Exploring Traditional and Modern African Agriculture Practices
African agriculture is the backbone of the continent’s economy and livelihood for millions. From ancient techniques passed down through generations to the integration of modern technology, African Agriculture Practice is a diverse and fascinating field. This exploration delves into the heart of African farming, examining its history, challenges, innovations, and the vital role it plays in global food security.
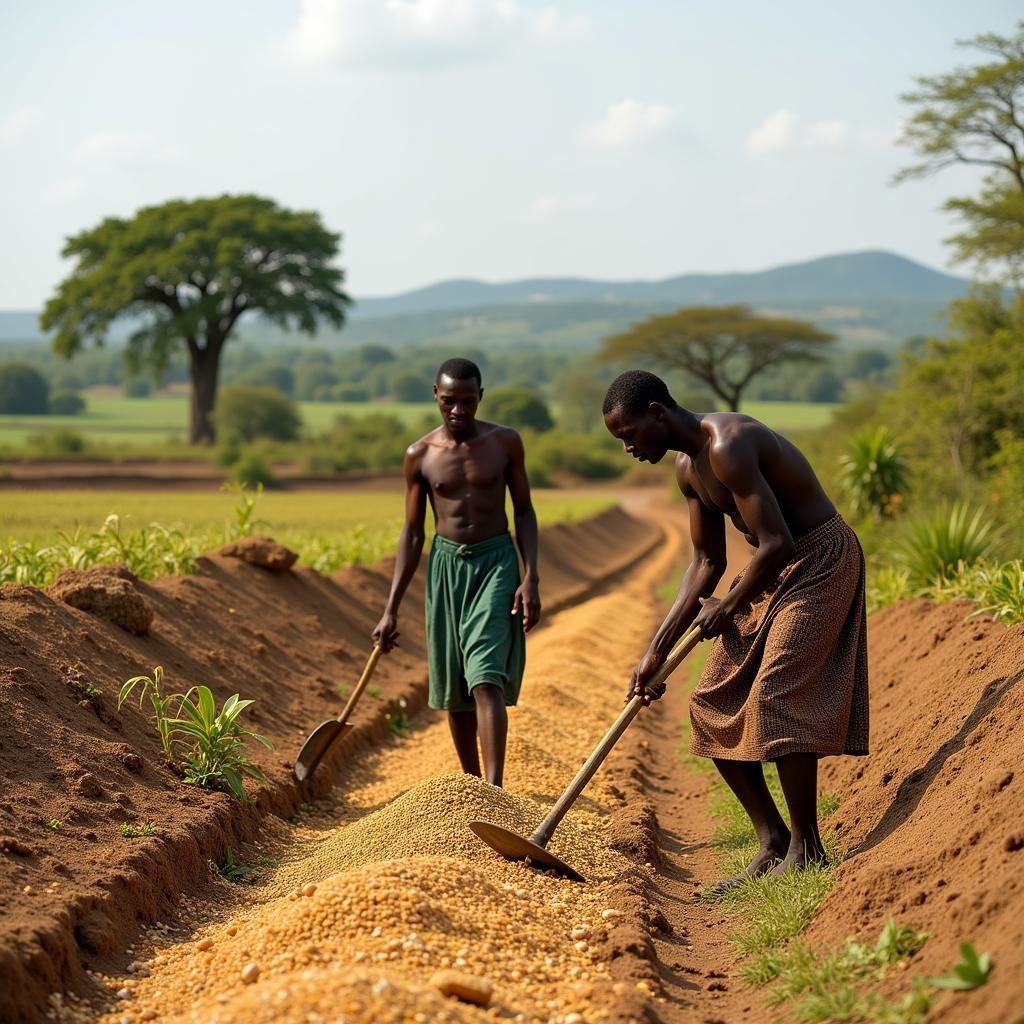 Traditional African Farming Practices: A Glimpse into the Past
Traditional African Farming Practices: A Glimpse into the Past
A History Rooted in Tradition
For centuries, African communities have cultivated their land, developing unique farming systems adapted to diverse climates and landscapes. Traditional methods, like shifting cultivation and intercropping, demonstrate a deep understanding of the environment and resource management.
- Shifting Cultivation: This method involves clearing small plots of land, farming them for a few years until the soil’s fertility declines, and then allowing the land to regenerate naturally.
- Intercropping: By planting different crops together, farmers maximize land use, control pests, and improve soil health. This method highlights the intricate knowledge of plant interactions developed over generations.
These practices, while effective in the past, now face challenges from growing populations and climate change, necessitating adaptation and evolution.
Challenges and Triumphs of Modern African Agriculture
Modern African agriculture faces a complex web of challenges: climate change, limited access to markets, and inadequate infrastructure all pose significant obstacles. Yet, amidst these hurdles, African farmers and innovators are developing ingenious solutions.
Embracing Technology for a Brighter Future
The rise of technology offers a beacon of hope for African agriculture. Mobile technology connects farmers to crucial information, weather forecasts, and market prices, empowering them to make informed decisions.
Sustainable Practices: A Path to Food Security
Recognizing the importance of environmental stewardship, many African farmers are turning towards sustainable practices like conservation agriculture and agroforestry. These methods prioritize soil health, water conservation, and biodiversity, ensuring long-term productivity and resilience.
- Conservation Agriculture: This approach minimizes soil disturbance, utilizes crop residues, and promotes crop rotation, enhancing soil fertility and water retention.
- Agroforestry: Integrating trees and shrubs into farming systems provides multiple benefits, including shade, soil improvement, and diversification of income sources.
The Global Significance of African Agriculture
African agriculture holds immense potential not only for the continent but for global food security. With its vast land resources and a growing youth population, Africa has the capacity to become a major food producer.
Investing in African agriculture, supporting smallholder farmers, and promoting sustainable practices are crucial steps towards unlocking this potential and creating a more food-secure future for all.
Conclusion
African agriculture practice is a tapestry woven with threads of tradition, resilience, and innovation. While facing significant challenges, the continent’s agricultural landscape is evolving. By supporting sustainable practices, investing in technology, and empowering farmers, we can help unlock the full potential of African agriculture, ensuring food security for Africa and the world.
FAQs about African Agriculture
1. What are the major crops grown in Africa?
Africa boasts a wide array of crops, with staples like maize, cassava, sorghum, and millet dominating production. Other important crops include cocoa, coffee, cotton, and various fruits and vegetables.
2. How is climate change impacting African agriculture?
Climate change poses a significant threat to African agriculture, with increasing temperatures, droughts, and floods affecting crop yields and livestock production. This emphasizes the urgency of adopting climate-smart agricultural practices.
3. What is being done to improve access to markets for African farmers?
Efforts are underway to improve infrastructure, promote cooperatives, and leverage technology to connect farmers directly to buyers, bypassing intermediaries and ensuring fairer prices.
4. What role do women play in African agriculture?
Women play a pivotal role in African agriculture, comprising a significant portion of the agricultural workforce. Empowering women farmers through land rights, access to finance, and education is crucial for agricultural development.
5. How can I support sustainable agriculture in Africa?
Supporting organizations working directly with African farmers, promoting fair trade practices, and raising awareness about the importance of sustainable agriculture are all meaningful ways to contribute.
For further assistance and inquiries, please do not hesitate to contact us:
Phone Number: +255768904061
Email: kaka.mag@gmail.com
Address: Mbarali DC Mawindi, Kangaga, Tanzania.
We are available 24/7 to address your needs and provide support.