African Great Lakes Region Conflicts: A Deep Dive
The African Great Lakes region, a geographically diverse and resource-rich area, has unfortunately been plagued by a complex web of interconnected conflicts for decades. These “African Great Lakes Region Conflicts” have had a devastating impact on the lives of millions, causing widespread displacement, human rights abuses, and hindering economic development. Understanding the root causes, key players, and consequences of these conflicts is crucial for fostering lasting peace and stability in the region.
Understanding the Roots of Conflict in the African Great Lakes Region
The causes of conflict in the Great Lakes region are multifaceted and deeply intertwined. Competition for scarce resources, such as land and minerals, plays a significant role. Ethnic tensions, often exacerbated by political manipulation, have fueled violence and mistrust. Weak governance and corruption further destabilize the region, creating a breeding ground for armed groups and militias. The legacy of colonialism and the arbitrary drawing of borders have also contributed to the complex political landscape. Additionally, the influx of refugees from neighboring countries often strains resources and exacerbates existing tensions.
The region’s rich mineral resources, including gold, coltan, and diamonds, have become a source of conflict rather than prosperity. Armed groups and corrupt officials often exploit these resources to finance their operations, perpetuating cycles of violence. Furthermore, the competition for arable land, particularly in densely populated areas, has led to land disputes and forced displacement.
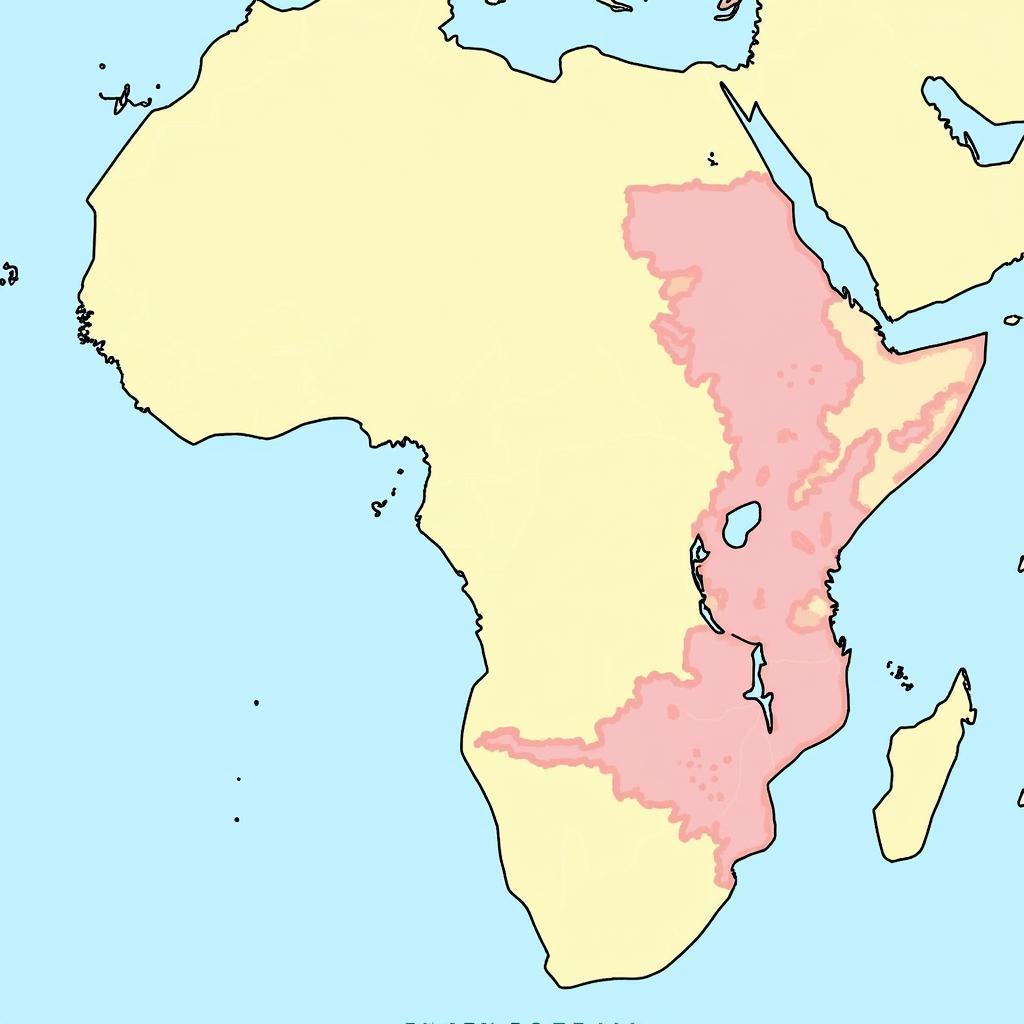 Conflict Map of the African Great Lakes Region
Conflict Map of the African Great Lakes Region
Key Players in the African Great Lakes Region Conflicts
The conflicts in the Great Lakes region involve a complex network of actors, including national governments, rebel groups, militias, and external actors. Understanding the motivations and strategies of these key players is essential for addressing the root causes of conflict. National governments often struggle to maintain control over their territory and face challenges in providing security and basic services to their citizens. Rebel groups and militias, driven by various political, economic, and ethnic agendas, engage in violence and destabilizing activities. External actors, including neighboring countries and international organizations, play a significant role in mediating conflicts and providing humanitarian assistance. The interplay between these actors shapes the dynamics of conflict and the prospects for peace.
The involvement of neighboring countries, both through direct intervention and support for armed groups, further complicates the situation. The porous borders of the region facilitate the movement of fighters and weapons, making it difficult to contain the spread of violence.
One can explore more about the Congo Basin’s geographical boundaries through this resource: African boundary of Congo.
The Consequences of Conflict: Human Cost and Economic Impact
The conflicts in the African Great Lakes region have had a devastating impact on human lives and livelihoods. Millions have been displaced from their homes, forced to live in overcrowded refugee camps or seek refuge in neighboring countries. Widespread human rights abuses, including sexual violence, recruitment of child soldiers, and mass killings, have traumatized communities and left deep scars on the region. The conflicts have also severely hampered economic development, disrupting trade, destroying infrastructure, and discouraging investment.
“The ongoing conflicts have created a generation of lost children, deprived of education and opportunities,” says Dr. Amani Kivu, a leading expert on conflict resolution in the Great Lakes region. “The international community must do more to support education and psychosocial programs for these vulnerable populations.”
The network of organizations working towards peace in the region is extensive. Learn more about the African Great Lakes Action Network. Understanding the hydrography of the area is crucial for grasping resource-driven conflicts. You can find a helpful African hydrographic map for further research. For those interested in the region’s unique biodiversity, exploring the African Cichlids species list can provide another lens to understand the ecological importance of the Great Lakes.
Conclusion
The “african great lakes region conflicts” represent a complex and enduring challenge. Addressing the root causes, promoting inclusive governance, and fostering regional cooperation are essential for achieving lasting peace and stability. The international community must continue to support humanitarian efforts, promote sustainable development, and work towards a future where the Great Lakes region can realize its full potential. Ignoring these conflicts will have long-term consequences for the region and the wider international community.
FAQ
- What are the main drivers of conflict in the African Great Lakes region?
- Who are the key actors involved in these conflicts?
- What are the humanitarian consequences of these conflicts?
- How has conflict impacted the economic development of the region?
- What role can the international community play in resolving these conflicts?
- What are some of the peacebuilding initiatives currently underway in the region?
- How can we support the victims of these conflicts?
Common Scenarios
- Refugee crisis: Conflicts often lead to massive displacement, requiring humanitarian assistance and long-term solutions for refugees.
- Resource exploitation: The abundance of natural resources can fuel conflict, as various groups compete for control.
- Political instability: Weak governance and corruption exacerbate conflicts and hinder peacebuilding efforts.
Further Exploration
Consider researching specific conflicts within the region, such as the Rwandan genocide or the Congolese wars, for a more in-depth understanding. Explore the role of international organizations like the United Nations and the African Union in mediating conflicts and providing humanitarian aid.
For support, please contact us: Phone: +255768904061, Email: [email protected], or visit us at: Mbarali DC Mawindi, Kangaga, Tanzania. We have a 24/7 customer service team.