Discovering the West African Tree Frog
The West African tree frog, a fascinating amphibian inhabiting the lush rainforests of West Africa, holds a unique place in the region’s diverse ecosystem. From its vibrant coloration to its nocturnal habits, this arboreal creature offers a glimpse into the wonders of the natural world.
West African Tree Frog: Habitat and Adaptations
West African tree frogs are highly adapted to their arboreal lifestyle. Their sticky toe pads allow them to effortlessly climb trees, branches, and even smooth leaves.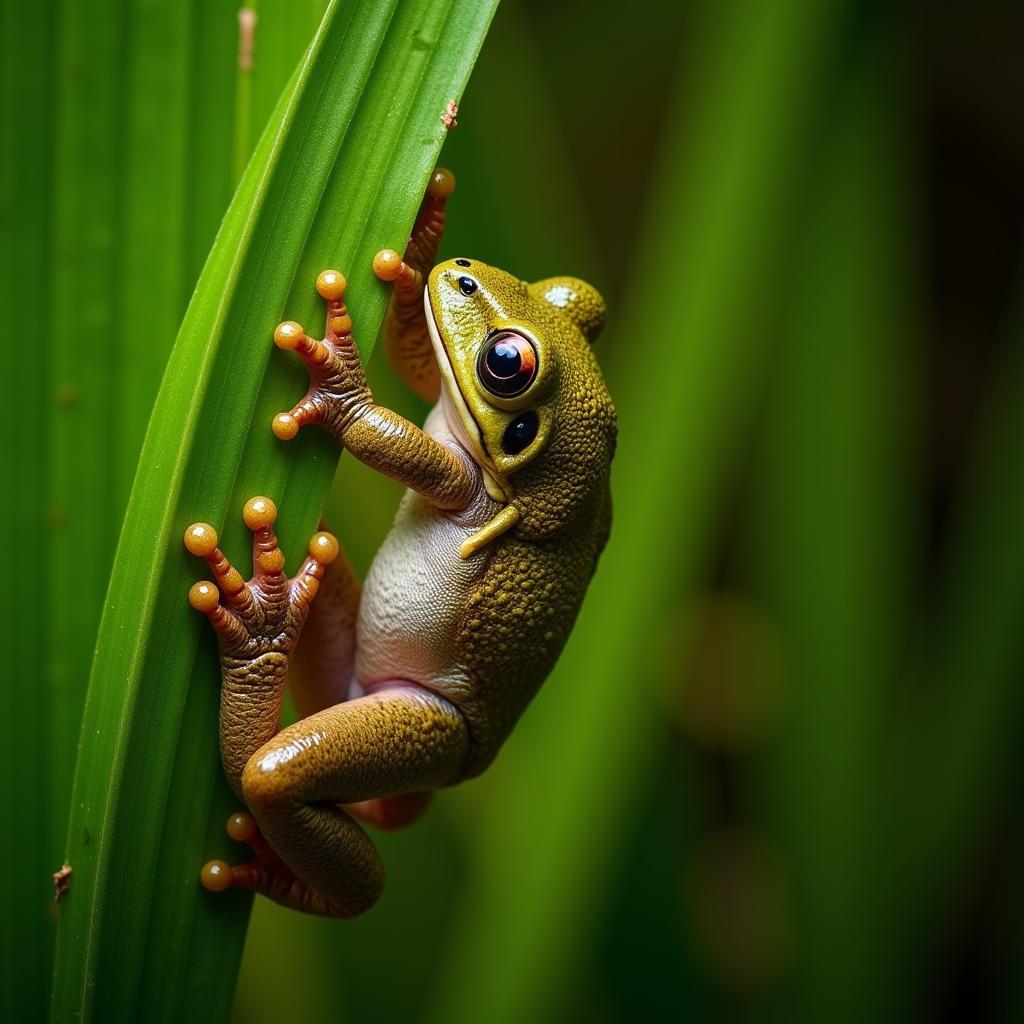  West African Tree Frog Climbing a Leaf This adaptation allows them to access a wide range of food sources and escape ground-dwelling predators. These frogs are typically found in the rainforests of countries like Ghana, Nigeria, and Cameroon, where the humid climate and dense vegetation provide ideal conditions for their survival.
West African Tree Frog Climbing a Leaf This adaptation allows them to access a wide range of food sources and escape ground-dwelling predators. These frogs are typically found in the rainforests of countries like Ghana, Nigeria, and Cameroon, where the humid climate and dense vegetation provide ideal conditions for their survival.
Their skin, often brightly colored, serves as camouflage amongst the foliage, protecting them from predators such as the african green snake. Moreover, their large eyes provide excellent night vision, essential for hunting insects in the dark.
The Nocturnal Life of the West African Tree Frog
What does A West African Tree Frog do at night? These primarily nocturnal creatures spend their days hidden amongst the leaves, emerging at dusk to begin their nightly activities. Their diet mainly consists of insects, which they catch with their long, sticky tongues.
A Symphony of Sounds: The West African Tree Frog’s Call
The male West African tree frog’s call is a distinctive and often loud chorus that echoes through the rainforest at night. This call serves to attract females and establish territory. The specific calls vary between species, creating a complex symphony of sound in the rainforest.
Dr. Kwame Asante, a renowned herpetologist specializing in West African amphibians, notes: “The vocalizations of these frogs are not just simple calls, they are complex communication systems that play a vital role in their social interactions and reproductive success.”
Conservation of the West African Tree Frog
Like many rainforest inhabitants, the West African tree frog faces threats from habitat loss due to deforestation and climate change. Protecting these fragile ecosystems is crucial for the survival of these unique creatures.
Dr. Abena Osei, a conservation biologist, adds, “Understanding the specific needs of the West African tree frog and its habitat is crucial for developing effective conservation strategies.”
Conclusion
The West African tree frog is a testament to the biodiversity of West African rainforests. From its remarkable adaptations to its nocturnal habits, this small amphibian plays an essential role in the delicate balance of its ecosystem. Protecting the West African tree frog and its habitat is essential for preserving the richness and beauty of the natural world.
FAQ
- What is the average lifespan of a West African tree frog?
- Are West African tree frogs poisonous?
- What are the main predators of the West African tree frog?
- How do West African tree frogs reproduce?
- What is the role of the West African tree frog in its ecosystem?
- How does climate change affect the West African tree frog?
- What can be done to protect the West African tree frog?
Need assistance? Contact us 24/7: Phone: +255768904061, Email: kaka.mag@gmail.com or visit us at Mbarali DC Mawindi, Kangaga, Tanzania. We have a dedicated customer service team ready to help.