African Bullfrog Adaptations: Surviving the Harsh Realities
The African bullfrog, Pyxicephalus adspersus, is a fascinating creature renowned for its impressive size and remarkable African Bullfrog Adaptations that allow it to thrive in the challenging environments of sub-Saharan Africa. These adaptations, honed over millennia, are crucial for their survival in regions characterized by extreme temperatures and unpredictable rainfall. african bullfrog adaptation
Thriving in Arid Landscapes: How the African Bullfrog Adapts
The African bullfrog faces a unique set of challenges in its arid habitat. These formidable amphibians have developed a range of remarkable survival strategies, from their impressive burrowing abilities to their unique breeding behaviors. Let’s delve into the intricate ways these creatures have adapted to conquer their harsh environment.
Burrowing: A Fortress Against the Elements
One of the most significant african bullfrog adaptations is their proficiency in burrowing. During the dry season, they create underground burrows, sometimes as deep as 2 feet, to escape the scorching heat and conserve moisture. These burrows act as a refuge, providing a stable microclimate where the frogs can enter a state of aestivation, a period of dormancy similar to hibernation.
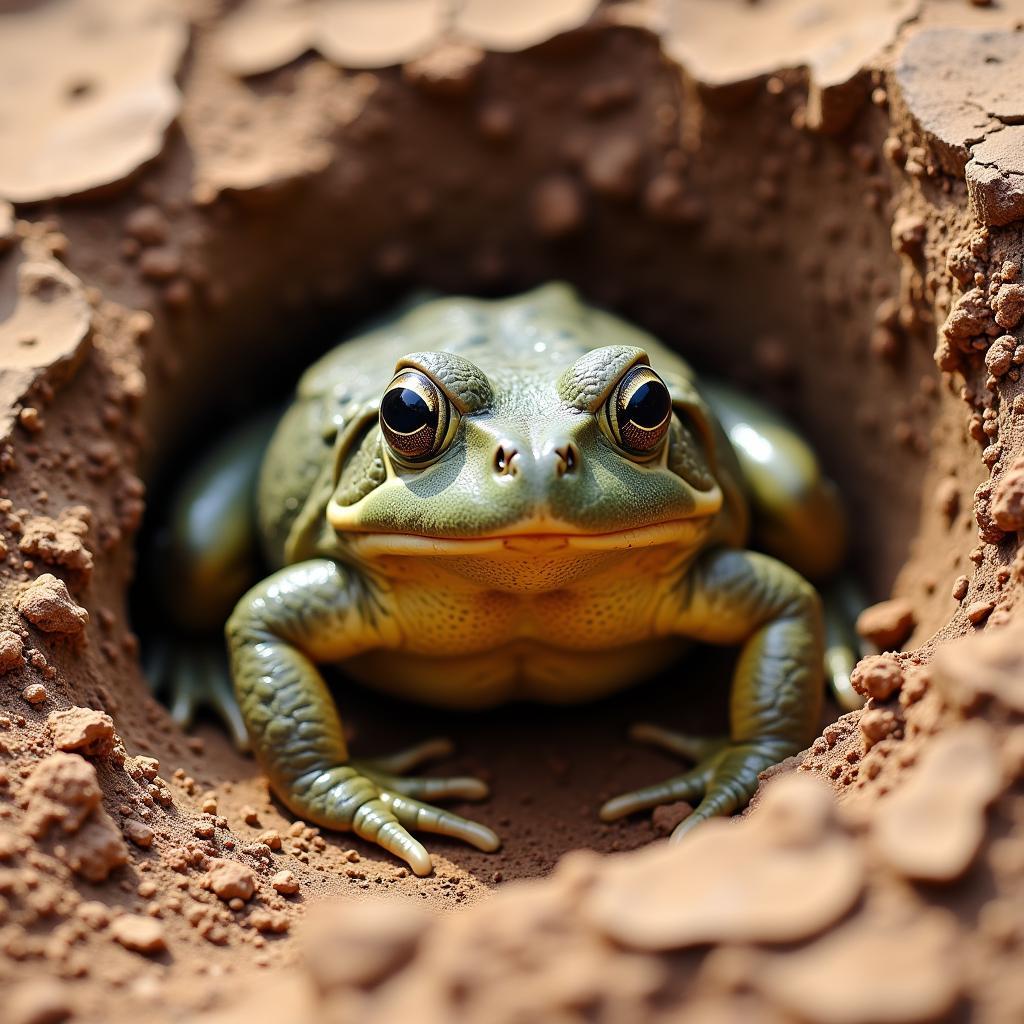 African Bullfrog Burrowing Adaptation
African Bullfrog Burrowing Adaptation
This incredible ability to effectively burrow allows them to survive for extended periods without access to water. This is essential in their native environment where water sources can be scarce and unpredictable.
Water Conservation: A Matter of Survival
Water conservation is paramount for survival in arid landscapes. African bullfrogs have developed several mechanisms to minimize water loss. Their skin secretes a waterproof mucus, helping to retain moisture. Additionally, during aestivation, they shed several layers of skin to form a protective cocoon. This cocoon further reduces water loss and protects the frog from dehydration. african bullfrog cocoon
“The cocoon is a remarkable example of adaptation,” explains Dr. Anika Nkosi, a herpetologist specializing in African amphibians. “It effectively seals the frog in a humid microenvironment, allowing it to survive for months, even years, without access to free water.”
Opportunistic Feeding: Making the Most of Every Meal
African bullfrogs are voracious predators with a diverse diet. They consume anything they can overpower, from insects and rodents to other frogs, even small birds. This opportunistic feeding strategy allows them to capitalize on the limited food resources available in their environment. african attack fish food
Breeding Strategies: Ensuring the Next Generation
The African bullfrog’s breeding behavior is also tightly linked to its environment. They breed explosively after heavy rains, taking advantage of the temporary pools and puddles that form. This strategy ensures that the tadpoles have sufficient time to develop before the water evaporates.
“The rapid development of tadpoles is crucial for their survival,” says Professor Jabari Okoro, an expert in African wildlife. “They must metamorphose into froglets before the pools dry up, a race against time that is a testament to their adaptive prowess.”
The Resilient Amphibian
The African bullfrog’s adaptations are a testament to its resilience and its ability to thrive in some of the harshest environments on Earth. From their burrowing skills to their opportunistic feeding habits, each adaptation plays a crucial role in their survival.
These adaptations not only allow them to survive but also contribute to their role as a key player in the ecosystem. african creatures Understanding these african bullfrog adaptations provides a deeper appreciation for the intricate web of life in the African wilderness.
FAQ
-
How long can an African bullfrog survive underground? They can survive for several months, even years, in a state of aestivation within their burrows.
-
What do African bullfrogs eat? They are opportunistic predators and will eat insects, rodents, other frogs, and even small birds.
-
How do African bullfrogs reproduce? They breed in temporary pools formed after heavy rains.
-
What is the purpose of the African bullfrog’s cocoon? The cocoon protects the frog from dehydration and maintains a humid microenvironment during aestivation.
-
Why is the African bullfrog considered an important part of the ecosystem? They are a key predator and prey species, playing a vital role in the food chain.
-
Where can I find more information on African bullfrog classification? You can learn more about their classification at african bull classification.
-
What are some other fascinating creatures found in Africa? Explore more about african creatures.
We can discuss more about other species if you are interested. Also, feel free to check out our other articles on African wildlife for more fascinating insights.
When you need assistance, please contact us by phone at +255768904061, email at kaka.mag@gmail.com, or visit us at Mbarali DC Mawindi, Kangaga, Tanzania. We have a 24/7 customer service team.