Unveiling the Mysterious African Angelshark
The African Angelshark (Squatina africana) is a captivating creature shrouded in mystery, inhabiting the sandy depths off the coasts of Africa. These fascinating sharks, with their flattened bodies and wing-like pectoral fins, are masters of camouflage, blending seamlessly into their sandy seabed habitats. Let’s delve into the intriguing world of the African angelshark, exploring its unique characteristics, behaviors, and the challenges it faces.
The Elusive Flat Shark: African Angelshark Characteristics
The African angelshark is a unique species of angelshark, distinguishable by its distinct physical attributes. Its flattened body, resembling a ray, allows it to lie perfectly still on the ocean floor, virtually invisible to unsuspecting prey. Their large, wing-like pectoral fins contribute to this flattened appearance, further enhancing their camouflage. They possess a mottled brown or grey coloration, speckled with darker spots, which perfectly mimics the sandy or muddy substrates they call home. Typically reaching lengths of up to 1.5 meters, the African angelshark is a formidable predator, equipped with rows of sharp teeth perfectly designed for ambushing prey.
These sharks are primarily nocturnal hunters, relying on their exceptional camouflage and electroreception to detect prey hidden beneath the sand. They feed primarily on bony fish, crustaceans, and cephalopods. African angelsharks are ovoviviparous, meaning the eggs hatch inside the female’s body, and she gives birth to live young. This reproductive strategy ensures a higher survival rate for the pups, as they are born fully developed and ready to navigate the challenges of their environment.
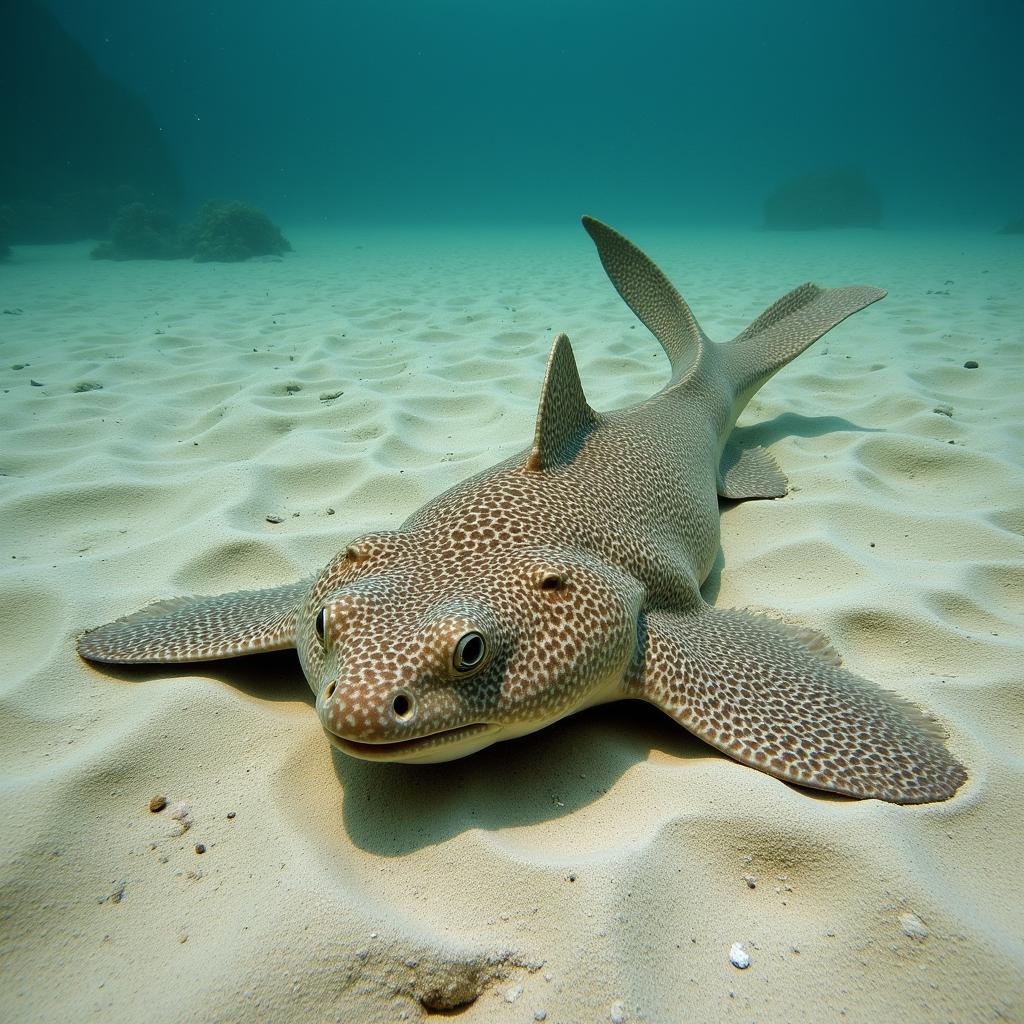 African Angelshark Camouflaged on Sandy Seabed
African Angelshark Camouflaged on Sandy Seabed
African Angelshark Habitat and Distribution
African angelsharks are endemic to the eastern Atlantic Ocean, ranging from southern Angola to southern Mozambique, including the waters surrounding Madagascar. They prefer warm, temperate waters and are typically found in shallow coastal waters, from the intertidal zone down to depths of approximately 100 meters. Their preferred habitat consists of sandy or muddy bottoms, where they can effectively bury themselves and lie in wait for unsuspecting prey. These environments also offer protection from larger predators.
Although they are widespread throughout their range, African angelsharks are considered a vulnerable species due to several threats. Habitat destruction, primarily caused by coastal development and bottom trawling, poses a significant risk to their survival. Bycatch in fisheries targeting other species also contributes to their declining population numbers.
 Map Showing the Distribution of the African Angelshark
Map Showing the Distribution of the African Angelshark
Conservation Efforts and the Future of the African Angelshark
Understanding the behavior and ecology of the African angelshark is crucial for developing effective conservation strategies. Research on their movement patterns, reproductive biology, and habitat preferences is ongoing. This information is essential for implementing measures to protect their critical habitats and mitigate the impact of human activities.
Several organizations are working to raise awareness about the plight of the African angelshark and advocate for stronger protections. Efforts are underway to reduce bycatch in fisheries and implement sustainable fishing practices. Protecting essential habitats, such as nursery grounds and feeding areas, is also a priority.
“Protecting the African angelshark is not just about preserving a species,” says Dr. Thomas Olsen, a marine biologist specializing in elasmobranch conservation. “It’s about safeguarding the delicate balance of the marine ecosystem. These sharks play a vital role in regulating prey populations and maintaining the health of their environment.”
Conclusion: Ensuring the Survival of the African Angelshark
The African angelshark, a master of camouflage and a vital component of the African marine ecosystem, faces significant challenges. By understanding its unique characteristics, distribution, and the threats it faces, we can work towards ensuring its survival for future generations. Continued research, conservation efforts, and responsible fishing practices are crucial for protecting this fascinating and vulnerable species. The future of the African angelshark depends on our collective efforts to safeguard its habitat and mitigate the impact of human activities. Remember, every action, no matter how small, can contribute to the preservation of this remarkable creature and the health of our oceans.
FAQ
- What does the African angelshark eat? They primarily feed on bony fish, crustaceans, and cephalopods.
- Where is the African angelshark found? It is found in the eastern Atlantic Ocean, from southern Angola to southern Mozambique.
- Is the African angelshark endangered? It is considered a vulnerable species.
- What are the main threats to the African angelshark? Habitat destruction and bycatch in fisheries are the primary threats.
- How big does the African angelshark get? They can grow up to 1.5 meters in length.
- What is unique about the African angelshark’s appearance? It has a flattened body and wing-like pectoral fins, allowing it to blend into the seabed.
- How does the African angelshark reproduce? It is ovoviviparous, meaning the eggs hatch inside the female’s body.
You might also be interested in reading our articles about other shark species and marine conservation efforts in Africa.
Need help? Contact us 24/7! Phone: +255768904061, Email: kaka.mag@gmail.com, or visit us at Mbarali DC Mawindi, Kangaga, Tanzania.

