African Apple Snail’s Impact in India
The African apple snail (Pomacea canaliculata) has made its presence known in India, posing significant challenges to the nation’s agriculture and ecosystems. This invasive species has spread rapidly across various regions, impacting local biodiversity and agricultural practices. This article will delve into the African apple snail’s impact in India, examining its ecological and economic consequences.
The Uninvited Guest: Understanding the African Apple Snail in India
The African apple snail, also known as the channeled apple snail, is native to South America but has become a notorious invasive species globally, including India. It’s easily recognizable by its large, globular shell, which can grow up to the size of a tennis ball. The snail thrives in freshwater habitats such as rivers, ponds, and rice paddies, making India’s abundant water resources a suitable environment for its proliferation. Its voracious appetite for a wide variety of aquatic plants, including rice crops, poses a direct threat to food security and farmers’ livelihoods.
These snails are incredibly adaptable, capable of surviving in harsh conditions and reproducing at an alarming rate. Their ability to lay hundreds of bright pink eggs above the waterline makes them difficult to control, as the eggs are often out of reach of traditional control methods. This rapid reproduction cycle allows them to quickly establish populations and overwhelm native species.
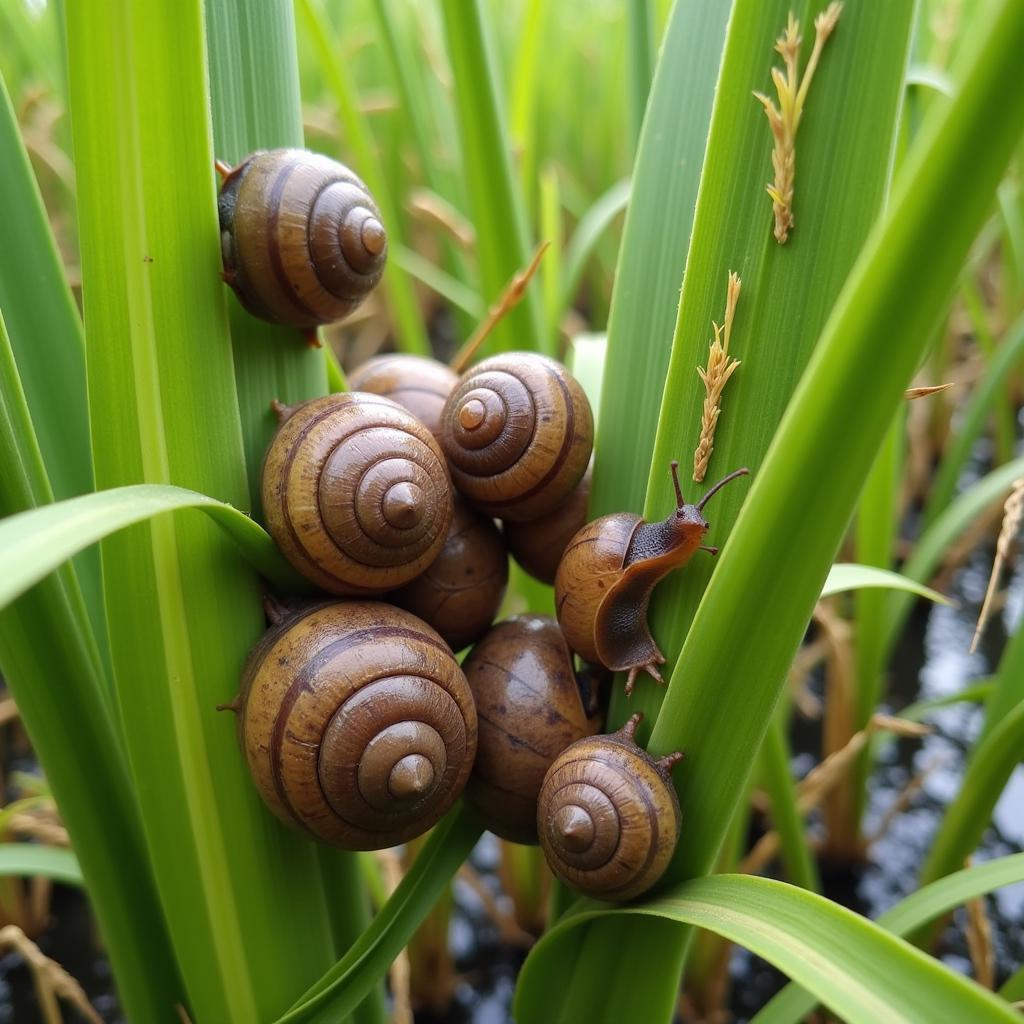 African Apple Snail in Indian Rice Paddies
African Apple Snail in Indian Rice Paddies
Ecological Consequences: A Threat to Biodiversity
The African apple snail’s introduction to India has caused significant disruptions to local ecosystems. As a highly competitive species, it outcompetes native snails for resources, leading to their decline and potential extinction. The snail’s consumption of native aquatic plants disrupts the food chain and can negatively impact other organisms that depend on these plants for survival. Furthermore, the snail can serve as a host for parasites and diseases, which can be transmitted to other aquatic life and even humans.
The disruption of the natural balance of aquatic ecosystems can have cascading effects, impacting the overall health and stability of these environments. This includes changes in water quality, decreased oxygen levels, and altered nutrient cycles.
Economic Impact: A Burden on Indian Agriculture
The most significant economic impact of the African apple snail in India is on rice cultivation. The snail’s preference for rice plants makes it a major pest for farmers, leading to reduced yields and significant economic losses. The snail’s rapid reproduction rate and resilience make it difficult to control, requiring intensive and costly management strategies.
The cost of controlling the snail, including the use of pesticides and other management techniques, adds to the financial burden on farmers, particularly small-scale farmers who may lack the resources to implement effective control measures. The overall impact on the Indian economy, although difficult to quantify precisely, is undoubtedly substantial.
Managing the Menace: Control Strategies for African Apple Snail
Controlling the African apple snail requires a multifaceted approach that integrates various methods. These include manual collection and destruction of snails and egg masses, the introduction of natural predators, and the judicious use of molluscicides. Biological control methods, such as introducing snail-eating fish or ducks, can be effective in reducing snail populations while minimizing environmental impact.
Community involvement is crucial for successful management. Educating farmers and local communities about the snail’s life cycle, its impact, and effective control methods is essential. Encouraging community-based efforts for manual collection and promoting sustainable agricultural practices can significantly contribute to mitigating the snail’s spread and impact.
Conclusion: Addressing the African Apple Snail Challenge in India
The African apple snail poses a serious threat to India’s biodiversity and agricultural sector. Addressing this challenge requires collaborative efforts from researchers, policymakers, and local communities. Developing sustainable and integrated management strategies is crucial for mitigating the snail’s impact and safeguarding India’s ecological and economic security. The African apple snail problem demands immediate attention and proactive measures to prevent further spread and minimize its long-term consequences.
FAQ
- What is the African apple snail? (An invasive freshwater snail species.)
- Why is the African apple snail a problem in India? (It damages crops, particularly rice, and disrupts ecosystems.)
- How can I identify an African apple snail? (Look for its large, globular shell, often the size of a tennis ball.)
- What can be done to control the snail’s population? (Manual removal, introduction of predators, and careful use of molluscicides.)
- How can I contribute to controlling the spread of the snail? (Participate in community collection efforts and avoid releasing snails into natural water bodies.)
- What are the long-term effects of the snail’s presence? (Loss of biodiversity, reduced agricultural productivity, and potential health risks.)
- Where can I find more information about the African apple snail? (Research online and contact local agricultural authorities.)
Other Questions Related to the African Apple Snail in India:
- Are there any specific regions in India more affected than others?
- What are the government’s initiatives to control the snail?
- How does climate change affect the snail’s spread?
For further assistance please contact us: Phone: +255768904061, Email: kaka.mag@gmail.com or visit our office at Mbarali DC Mawindi, Kangaga, Tanzania. We have a 24/7 customer service team.