Where Do African Elephants Migrate In Search of Resources?
African elephants, the planet’s largest land mammals, are iconic symbols of Africa’s wild spaces. These majestic creatures are known for their intelligence, complex social structures, and incredible journeys across the African landscape. But where exactly do African elephants migrate, and what drives these impressive movements?
African elephants undertake migrations for a variety of reasons, the most pressing being the search for food and water. Their movements are often dictated by seasonal changes and the availability of resources. During the dry season, when water and vegetation become scarce, elephants embark on long journeys, sometimes covering hundreds of kilometers, to reach areas with more favorable conditions. These migrations are crucial for their survival, allowing them to access the vast quantities of food and water they need to sustain their massive size.
Following Ancient Paths: Traditional Elephant Migration Routes
For centuries, African elephants have followed traditional migration routes, passed down through generations. These routes, often carved into the landscape itself, represent an intricate understanding of the environment and its resources. Elephants have impressive memories and can recall these paths even after years of absence. They navigate using a combination of memory, landmarks, and even their sense of smell, which can detect water sources from miles away.
One famous example of a traditional elephant migration route is in Botswana, where thousands of elephants undertake an annual journey between the Okavango Delta and the Makgadikgadi Pans. This epic migration, spanning hundreds of kilometers, is a spectacle of nature, with elephants crossing rivers, navigating challenging terrain, and gathering in massive numbers at key resource hotspots.
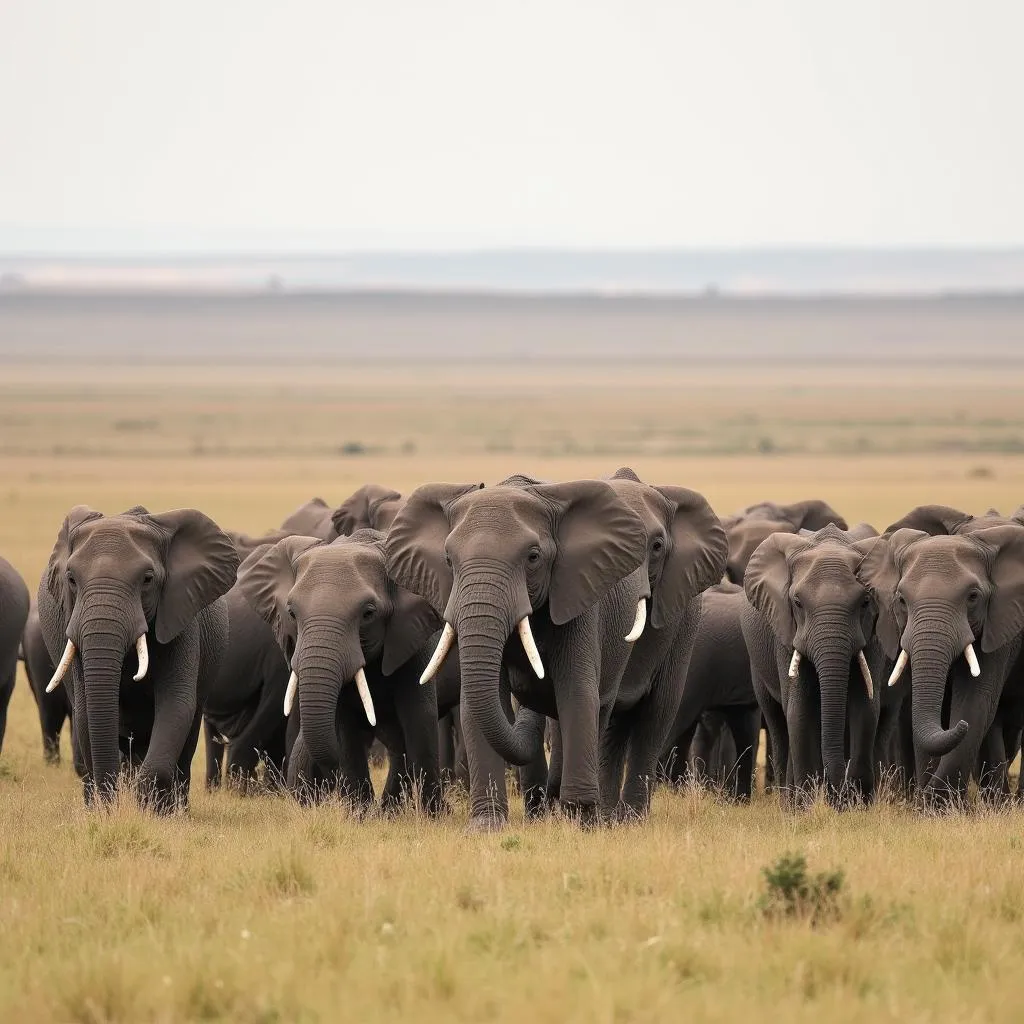 African elephants migrating across Botswana
African elephants migrating across Botswana
The Impact of Human Activity on Elephant Migration
However, these ancient migration routes are increasingly being disrupted by human activities. Habitat loss due to agriculture, expanding human settlements, and infrastructure development, such as roads and fences, are fragmenting elephant habitats and obstructing their traditional migratory paths. This disruption can have severe consequences for elephants, limiting their access to vital resources, increasing the risk of human-elephant conflict, and isolating populations, which can have negative genetic implications.
In addition to physical barriers, poaching for ivory remains a significant threat to African elephants and further disrupts their migratory patterns. Elephants may avoid areas where poaching is prevalent, altering their movements and potentially pushing them into areas with fewer resources or higher risks.
Conservation Efforts: Protecting Elephant Migratory Corridors
Recognizing the importance of elephant migration, conservationists and governments are working together to protect these vital pathways. This involves establishing protected areas that encompass key migration corridors, implementing land-use planning that minimizes habitat fragmentation, and working with local communities to reduce human-elephant conflict.
One innovative approach is the establishment of “elephant corridors,” strips of land connecting fragmented habitats specifically designed to facilitate elephant movement. These corridors allow elephants to access resources, maintain genetic diversity, and continue their ancient migrations, ensuring the long-term survival of these magnificent creatures.
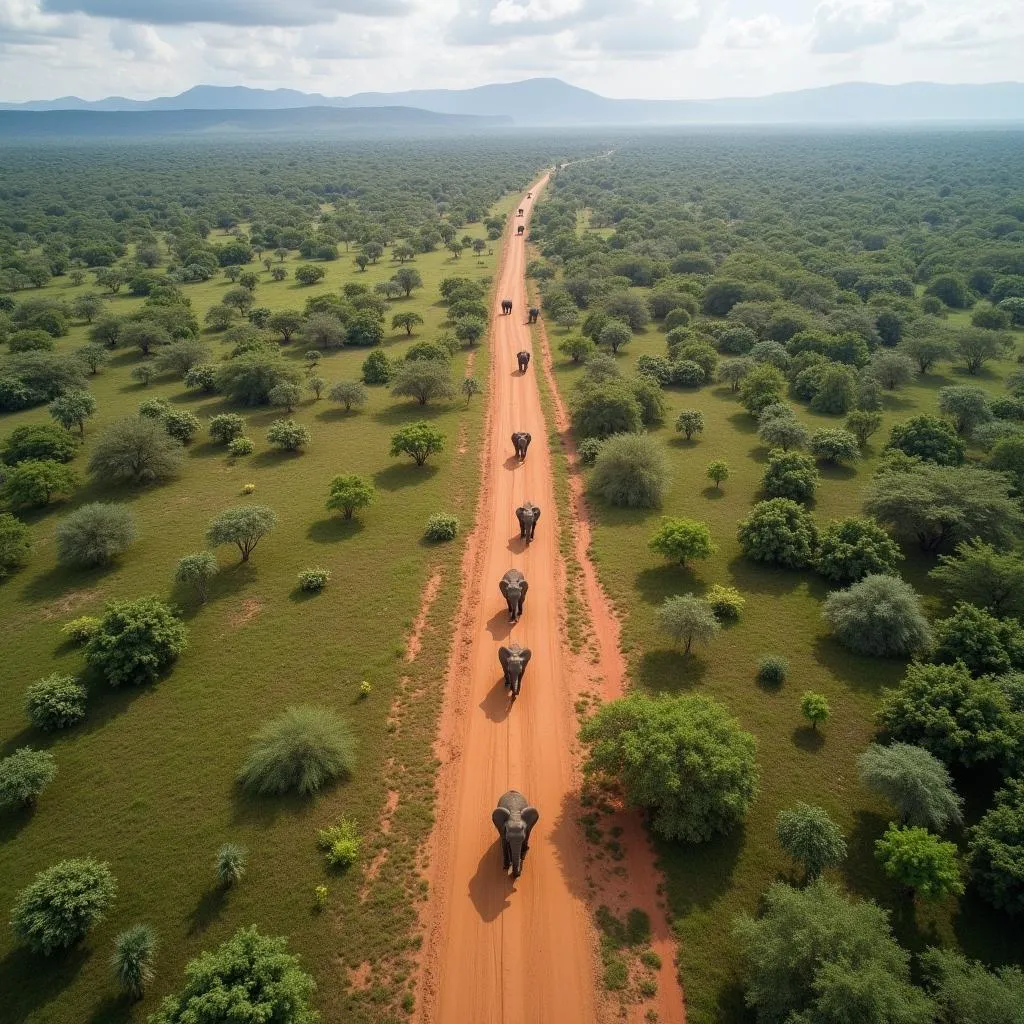 Aerial view of an elephant corridor
Aerial view of an elephant corridor
The Future of Elephant Migration: Challenges and Hope
The future of African elephant migration faces challenges, but there is hope. Through continued conservation efforts, community engagement, and a global commitment to protecting these magnificent animals and their habitats, we can ensure that African elephants continue their ancient journeys across the African landscape for generations to come.
Understanding where and why African elephants migrate is not just an academic exercise; it’s crucial for their survival. By protecting their migratory routes and ensuring they have access to the resources they need, we can help ensure that these iconic animals continue to roam free, embodying the wild spirit of Africa for generations to come.
FAQ:
- Why do African elephants migrate? African elephants migrate primarily in search of food and water, especially during the dry season when these resources become scarce.
- How far do African elephants migrate? The distance elephants migrate varies depending on factors like resource availability and terrain, but they can travel hundreds of kilometers during their migrations.
- How do elephants find their way during migration? Elephants have an impressive memory and use landmarks, their sense of smell, and traditional routes passed down through generations to navigate.
- What are the biggest threats to elephant migration? Habitat loss, fragmentation due to human activities like agriculture and infrastructure development, and poaching are major threats to elephant migration.
- What is being done to protect elephant migration routes? Conservation efforts include establishing protected areas, creating elephant corridors to connect fragmented habitats, and working with local communities to minimize human-elephant conflict.
Need More Information?
Explore more about African animal migration patterns:
Learn about the stunning landscapes these animals traverse:
Interested in the geography shaping these migrations?
Contact us for any assistance:
Phone Number: +255768904061
Email: [email protected]
Address: Mbarali DC Mawindi, Kangaga, Tanzania.
Our customer service team is available 24/7.