African Countries Colonized by France: A Deep Dive into History and Legacy
France’s colonial footprint in Africa was vast and enduring, shaping the political, economic, and social landscapes of numerous nations. This article explores the history of African Countries Colonized By France, examining the impact of French rule and its lasting consequences. african countries and their colonial rulers
The Extent of French Colonialism in Africa
French colonialism in Africa began in the 16th century, reaching its zenith in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Driven by economic interests and a desire for global power, France established colonies across vast swathes of the continent, primarily in West and North Africa. The colonization process involved military conquest, political manipulation, and economic exploitation, leaving an indelible mark on the colonized nations.
Key African Countries Colonized by France
Several African countries experienced extended periods under French rule. These include Algeria, Benin, Burkina Faso, Cameroon, Central African Republic, Chad, Comoros, Congo Republic, Côte d’Ivoire, Djibouti, Gabon, Guinea, Madagascar, Mali, Mauritania, Morocco, Niger, Senegal, Togo, and Tunisia. Each country’s experience with French colonialism was unique, influenced by local dynamics and the specific policies implemented by the French administration.
Which countries speak French in Africa today? Many of the former French colonies retain French as an official language, highlighting the lasting linguistic legacy of French colonization. Understanding the nuanced history of each country is crucial to comprehending the complexities of modern Africa.
Impact of French Colonialism: A Mixed Legacy
French colonial rule brought about significant transformations in the colonized countries. The introduction of new infrastructure, such as railways and roads, facilitated trade and communication. However, this development often served the interests of the colonial power rather than the local population.
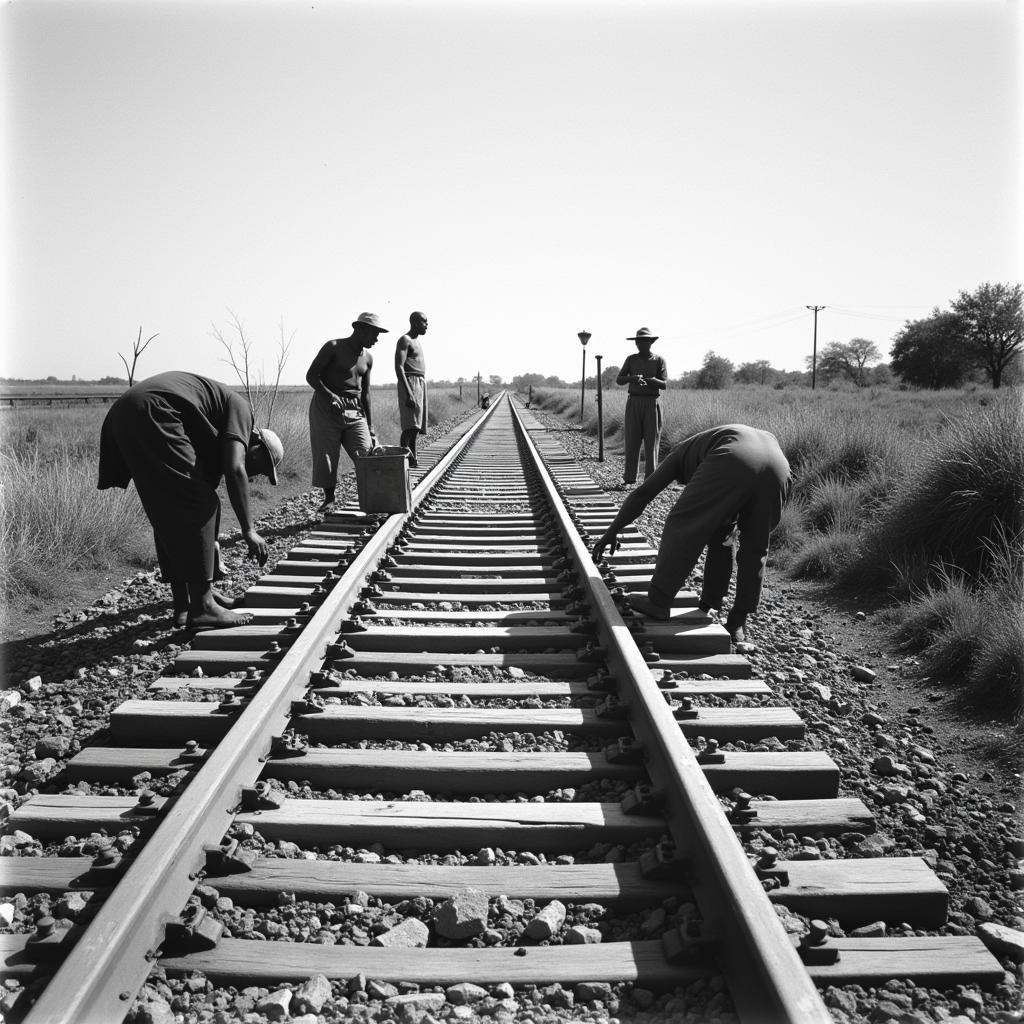 French Colonial Infrastructure in Africa
French Colonial Infrastructure in Africa
The French educational system, implemented across the colonies, played a role in shaping intellectual elites and fostering new forms of cultural expression. However, this system also prioritized French language and culture, often at the expense of indigenous knowledge and traditions. What African countries were colonized? Many experienced a suppression of their local cultures and traditions due to the imposition of French customs and administrative systems.
“French colonialism was a complex phenomenon,” explains Dr. Fatima Diallo, a prominent historian specializing in Franco-African relations. “While it introduced certain modernizing elements, it also caused significant disruption and exploitation, leaving a legacy that continues to shape these nations today.”
Post-Colonial Challenges and Resilience
Following independence, many former French colonies faced numerous challenges. Political instability, economic dependency, and social inequalities were often exacerbated by the legacy of colonial rule. However, these nations also demonstrated remarkable resilience, forging new paths towards development and self-determination. What were the long-term effects of French colonialism? This is a complex question with varying answers depending on the specific country. However, common themes include economic exploitation, political instability, and the erosion of cultural identities. You can learn more about the African colonies of 1914. african colonies 1914
 Post-Colonial Development in Africa
Post-Colonial Development in Africa
Conclusion: Understanding the Impact of French Colonialism
Examining the African countries colonized by France provides crucial insights into the complexities of African history and the enduring legacy of colonialism. Understanding this history is essential for fostering informed discussions about contemporary Africa and its future. Learning about the lasting impact of French colonization on African countries allows us to better comprehend the challenges and opportunities facing these nations today. african countries colonized by italy
FAQ
-
How many African countries were colonized by France? France colonized a significant portion of Africa, including over 20 countries.
-
When did French colonization in Africa begin? French colonial activities began in the 16th century.
-
What were the main motivations behind French colonialism? France’s colonial pursuits were driven by economic interests, political ambition, and a desire for global power.
-
What is the lasting impact of French colonialism on language? French remains an official language in many former colonies.
-
What were some of the negative consequences of French colonialism? Negative consequences included economic exploitation, political instability, and cultural suppression. african countries that were colonized]
-
How has post-colonial Africa addressed the challenges of the past? Post-colonial African nations have shown resilience in their pursuit of development and self-determination, while grappling with the complex legacy of colonial rule.
-
Where can I find more resources on African history and colonialism? Numerous academic institutions and online resources offer valuable information on this topic.
Need support? Contact us 24/7: Phone: +255768904061, Email: [email protected], or visit us at Mbarali DC Mawindi, Kangaga, Tanzania.