Majestic African Big Male Lions: Kings of the Savanna
African Big Male Lions, with their impressive manes and powerful roars, are iconic symbols of the African savanna. These apex predators command respect and awe, playing a crucial role in the delicate balance of their ecosystem.
The Mane Attraction: What Makes Male Lions Unique
Unlike their female counterparts, adult male lions possess a distinctive mane, a thick growth of hair encircling their heads and necks. The mane serves multiple purposes, from intimidating rivals to attracting potential mates. The size, color, and fullness of the mane can vary significantly depending on factors such as genetics, age, and hormone levels.
Interestingly, a darker, fuller mane is often associated with higher testosterone levels, making these males more attractive to lionesses. However, a larger mane can also make the lion more visible to prey and increase heat stress. This delicate balance between attractiveness and functionality highlights the fascinating adaptations of these incredible animals.
A Lion’s Role: Kings of their Pride
African big male lions live in social groups called prides, typically consisting of several related females, their cubs, and one or two adult males. While lionesses are the primary hunters, the males play a crucial role in protecting the pride’s territory and offspring from rivals and predators. Their size and strength make them formidable opponents, capable of fending off threats from hyenas, leopards, and even other lions.
The leadership of a pride often changes hands as new, stronger males challenge the resident male. These battles can be fierce and even fatal, with the victor claiming dominance over the pride and the right to mate with the females. This ensures the strongest genes are passed down, contributing to the overall health and survival of the pride.
Threats to African Big Male Lions
Despite their power and majesty, African big male lions face numerous threats, many of which are human-induced. Habitat loss due to human encroachment and agriculture is a significant concern, as it fragments lion populations and reduces their access to prey.
Poaching for their bones and other body parts, often used in traditional medicine in some parts of the world, is another pressing issue. Moreover, human-wildlife conflict, driven by competition for resources and livestock depredation, also poses a significant threat to lion populations across Africa.
Conservation Efforts: Protecting the Kings
Recognizing these threats, various organizations and initiatives are working tirelessly to protect African big male lions and ensure their long-term survival. Conservation efforts focus on mitigating human-wildlife conflict, combating poaching, and protecting and restoring lion habitats.
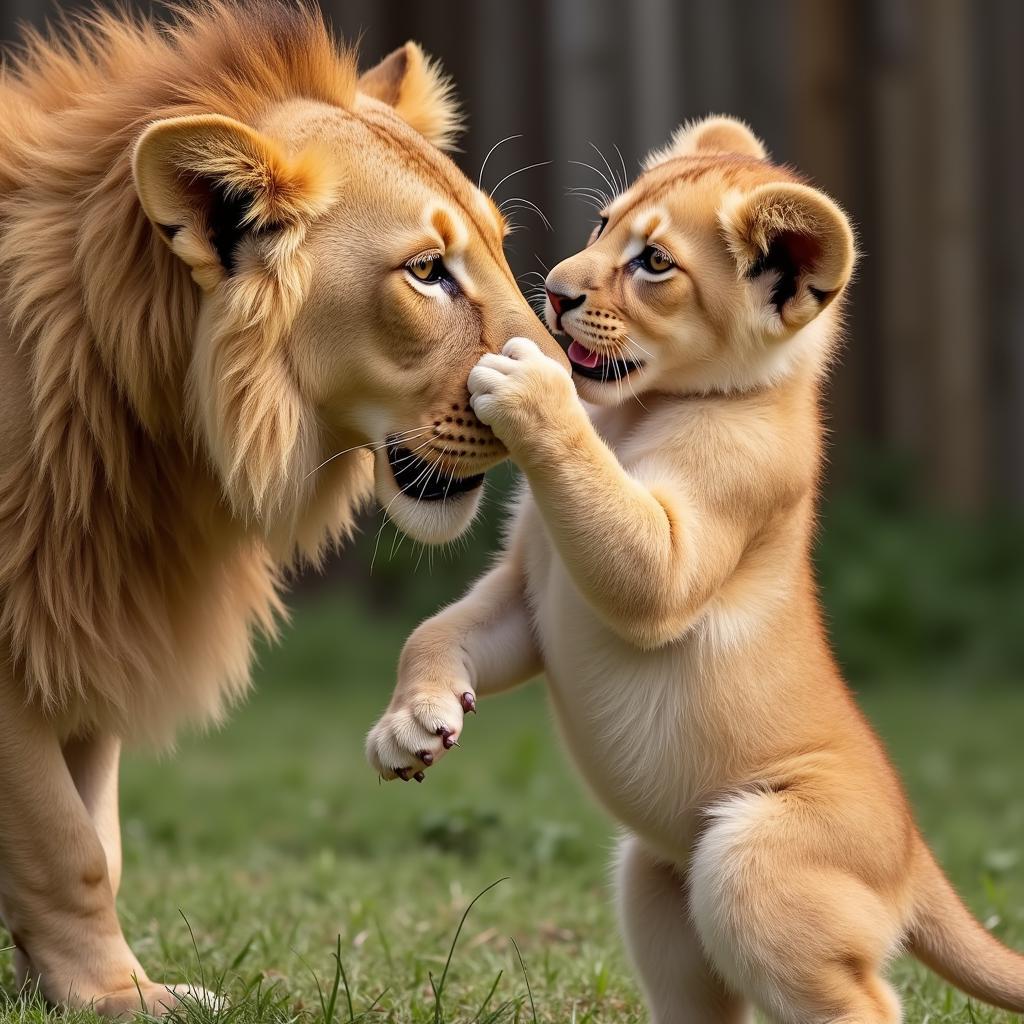 African Male Lion Cub Playing
African Male Lion Cub Playing
Community-based conservation programs, anti-poaching patrols, and educational initiatives are crucial to raising awareness and fostering coexistence between humans and these iconic animals. By supporting these efforts, we can all contribute to safeguarding the future of African big male lions, ensuring that these magnificent creatures continue to roam the African savanna for generations to come.
FAQs About African Big Male Lions
How big do African male lions get?
African male lions can grow up to 10 feet long and weigh over 550 pounds.
How long do African male lions live?
In the wild, African male lions typically live for 10-14 years, while in captivity, they can live up to 20 years.
Why do some male lions have bigger manes than others?
Mane size is influenced by genetics, age, and testosterone levels. Larger, darker manes often signal higher testosterone and attractiveness to females.
What is the biggest threat to African lions?
Habitat loss, poaching, and human-wildlife conflict are the biggest threats to African lions today.
How can I help protect African lions?
You can support conservation organizations, spread awareness, and advocate for responsible tourism practices to help protect African lions.
Need More Information?
For more fascinating insights about African wildlife, check out these articles:
Contact Us
For any inquiries or assistance, please contact us at:
Phone Number: +255768904061
Email: kaka.mag@gmail.com
Address: Mbarali DC Mawindi, Kangaga, Tanzania.
Our customer care team is available 24/7 to assist you.