African Adult Bush Elephant vs. Indian Adult Elephant: A Detailed Comparison
The African adult bush elephant and the Indian adult elephant, while both majestic creatures, exhibit distinct differences in their physical attributes, habitats, and behaviors. This article delves into a comprehensive comparison of these two iconic elephant species, highlighting their unique characteristics and adaptations.
Size and Physical Characteristics: Spotting the Differences
The most obvious difference between the African and Indian elephant lies in their size. African bush elephants are significantly larger, with males reaching heights of up to 13 feet at the shoulder and weighing up to 6 tons. Indian elephants, on the other hand, are smaller, with males averaging around 9 feet tall and weighing up to 5 tons.
Beyond size, their physical features also vary. African elephants have larger ears shaped like the African continent, while Indian elephants have smaller, more rounded ears. Both male and female African elephants have tusks, whereas only male Indian elephants typically have prominent tusks. The forehead of an African elephant is characterized by two distinct domes, while the Indian elephant’s forehead has a single dome. Furthermore, the back of the African elephant slopes downwards, while the Indian elephant’s back is more level or slightly arched.
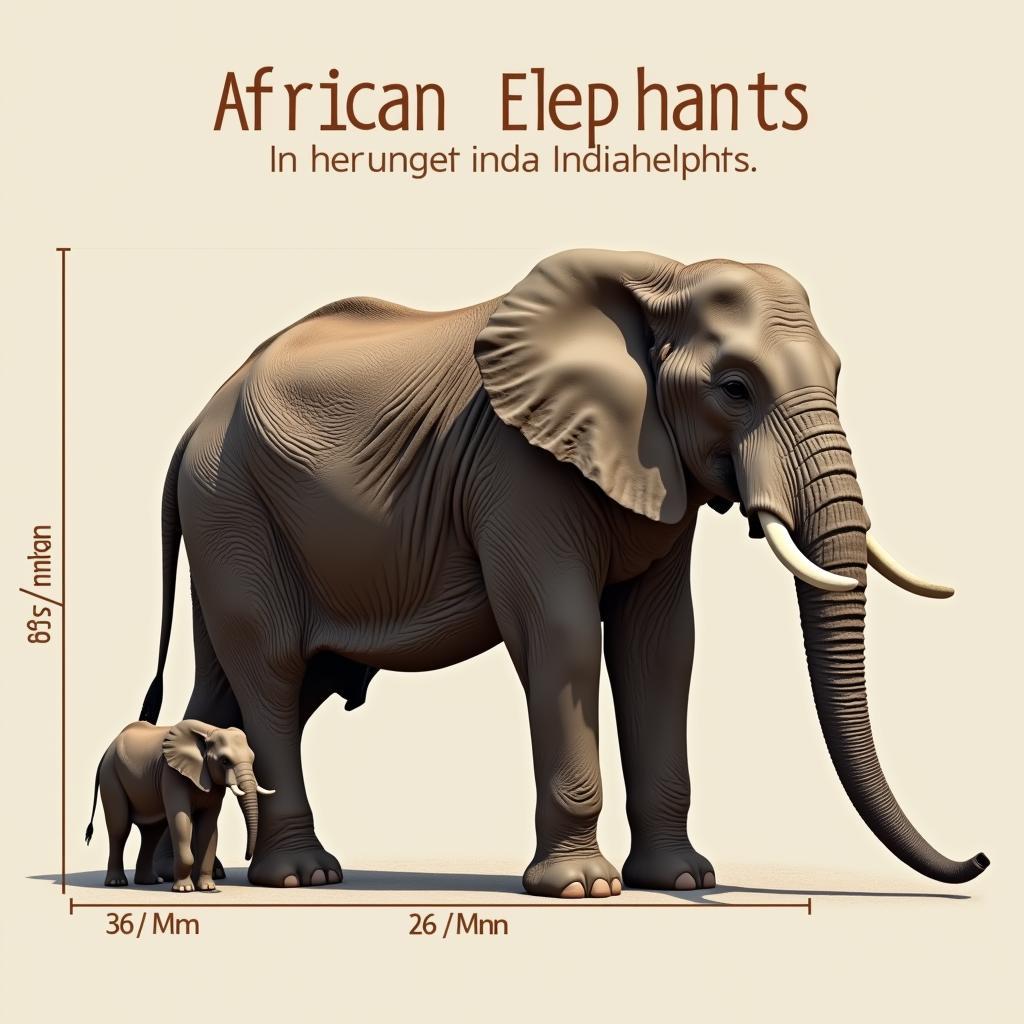 African Bush Elephant vs Indian Elephant Size Comparison
African Bush Elephant vs Indian Elephant Size Comparison
Habitat and Distribution: Where They Roam
African bush elephants are found across sub-Saharan Africa, inhabiting a variety of environments, from savannas and grasslands to forests and deserts. Indian elephants are native to the Indian subcontinent and parts of Southeast Asia, primarily residing in forested areas and grasslands. This geographical separation has played a significant role in the evolutionary divergence of these two species.
The African elephant’s vast range necessitates its adaptability to diverse landscapes and food sources. Indian elephants, however, are more specialized in their habitat preferences, thriving in more densely vegetated regions.
 African and Indian Elephant Habitat Map
African and Indian Elephant Habitat Map
Social Behavior and Intelligence: Family Matters
Both African and Indian elephants are highly social animals, living in complex family groups led by a matriarch. However, there are subtle differences in their social structures. African elephant herds are generally larger and more fluid, while Indian elephant herds tend to be smaller and more cohesive.
Both species exhibit remarkable intelligence and emotional depth, demonstrating empathy, grief, and complex communication. They use a variety of vocalizations, including rumbles, trumpets, and roars, to communicate with each other.
Diet and Feeding Habits: What’s on the Menu?
Being herbivores, both African and Indian elephants consume vast quantities of vegetation. African elephants have a more varied diet, feeding on grasses, leaves, bark, and fruits. Indian elephants, due to their forest habitat, primarily consume leaves, bamboo, fruits, and bark. Their dietary preferences reflect the available food sources within their respective environments.
“Observing elephants in their natural habitat highlights the distinct foraging strategies employed by each species,” notes Dr. Anya Sharma, a wildlife biologist specializing in elephant behavior. “The African elephant’s trunk, with its two finger-like projections, is well-suited for grasping grass and branches, while the Indian elephant’s single finger-like projection is adept at stripping leaves and picking up smaller items.”
Conservation Status: Protecting Giants
Both African and Indian elephants face significant conservation challenges. Poaching for ivory, habitat loss due to deforestation and human encroachment, and human-wildlife conflict pose serious threats to their survival. Conservation efforts are crucial for ensuring the long-term survival of these magnificent animals.
“Protecting these keystone species is paramount for maintaining the ecological balance of their respective ecosystems,” adds Dr. Sharma. “Effective conservation strategies must address the root causes of poaching and habitat destruction while promoting co-existence between humans and elephants.”
Conclusion: Celebrating Diversity
The African adult bush elephant and the Indian adult elephant, while sharing a common ancestry, have evolved distinct characteristics that make them uniquely adapted to their respective environments. Understanding these differences is crucial for appreciating the biodiversity of our planet and promoting effective conservation efforts. By protecting these gentle giants, we safeguard not only their future but also the health of the ecosystems they inhabit.
FAQ
-
What is the main difference in size between African and Indian elephants?
African elephants are significantly larger than Indian elephants. -
Do both male and female African elephants have tusks?
Yes, both male and female African elephants have tusks. -
Where are Indian elephants found?
Indian elephants are found in the Indian subcontinent and parts of Southeast Asia. -
What are the primary threats to both species?
Poaching, habitat loss, and human-wildlife conflict are the primary threats. -
Why are elephants considered keystone species?
Elephants play a vital role in shaping their environment, impacting vegetation and creating habitats for other animals. -
How can I contribute to elephant conservation?
Supporting reputable conservation organizations and raising awareness about the challenges facing elephants are valuable contributions. -
What are some of the key differences in their social behavior?
African elephant herds are generally larger and more fluid than Indian elephant herds.
For further information on African wildlife and conservation efforts, explore our other articles on African lions, rhinos, and the diverse ecosystems of the continent.
Need assistance? Contact us 24/7: Phone: +255768904061, Email: kaka.mag@gmail.com, or visit us at Mbarali DC Mawindi, Kangaga, Tanzania.



