Unveiling the African Bison: A Majestic Giant of the Savannah
The African Bison, also known as the Cape buffalo, is a powerful and iconic symbol of African wildlife. These impressive bovines play a vital role in the savannah ecosystem and are a sought-after sight for safari-goers. Let’s delve into the fascinating world of the African bison, exploring their behavior, habitat, and the challenges they face.
The African Bison: Physical Characteristics and Behavior
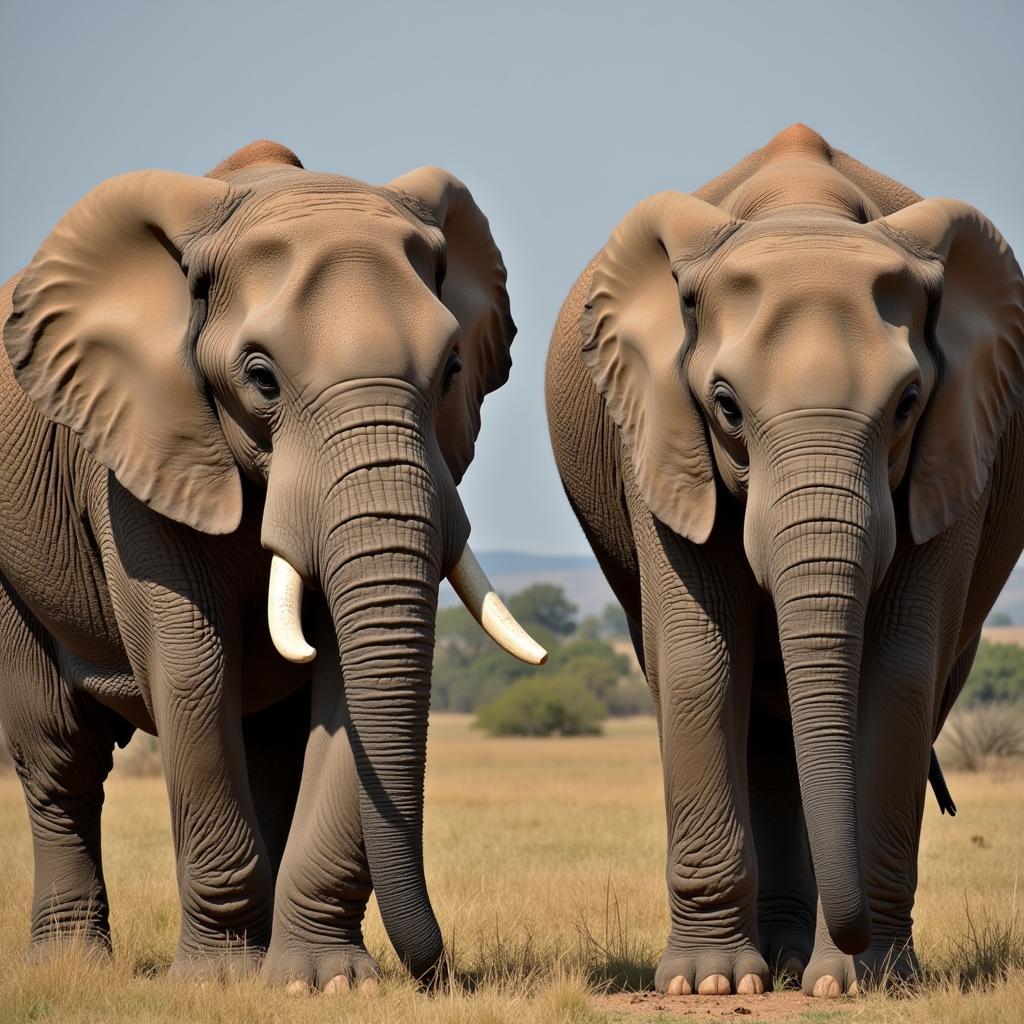
African bison are massive creatures, immediately recognizable by their thick horns that form a boss covering the top of their head. These horns can reach impressive lengths, adding to their intimidating appearance. Their shaggy coat varies in color from reddish-brown to black, and their powerful build allows them to navigate diverse terrains. They are highly social animals, living in herds that can range from a few dozen to hundreds of individuals. These herds provide protection against predators such as lions and crocodiles. african bison mating is a complex social interaction within the herd.
The social dynamics within a bison herd are fascinating. Dominance hierarchies exist, with older bulls often leading the herd. Communication within the herd is crucial for coordinated movement and defense. They use a variety of vocalizations, including grunts and bellows, to communicate with each other. Their collective strength makes them formidable opponents, even for the fiercest predators. Their impressive african bison weight also contributes to their dominance in the ecosystem.
Habitat and Distribution of the African Bison
African bison are found throughout sub-Saharan Africa, inhabiting a variety of ecosystems, from open savannas and grasslands to woodlands and forests. They are adaptable animals, able to thrive in diverse environments as long as water sources are available. african bison habitat plays a crucial role in their survival.
What are the primary threats to African bison?
Habitat loss due to human encroachment and agricultural expansion is a major threat. Disease outbreaks, particularly from domestic cattle, also pose a significant risk. Poaching, although less prevalent than for other species, remains a concern.
How do African bison contribute to the ecosystem?
Their grazing habits influence vegetation structure, creating habitats for other species. They are also an important prey source for large predators. Their dung contributes to nutrient cycling, enriching the soil.
The Future of the African Bison: Conservation Efforts
The future of the African bison depends on continued conservation efforts. Protecting their habitat through the establishment of national parks and reserves is crucial. Managing disease outbreaks and combating poaching are also essential.
“Protecting the African bison is not just about preserving a species, it’s about maintaining the ecological balance of the entire savannah ecosystem,” explains Dr. Amani Nkosi, a leading wildlife biologist specializing in African megafauna.
What does an African bison look like?
Imagine a powerful bovine with thick, curved horns forming a boss on its head, a shaggy coat ranging from reddish-brown to black, and a stocky build. That’s the majestic African bison. For a better visualization, check out some african bison images.
Conclusion: The Enduring Legacy of the African Bison
The African bison is more than just a large herbivore; it’s a vital component of the African landscape. Protecting this magnificent creature and its habitat is crucial for the continued biodiversity of the continent. Learn more about similar animals through exploring african bison like animal. The African bison stands as a testament to the power and resilience of nature.
FAQ
- What is the lifespan of an African bison? Typically 15-25 years in the wild.
- What is the difference between an African bison and a Cape buffalo? They are the same species, with “Cape buffalo” being a common name.
- What do African bison eat? They are grazers, primarily feeding on grasses.
- How fast can an African bison run? Up to 56 km/h (35 mph) in short bursts.
- Are African bison dangerous? Yes, they are powerful animals and can be aggressive, especially when threatened.
- How large is a typical African bison herd? Herds can range from a few dozen to several hundred individuals.
- What are the main predators of African bison? Lions, crocodiles, and hyenas.
Need assistance? Contact us 24/7: Phone: +255768904061, Email: kaka.mag@gmail.com, or visit us at Mbarali DC Mawindi, Kangaga, Tanzania.