Unveiling the Secrets of African Bush Elephant Teeth
African Bush Elephant Teeth, remarkable tools of survival, play a crucial role in the lives of these majestic creatures. They are not just for chewing; they tell a story of age, diet, and even hardship. Let’s delve into the fascinating world of these ivory wonders.
The Anatomy and Function of African Bush Elephant Teeth
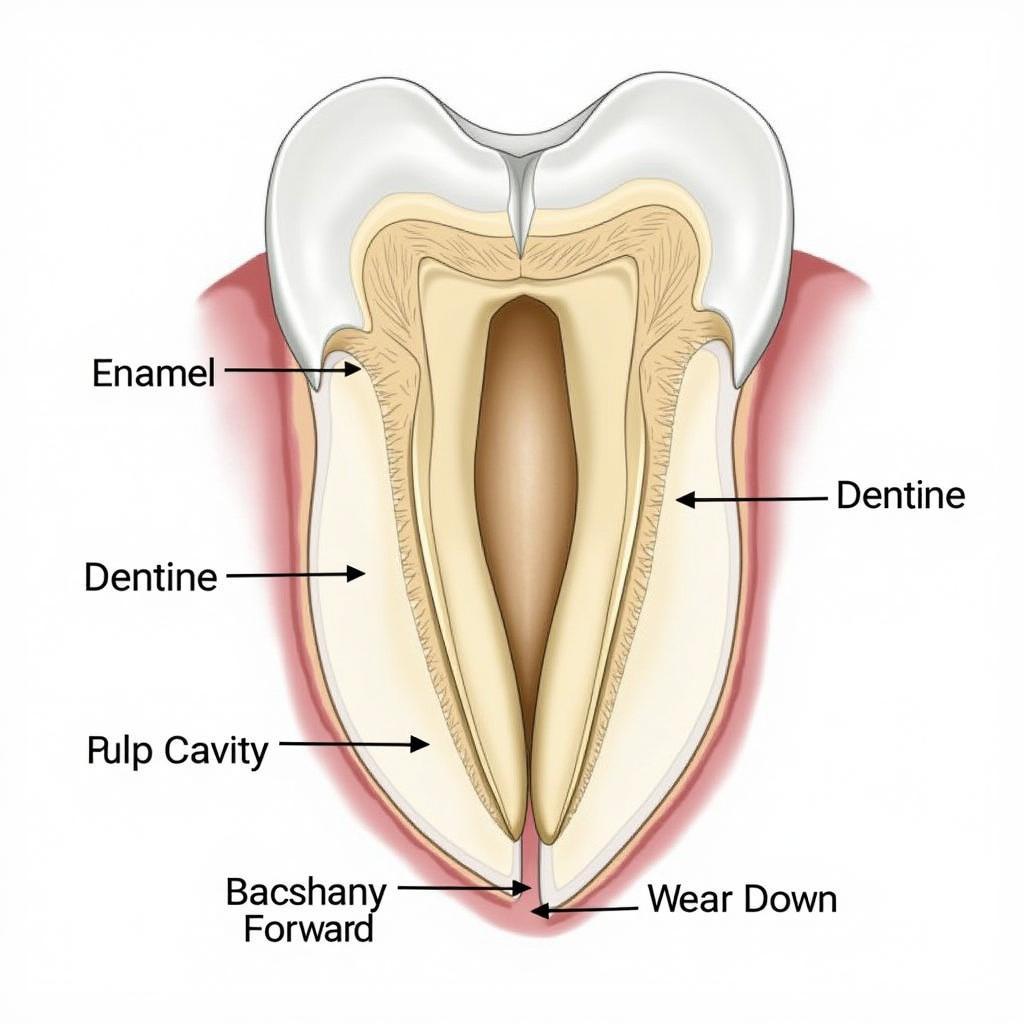 African Bush Elephant Teeth Structure
African Bush Elephant Teeth Structure
African bush elephant teeth are highly specialized molars designed for grinding tough vegetation. Unlike humans who have two sets of teeth, elephants have six sets of molars throughout their lifetime. These molars erupt sequentially from the back of the jaw and slowly move forward as they wear down, eventually being pushed out at the front. This unique process, known as horizontal tooth replacement, ensures the elephant always has a functional grinding surface.
How Many Teeth Does an African Bush Elephant Have at Once?
At any given time, an adult African bush elephant typically has one or parts of two molars in each quadrant of its jaw, for a total of four to eight teeth. These teeth are massive, with complex ridges of enamel and dentine that provide a powerful grinding surface. As the elephant ages, the later sets of molars are larger and have more ridges to cope with the increasing wear and tear.
The Role of African Bush Elephant Teeth in Diet
 African Bush Elephant Diet and Teeth
African Bush Elephant Diet and Teeth
African bush elephants are herbivores, their diet consisting of a wide variety of plant material. Their teeth are essential for processing this fibrous food. The ridges on the molars act like a millstone, grinding tough grasses, leaves, bark, and even roots into a digestible pulp. The efficiency of these teeth is crucial for extracting the maximum nutrients from their food, supporting their enormous body size.
What do african bush elephant teeth are called?
African bush elephant teeth, particularly the tusks, are often referred to as ivory, although the term also applies to the molars. The molars are sometimes referred to as grinding teeth, cheek teeth, or simply molars.
African Bush Elephant Teeth and Conservation
The sad reality is that african bush elephant teeth name, especially their tusks, have driven them to the brink of extinction due to poaching for ivory. While the molars themselves are not targeted, the overall decline in elephant populations due to ivory poaching also affects the genetic diversity and survival of the species. This illegal trade has devastating consequences for elephant populations across Africa. The demand for ivory has decimated elephant numbers, leaving many populations vulnerable.
How can we protect African bush elephants?
Supporting conservation efforts, raising awareness about the illegal ivory trade, and advocating for stricter regulations are crucial steps in protecting these magnificent animals. Understanding the value and function of their teeth, including the tusks, helps us appreciate the vital role they play in the elephant’s life and underscores the need for their protection.
Comparing african elephant compared to asian elephant Teeth
African and Asian elephants have different tooth structures. Asian elephants tend to have more enamel ridges on their molars than African elephants. This difference reflects their dietary preferences, with Asian elephants consuming more grasses and African elephants eating a broader range of vegetation, including more browse.
 African vs. Asian Elephant Teeth Comparison
African vs. Asian Elephant Teeth Comparison
The Impact of Tusks on African Bush Elephants
While not technically teeth, tusks are elongated incisors that play a significant role in the lives of African bush elephants. They are used for digging, foraging, defense, and social interactions. Unfortunately, tusks are the primary target of poachers. This has led to an increase in the number of african elephants without tusks in some populations, a tragic consequence of human greed.
Dr. Anika Nyerere, a renowned wildlife biologist based in Tanzania, states, “The evolution of tusklessness in response to poaching pressure is a stark reminder of the impact humans have on wildlife. It’s a desperate adaptation for survival.”
Conclusion
African bush elephant teeth are more than just tools for eating; they are essential for survival, reflecting the unique adaptations of these incredible animals. Understanding the structure, function, and importance of their teeth, along with the threats posed by the ivory trade, is crucial for their conservation. Let’s work together to protect these magnificent creatures and ensure their future generations continue to roam the African savanna. The survival of these giants depends on our collective action.
FAQ
- How many sets of teeth do African bush elephants have in their lifetime? (Six sets)
- What is the process of horizontal tooth replacement? (The sequential eruption and forward movement of molars)
- Why are African bush elephant teeth important for their diet? (They grind tough vegetation into a digestible pulp)
- What are the threats to African bush elephant teeth? (Poaching for ivory)
- How can we help protect African bush elephants? (Support conservation efforts and raise awareness about the illegal ivory trade)
- What is the difference between African and Asian elephant molars? (Asian elephant molars tend to have more enamel ridges)
- What role do tusks play in the lives of African bush elephants? (Digging, foraging, defense, and social interactions)
For further exploration on the fascinating size comparison between african elephants humans size comparison, please visit our dedicated page. You might also be interested in learning more about elephant behavior and social structures.
When you need support please contact Phone Number: +255768904061, Email: kaka.mag@gmail.com Or visit us at: Mbarali DC Mawindi, Kangaga, Tanzania. We have a 24/7 customer care team.


