Understanding African Bush Elephant Behavior
African Bush Elephant Behavior is a complex and fascinating subject, encompassing a wide range of social interactions, communication methods, and survival strategies. These magnificent creatures, the largest land animals on Earth, exhibit intelligence, empathy, and complex family structures that continue to captivate researchers and wildlife enthusiasts alike. Let’s delve into the intricacies of their lives.
The Matriarchal Society of African Bush Elephants
African bush elephants live in complex matriarchal societies led by the oldest and most experienced female, the matriarch. She guides the herd in their search for food and water and makes crucial decisions that impact the survival of the group. This social structure offers stability and ensures the passing down of vital knowledge from one generation to the next. Younger females learn from the matriarch, acquiring essential skills like raising calves and navigating their environment. For example, the matriarch remembers the location of water sources during droughts, which can save the whole herd. What is fascinating is that when the matriarch dies, the herd can be deeply affected and may even split into smaller groups.
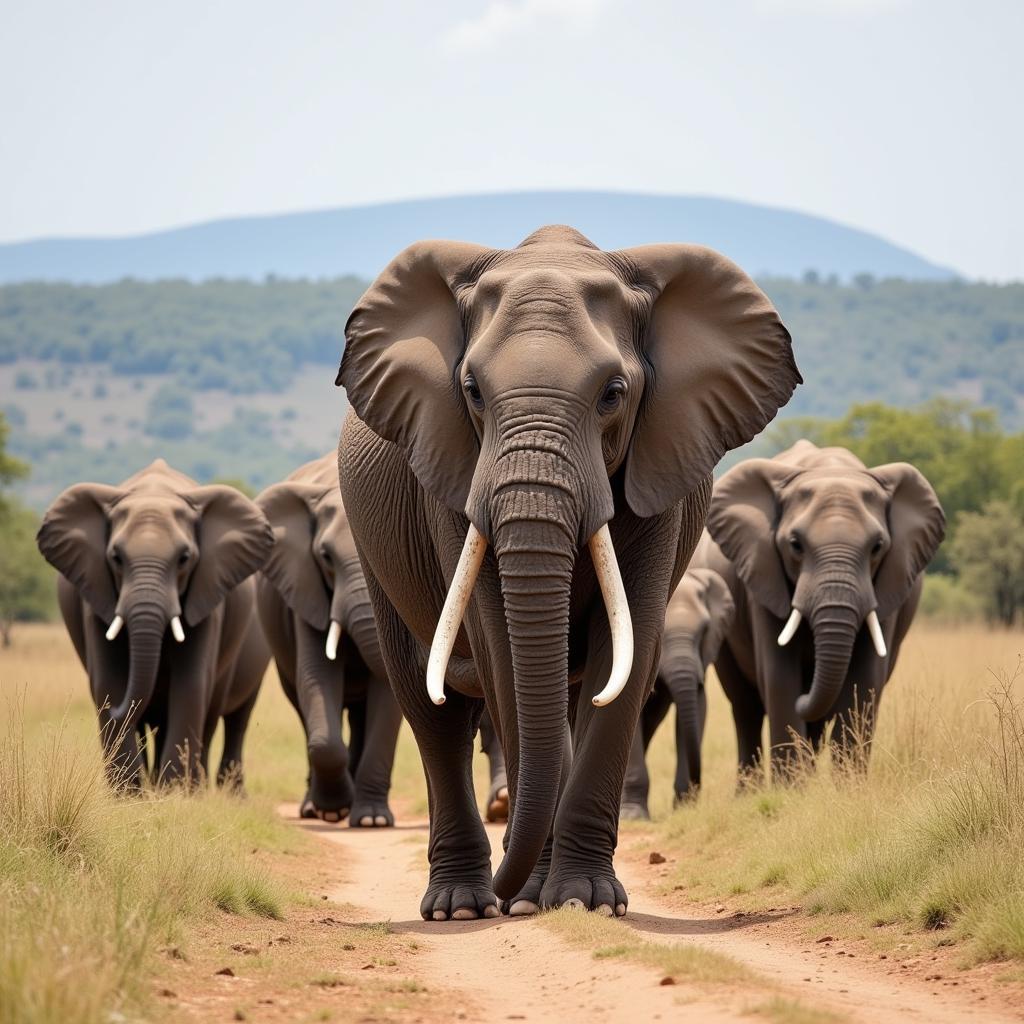 African Bush Elephant Matriarch Leading Herd
African Bush Elephant Matriarch Leading Herd
Communication: A Symphony of Sounds and Signals
How do African bush elephants communicate? They employ a range of vocalizations, including rumbles, trumpets, and roars, to communicate across long distances. These sounds can travel for miles, allowing elephants to stay in contact even when separated. Beyond vocalizations, they also use infrasound, low-frequency sounds that humans can’t hear, to communicate over even greater distances. These low rumbles can travel through the ground, allowing elephants to detect the presence of other herds from miles away. Additionally, they utilize body language, such as ear flapping and tail swishing, to convey emotions and intentions to other members of the herd. This includes subtle signals like a slight shift in weight, which can signal a change in the elephant’s mood. Check out the differences between the African bush elephant and its Asian cousin in this article: african bush elephant vs indian elephant.
The Importance of Touch in Elephant Communication
Touch plays a crucial role in African bush elephant behavior. Elephants frequently use their trunks to greet each other, console distressed individuals, and discipline younger members of the herd. This physical contact reinforces social bonds and strengthens the cohesive nature of the herd. Calves, in particular, rely heavily on touch for comfort and reassurance. They often stay in close physical contact with their mothers and other female relatives, seeking protection and guidance.
Feeding Habits: A Vegetarian’s Life
African bush elephants are herbivores, consuming vast quantities of vegetation daily. Their diet consists of grasses, leaves, bark, fruits, and roots. They use their powerful trunks to strip branches, dig for roots, and pull down leaves. An adult elephant can consume up to 300 pounds of food in a single day. Their feeding habits have a significant impact on the savanna ecosystem, shaping the landscape and influencing the distribution of plant species. Their feeding behavior can also influence the availability of food for other animals.
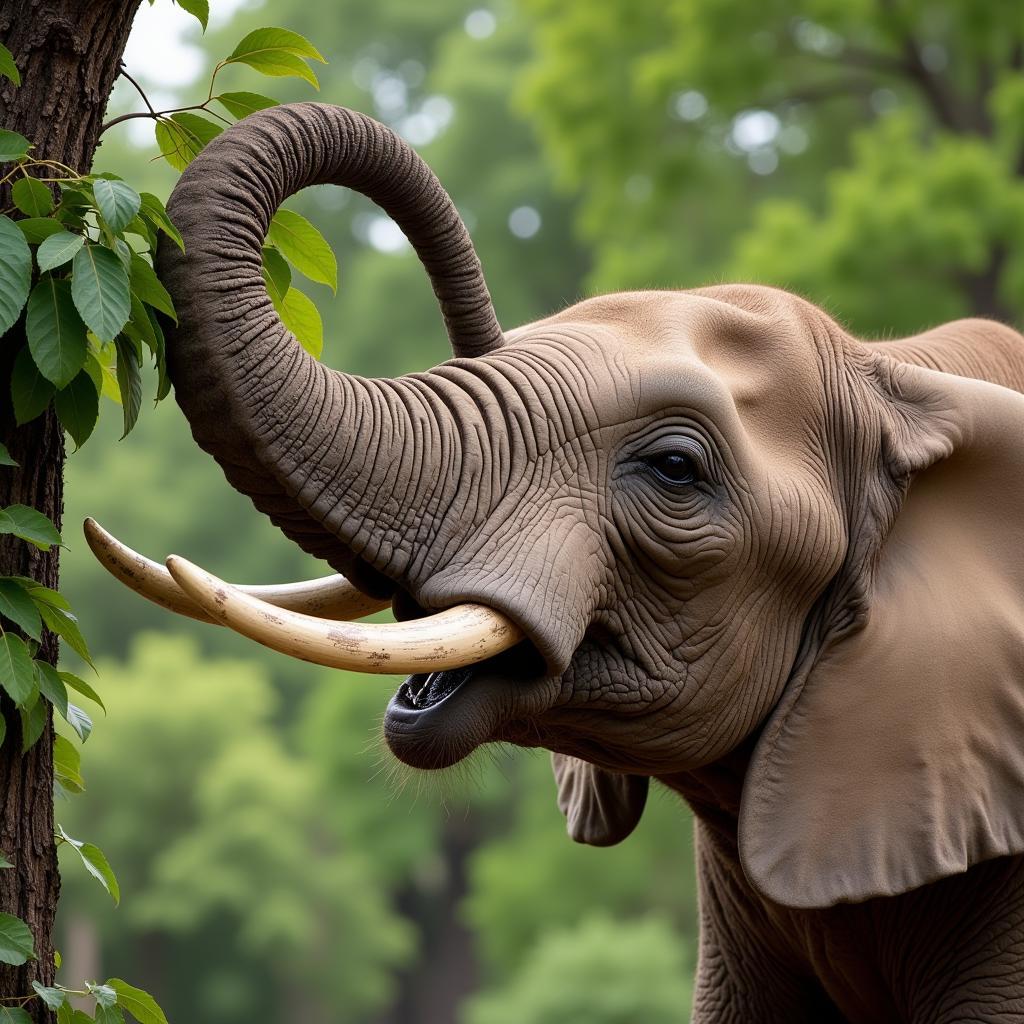 African Bush Elephant Feeding on Vegetation
African Bush Elephant Feeding on Vegetation
African Bush Elephant Behavior and Conservation
Understanding African bush elephant behavior is essential for effective conservation efforts. Poaching, habitat loss, and human-wildlife conflict pose significant threats to their survival. By studying their social structures, communication methods, and migratory patterns, conservationists can develop strategies to protect these magnificent creatures and ensure their long-term survival. For instance, understanding their migratory routes helps to establish protected corridors that allow elephants to move freely between different areas, minimizing human-wildlife conflict. Learning more about the intricacies of african elephant birth is crucial for population management. Even the bond between an african elephant with calf informs conservation strategies focused on family group protection.
Conclusion: Protecting the Giants of Africa
African bush elephant behavior is a testament to the intelligence and complexity of these remarkable animals. Their social bonds, communication methods, and survival strategies have enabled them to thrive in diverse African environments. However, continued conservation efforts are crucial to protect them from the threats they face. By understanding their behavior, we can better appreciate their importance in the ecosystem and work towards ensuring their survival for generations to come. Discover more about the heartwarming relationship between an african elephant baby indian elephant baby.
FAQ
- What is the social structure of African bush elephants? They live in matriarchal societies led by the oldest female.
- How do elephants communicate? They use vocalizations, infrasound, and body language.
- What do African bush elephants eat? They are herbivores, consuming a variety of vegetation.
- Why is understanding their behavior important for conservation? It helps develop effective protection strategies.
- What are the main threats to African bush elephants? Poaching, habitat loss, and human-wildlife conflict.
- How far can elephant communication travel? Miles, using a combination of vocalizations and infrasound.
- What is the role of the matriarch in an elephant herd? She leads the herd, makes decisions, and passes on knowledge.
Common Scenarios and Questions
-
Scenario: You see a group of elephants with their ears spread wide. Question: What does this behavior indicate? Answer: Spread ears can indicate aggression or excitement.
-
Scenario: An elephant calf is constantly touching its mother with its trunk. Question: Why is it doing this? Answer: The calf is seeking comfort and reassurance.
Further Exploration
For those interested in other African wildlife, check out our article on african cat fishes.
Contact Us
Need help or more information? Contact us 24/7: Phone: +255768904061, Email: kaka.mag@gmail.com, or visit us in Mbarali DC Mawindi, Kangaga, Tanzania.