African Bullfrog Ecology: A Fascinating Look at the Amphibian of the African Savanna
The African bullfrog, scientifically known as Pyxicephalus adspersus, is a remarkable amphibian found throughout sub-Saharan Africa. Renowned for its imposing size and booming call, this frog is an integral part of the savanna ecosystem, playing a crucial role in the intricate web of life. Let’s delve into the fascinating world of African Bullfrog Ecology, exploring its habitat, diet, breeding behavior, and its unique adaptations to survive in the harsh African landscape.
The African Bullfrog’s Habitat: A Life in the Savanna
The African bullfrog is a true inhabitant of the African savanna, a vast grassland ecosystem characterized by dry seasons and wet seasons. During the wet season, when the rains bring life to the parched landscape, these frogs are found in abundance, inhabiting temporary pools, swamps, and water-filled depressions.
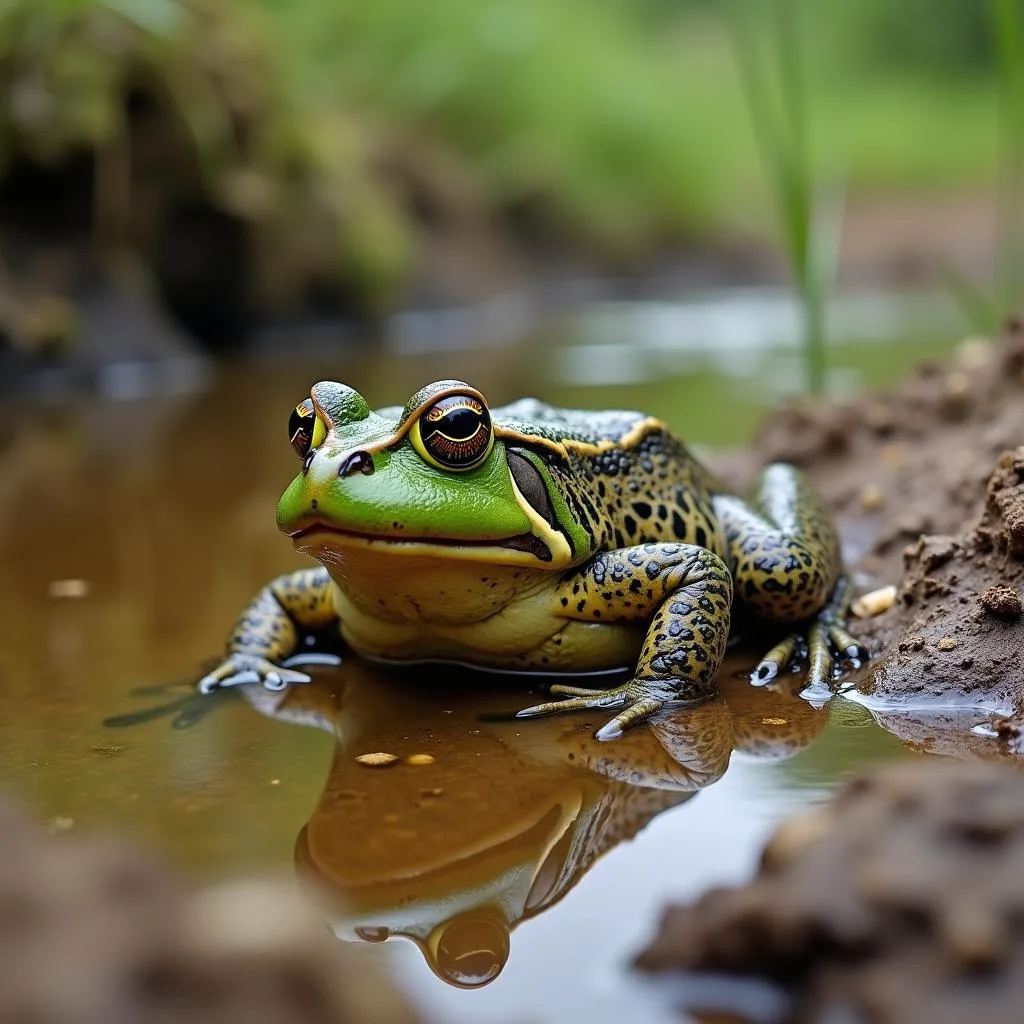 African bullfrog in its savanna habitat
African bullfrog in its savanna habitat
As the dry season sets in, the temporary pools begin to dry up, forcing the African bullfrogs to adopt a unique survival strategy. They burrow into the soft soil, often near their breeding sites, and enter a state of estivation, a type of dormancy that allows them to survive the harsh dry conditions. This is where they remain until the rains return, signaling the beginning of a new breeding cycle.
Feeding Habits: A Carnivorous Amphibian
The African bullfrog is a voracious predator, feeding on a wide variety of invertebrates and even small vertebrates. Its diet consists primarily of:
- Insects: Grasshoppers, beetles, crickets, ants, and termites are common prey items.
- Other Amphibians: Smaller frogs and tadpoles are also part of their diet.
- Small Vertebrates: Snakes, lizards, and even small rodents have been known to fall victim to the bullfrog’s powerful jaws.
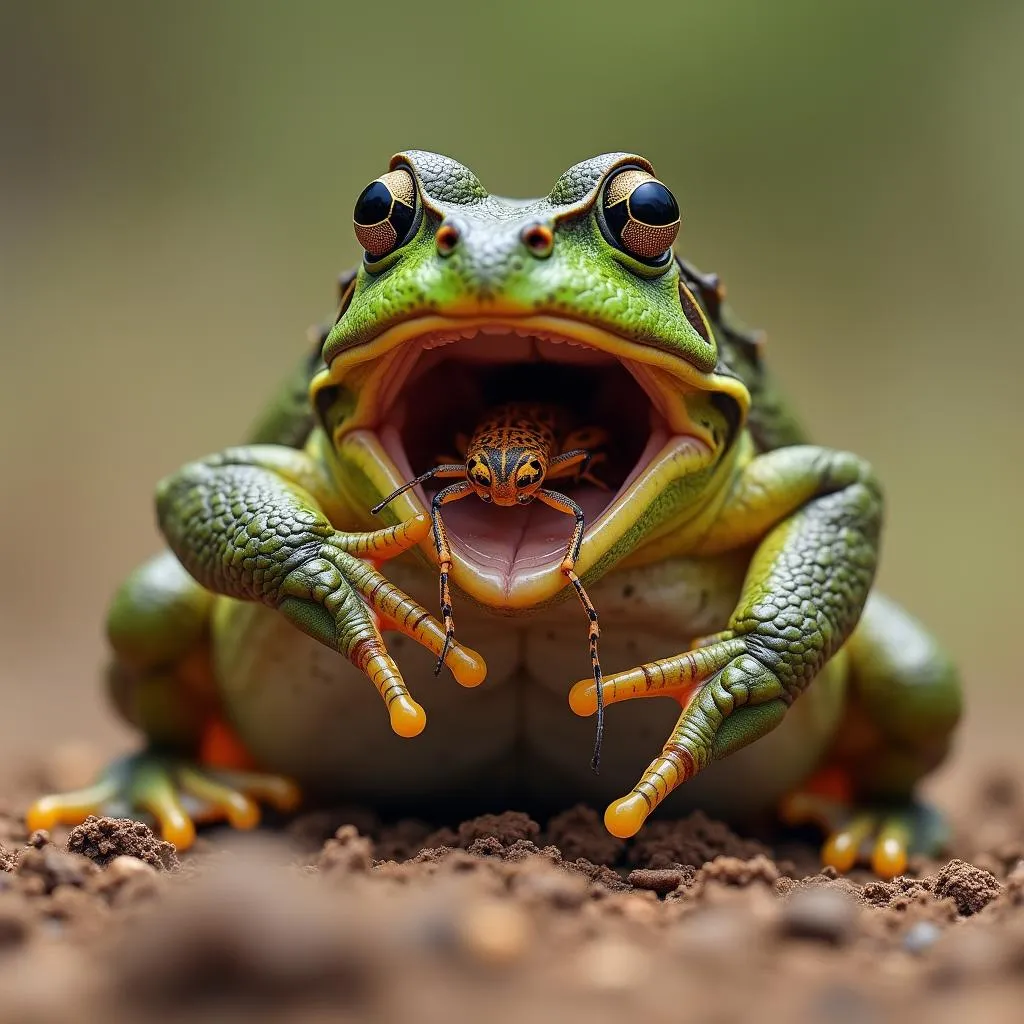 African bullfrog feeding on insects
African bullfrog feeding on insects
The bullfrog’s hunting technique is remarkably efficient. It sits patiently, camouflaged among the vegetation, waiting for unsuspecting prey to come within range. Then, with lightning speed, it leaps forward, extending its long, sticky tongue to capture its meal.
Breeding Season: A Symphony of Sounds
The African bullfrog’s breeding season coincides with the onset of the wet season. As the rains begin, the males emerge from their burrows and gather at suitable breeding sites, which are usually shallow, temporary pools. These pools provide ample space for eggs to develop and tadpoles to grow.
One of the most fascinating aspects of the bullfrog’s life cycle is its distinctive mating call. The male frogs produce a loud, booming sound, described as a deep “moo” or “bough,” which can be heard for miles across the savanna. This powerful call serves to attract females and establish territories.
 African bullfrog vocalizing its breeding call
African bullfrog vocalizing its breeding call
After the female chooses a mate, she lays hundreds of eggs in the shallow water. The male then guards the eggs, keeping them moist and protected from predators. The eggs hatch into tadpoles, which undergo a metamorphosis over a few weeks, eventually transforming into miniature versions of their adult parents.
Adaptations to Survive: A Master of Camouflage and Estivation
The African bullfrog has evolved several remarkable adaptations to thrive in the challenging savanna environment.
- Camouflage: Their mottled skin provides excellent camouflage among the dry grasses and vegetation, helping them to ambush prey and evade predators.
- Estivation: Their ability to enter a state of estivation during the dry season allows them to conserve energy and water, ensuring survival until the next rainy season.
- Powerful Legs: The African bullfrog has powerful hind legs that enable it to leap great distances, both for hunting and escaping predators.
The Importance of the African Bullfrog: An Essential Role in the Ecosystem
The African bullfrog plays a vital role in the savanna ecosystem.
- Predator Control: By consuming a wide range of insects, the bullfrog helps to control insect populations, thus preventing potential outbreaks.
- Nutrient Cycling: Their waste products contribute to the nutrient cycling within the ecosystem, enriching the soil and supporting plant growth.
- Food Source: They serve as a food source for larger predators such as birds, snakes, and crocodiles, contributing to the balance of the food web.
The Threats to African Bullfrogs: Facing the Challenges of Habitat Loss
Despite their adaptability, African bullfrogs face increasing threats from human activities.
- Habitat Loss: The expansion of agriculture, urbanization, and deforestation are encroaching on their natural habitats, reducing the availability of suitable breeding sites.
- Pollution: Runoff from agricultural areas and industrial waste can contaminate their water sources, impacting their health and survival.
- Over-harvesting: In some areas, bullfrogs are hunted for food or traded for the pet market, leading to population declines.
 African bullfrog habitat impacted by human activities
African bullfrog habitat impacted by human activities
Conservation Efforts: Protecting the Future of the African Bullfrog
Efforts are underway to conserve the African bullfrog and ensure its continued existence.
- Protected Areas: Establishing protected areas helps to safeguard their habitats from human activities.
- Sustainable Land Management: Promoting sustainable agricultural practices can reduce pollution and habitat loss.
- Education and Awareness: Raising awareness about the importance of the bullfrog and the threats it faces can encourage conservation efforts.
The Fascinating World of African Bullfrogs: A Journey of Discovery
Exploring the world of the African bullfrog offers a glimpse into the intricate workings of the savanna ecosystem. This remarkable amphibian is a testament to the power of adaptation and the vital role it plays in the delicate balance of nature. By understanding their ecological significance and the threats they face, we can work towards ensuring their survival for future generations.
FAQ
Q: How big can African bullfrogs get?
A: African bullfrogs can grow to be quite large, with some individuals reaching up to 8 inches (20 cm) in length.
Q: Are African bullfrogs poisonous?
A: While not poisonous, African bullfrogs can secrete a milky substance from their skin that can irritate the eyes and skin.
Q: What is the lifespan of an African bullfrog?
A: The average lifespan of an African bullfrog is about 10 to 15 years.
Q: What can I do to help conserve African bullfrogs?
A: You can support conservation efforts by learning more about their ecology, reducing your environmental footprint, and advocating for the protection of their habitats.

