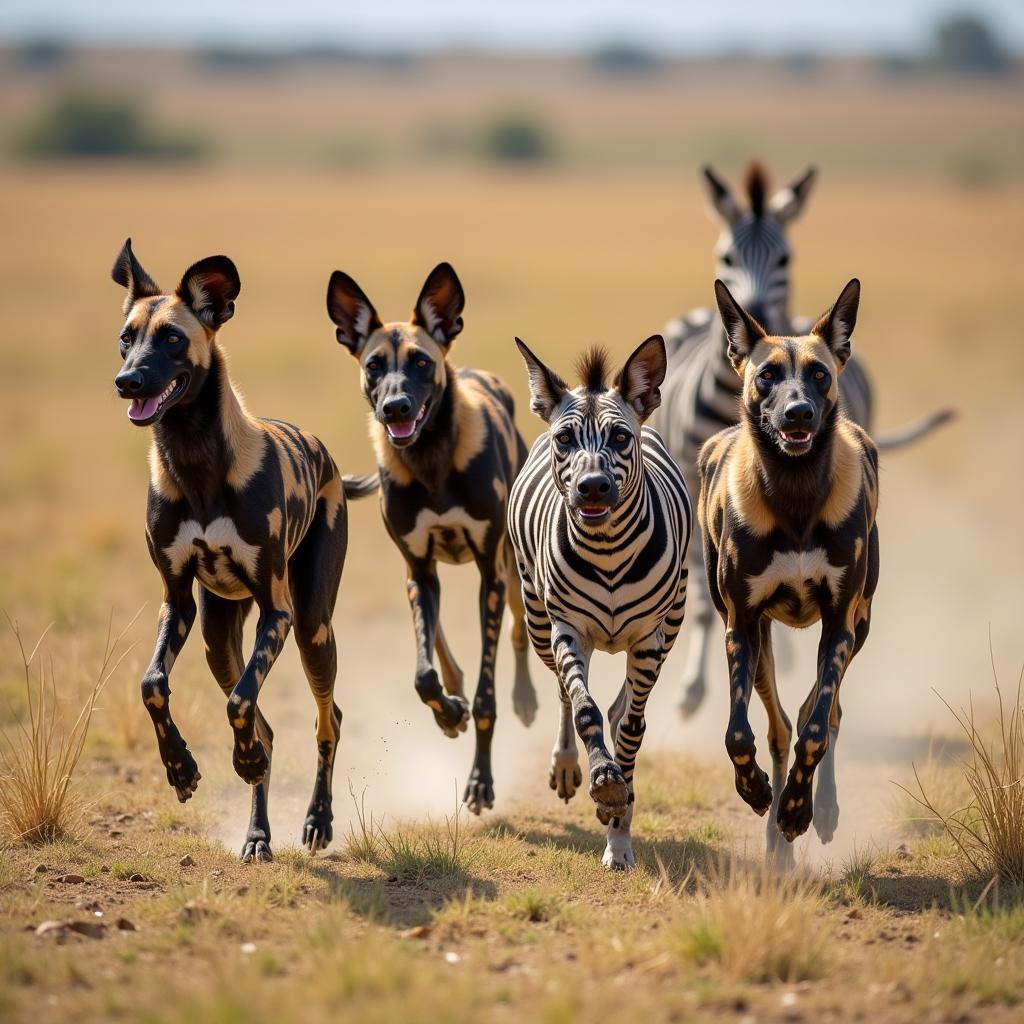 African Hunting Dog Pack Hunting Zebra
African Hunting Dog Pack Hunting Zebra
One of the most remarkable African hunting dog facts is their altruistic behavior. After a successful hunt, they regurgitate food for pups and other pack members who were unable to participate, demonstrating a strong sense of community and shared responsibility. This cooperative spirit extends beyond hunting and is integral to their social structure and overall survival.
Unveiling the Social Dynamics of African Hunting Dogs
The social structure of African hunting dogs is complex and highly organized. The alpha pair is responsible for breeding, while the other pack members assist in raising the pups and defending their territory. This cooperative breeding system ensures the survival of the next generation and strengthens the bonds within the pack. Unlike many other canine species, African hunting dogs exhibit low levels of aggression within their packs, fostering a harmonious and collaborative environment. They maintain their social cohesion through frequent physical contact, including grooming and playful interactions.
Are African Hunting Dogs Endangered?
Sadly, African hunting dogs face numerous threats, including habitat loss, human conflict, and disease. These factors have led to a significant decline in their population, classifying them as endangered by the IUCN. Conservation efforts are crucial to protect these remarkable animals and ensure their continued existence in the wild. These efforts include mitigating human-wildlife conflict, protecting their remaining habitat, and combating diseases like rabies and canine distemper. You can check out more information on the african golden cat iucn.
What Do African Hunting Dogs Eat?
As mentioned earlier, African hunting dogs primarily prey on medium to large-sized ungulates, such as impala, gazelle, and wildebeest. Their diet occasionally includes smaller mammals and birds. Their hunting strategy relies on endurance and teamwork, chasing their prey until it is exhausted.
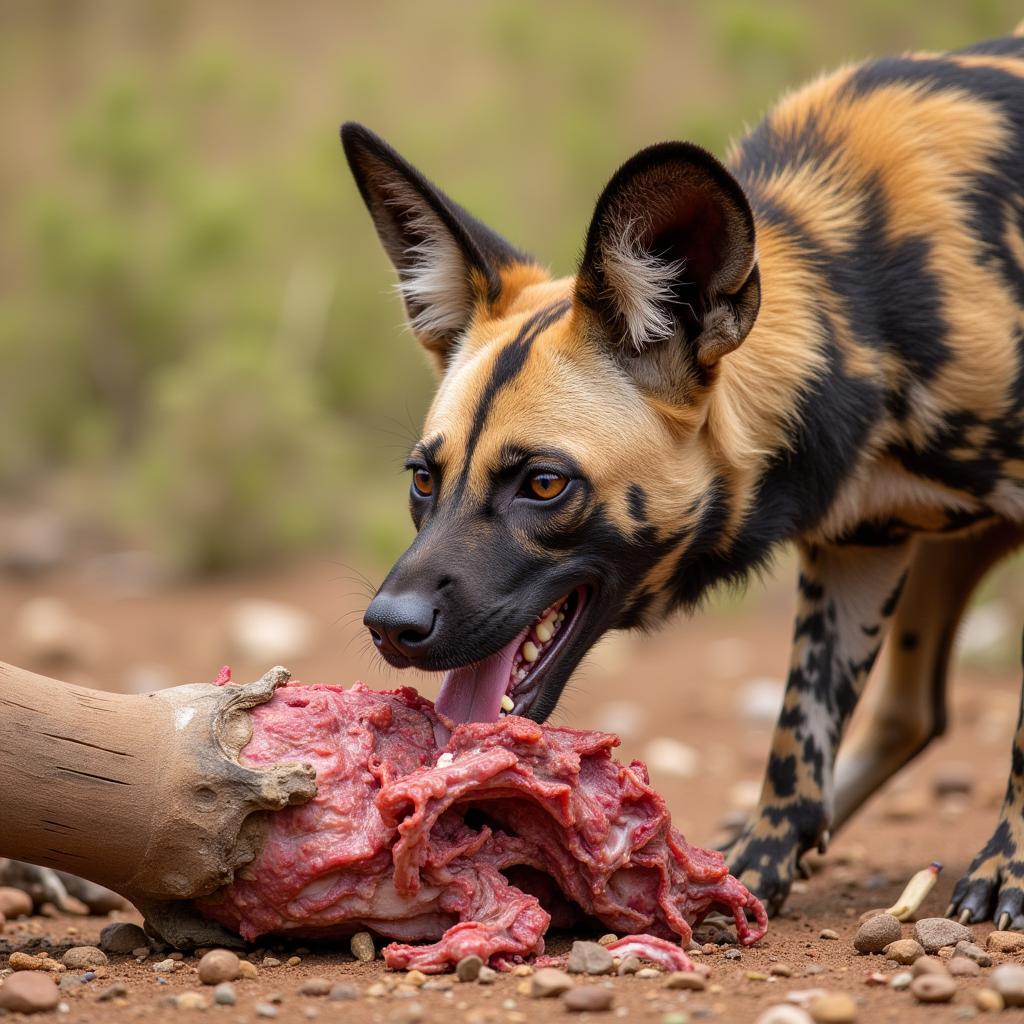 African Hunting Dog Eating Impala
African Hunting Dog Eating Impala
Unraveling More African Hunting Dog Facts
African hunting dogs are truly unique animals with a range of fascinating characteristics. They exhibit a complex social structure, remarkable hunting skills, and a strong sense of community. Learning about these animals is crucial for appreciating their importance in the ecosystem and supporting conservation efforts to protect them. You might also be interested in learning more about the black african lion.
Conclusion: Protecting the Painted Wolves of Africa
African hunting dogs, with their striking coats and cooperative hunting strategies, are a vital part of the African ecosystem. Understanding these fascinating African hunting dog facts helps us appreciate their unique role and the importance of protecting them from the threats they face. Let’s work together to ensure the survival of these incredible painted wolves for generations to come. For a closer look at another majestic African feline, explore these african lion pictures. Have you ever wondered about an African dog no bark? It’s a fascinating subject worth exploring. You might also be interested in the African birth animal by month.
FAQ
- What is the lifespan of an African hunting dog? Around 10-12 years in the wild.
- How many pups do African hunting dogs usually have? Litters typically range from 2-20 pups.
- What is the scientific name for the African hunting dog? Lycaon pictus.
- Where do African hunting dogs live? Sub-Saharan Africa.
- What are the main threats to African hunting dogs? Habitat loss, human conflict, and disease.
- How fast can an African hunting dog run? Up to 44 miles per hour.
- Are African hunting dogs related to domestic dogs? Yes, they belong to the same family, Canidae.
Other questions about African Hunting Dogs:
- How do African hunting dogs communicate with each other?
- What is the role of the alpha pair in a pack of African hunting dogs?
- What are the current conservation efforts to protect African hunting dogs?
Check out other articles on our website for more information on African wildlife.
For assistance, please contact us: Phone: +255768904061, Email: [email protected] or visit us at: Mbarali DC Mawindi, Kangaga, Tanzania. We have a 24/7 customer service team.