African Buffalo Information: The Mighty Bovine of the Savanna
The African buffalo, scientifically known as Syncerus caffer, is a powerful and iconic herbivore found throughout sub-Saharan Africa. Often referred to as the “Black Death” or “widowmaker”, this formidable creature plays a crucial role in the ecosystem and holds a significant place in African culture.
Unveiling the African Buffalo: Appearance and Subspecies
Characterized by its robust build and distinctive curved horns, the African buffalo possesses a formidable appearance. They are massive creatures, with males typically weighing between 600-900 kg, while females are slightly smaller, ranging from 500-700 kg. Their coat color varies depending on the subspecies, ranging from dark brown to black.
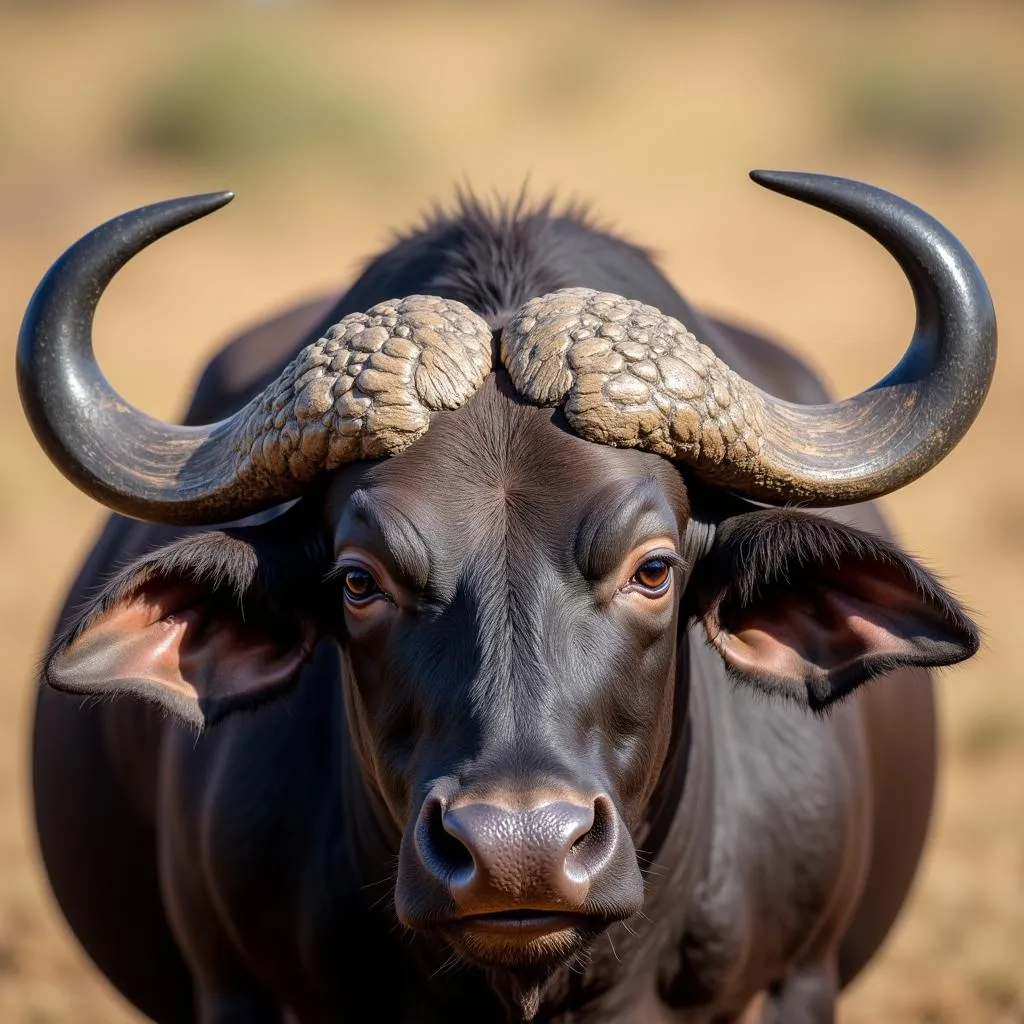 African Buffalo Horns
African Buffalo Horns
There are four recognized subspecies of African buffalo, each adapted to its particular environment:
- Cape buffalo (Syncerus caffer caffer): The largest and most widespread subspecies, found in Southern and East Africa.
- Forest buffalo (Syncerus caffer nanus): The smallest subspecies, inhabiting the rainforests of Central and West Africa.
- Sudan buffalo (Syncerus caffer brachyceros): Found in West Africa, characterized by its shorter horns.
- Nile buffalo (Syncerus caffer aequinoctialis): Residing in East Africa, known for its reddish-brown coat.
A Day in the Life: African Buffalo Behavior and Social Structure
African buffalo are highly social animals, living in herds that can range in size from a few dozen to several thousand individuals. These herds are complex social structures, with a defined hierarchy and intricate communication methods. They exhibit impressive synchronization in their movements, grazing, and defense mechanisms.
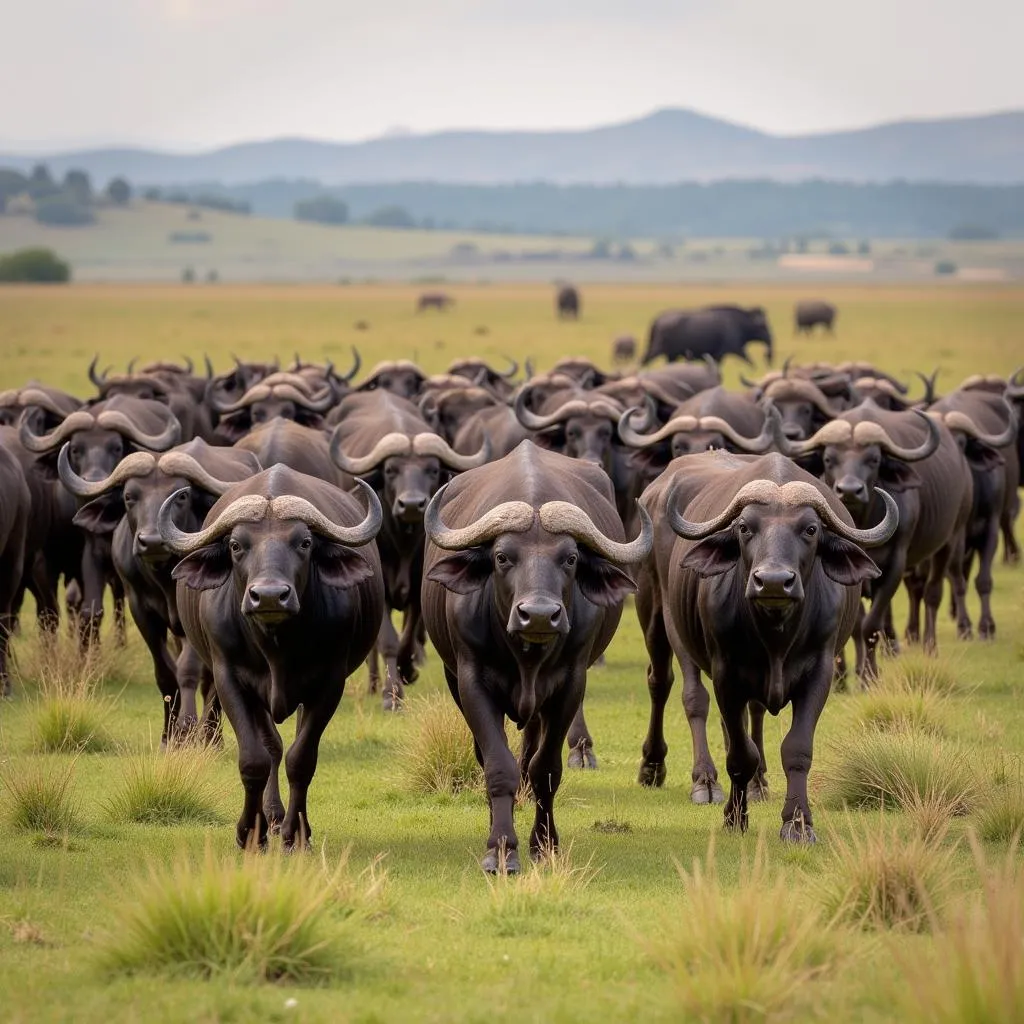 African Buffalo Herd
African Buffalo Herd
Communication within the herd is crucial for their survival. They utilize a range of vocalizations, including grunts, snorts, and bellows, to convey warnings, maintain social order, and coordinate movements.
The Circle of Life: Diet, Predators, and Ecosystem Role
As herbivores, African buffalo play a vital role in maintaining the delicate balance of the savanna ecosystem. Their diet primarily consists of grasses, but they also consume leaves, fruits, and bark. Their grazing habits help to control vegetation growth, which in turn influences the habitat of other species.
Despite their size and strength, African buffalo do face threats from predators. Lions, leopards, hyenas, and crocodiles are known to prey on calves and weaker individuals. However, a herd of buffalo can effectively defend itself against even the most formidable predators.
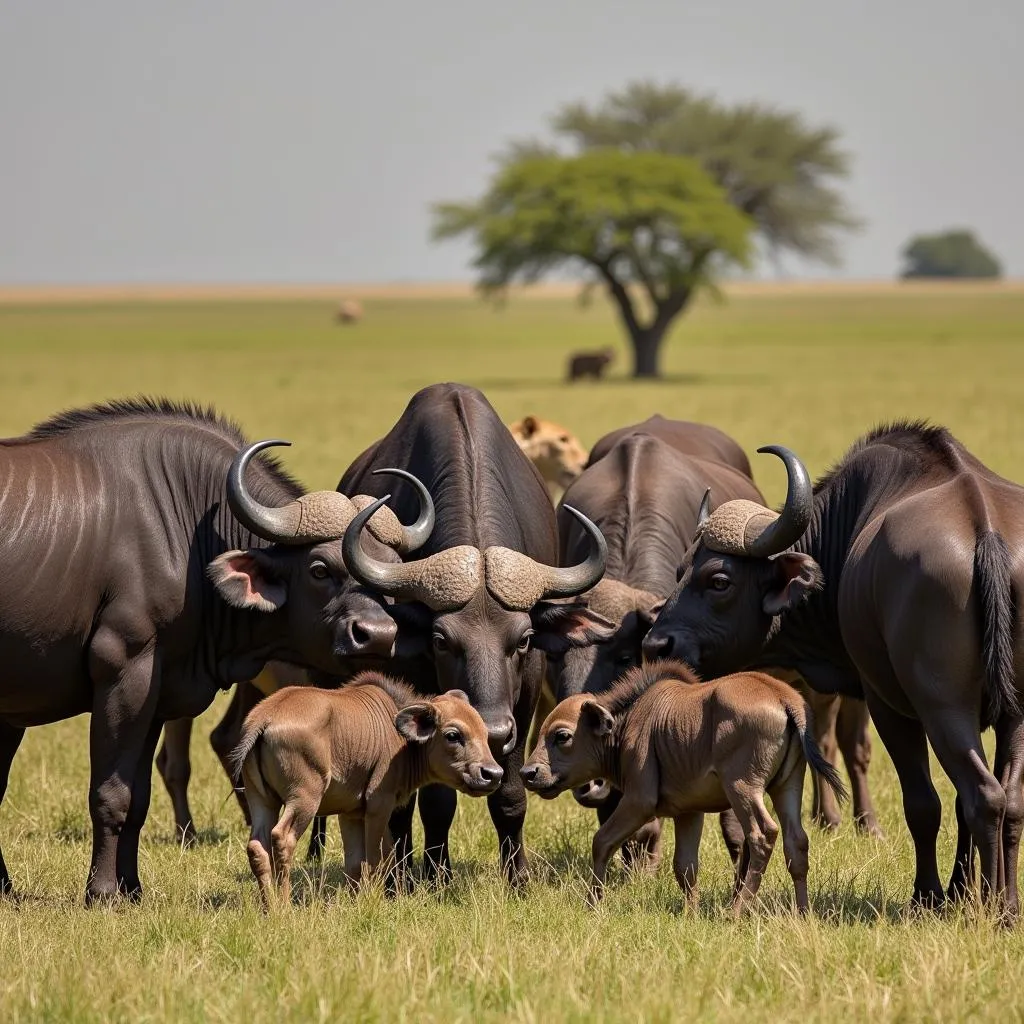 African Buffalo Defense
African Buffalo Defense
African Buffalo and Humans: A Complex Relationship
The relationship between African buffalo and humans is intricate and multifaceted. Throughout history, they have been a source of food, hides, and even traditional medicine in some cultures. However, they are also known for their unpredictable behavior and can be dangerous if threatened.
Today, African buffalo face challenges such as habitat loss due to human encroachment and the risk of diseases. Conservation efforts are crucial to ensure the survival of these magnificent creatures for generations to come.
African Buffalo: A Vital Thread in the Tapestry of Africa
The African buffalo, with its impressive strength, complex social structure, and ecological significance, embodies the raw beauty and power of the African wilderness. Understanding and appreciating these creatures is essential for fostering a greater understanding of the intricate web of life that thrives across the continent.
FAQs about African Buffalo
1. Are African buffalo dangerous to humans?
While they are herbivores, African buffalo are powerful animals that can be unpredictable and aggressive, especially when threatened or injured. It’s crucial to observe them from a safe distance and respect their space.
2. How long do African buffalo live?
The average lifespan of an African buffalo in the wild is around 15-20 years.
3. What is the biggest threat to African buffalo populations?
Habitat loss, disease outbreaks, and hunting are the most significant threats to African buffalo populations.
Explore More About African Wildlife
- For fascinating insights into other African bovine species, check out our article on African bovine.
- Discover the incredible diversity of African animals by region in our comprehensive guide.
- Learn about the critical conservation efforts being made by organizations like the African buffalo WWF.
We hope this information has provided valuable insights into the fascinating world of the African buffalo. If you need further assistance, please don’t hesitate to contact us at +255768904061, email us at kaka.mag@gmail.com, or visit us at our office in Mbarali DC Mawindi, Kangaga, Tanzania. Our dedicated customer support team is available 24/7 to assist you.