African Cat Eye: Unveiling the Mystery
The captivating gaze of an African cat, often referred to as “African cat eye,” holds a mesmerizing allure for wildlife enthusiasts and casual observers alike. This unique eye shape, characterized by its distinctive elliptical form, isn’t merely an aesthetic quirk but a crucial evolutionary adaptation that equips these predators to thrive in the diverse landscapes of Africa. This article delves into the science behind the African cat eye, exploring its evolutionary significance, the mechanics that empower their extraordinary vision, and the specific advantages it bestows upon these majestic creatures.
The Evolution of a Hunter’s Gaze
The distinctive “African cat eye” didn’t emerge overnight. It’s the product of millennia of natural selection, favoring traits that provided a survival advantage in the harsh realities of the African wilderness. These elliptical pupils, unlike the round pupils found in many other mammals, offer a wider field of vision, particularly in the vertical plane. This enhanced vertical vision is crucial for predators like lions, leopards, and cheetahs, who often stalk prey in tall grasslands where being able to detect the slightest movement amidst the swaying vegetation can mean the difference between a successful hunt and an empty stomach.
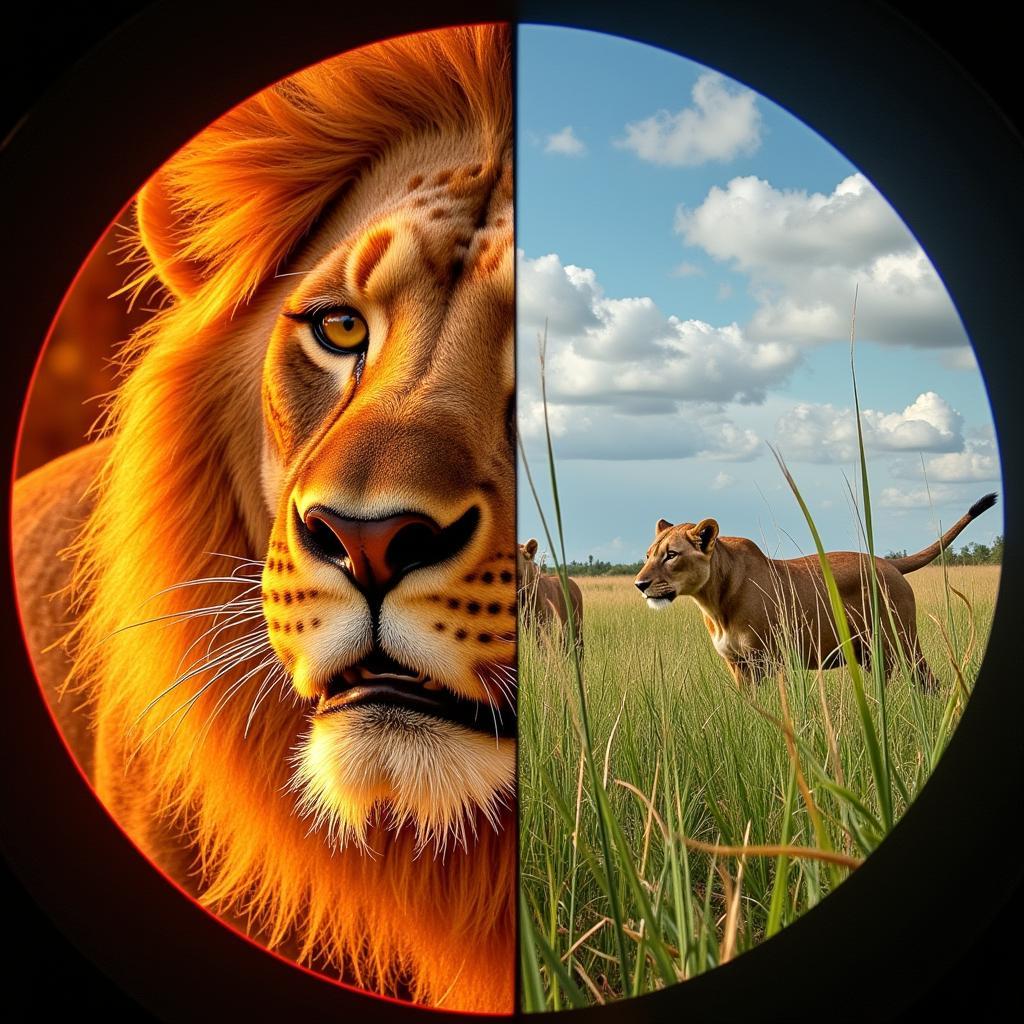 Evolution of the African Cat Eye
Evolution of the African Cat Eye
Seeing in the Dark: The Science of Night Vision
The African cat eye’s advantage extends beyond daylight hours. These predators are renowned for their exceptional night vision, a vital asset for hunting under the cover of darkness. Their eyes possess a high concentration of rod cells, specialized photoreceptor cells in the retina that are highly sensitive to light, allowing them to see in conditions six times dimmer than what humans perceive as pitch black.
Furthermore, a reflective layer behind the retina, called the tapetum lucidum, acts like a mirror, reflecting light that passes through the retina back onto the photoreceptor cells, effectively giving them a second chance to absorb the available light. This reflection is what causes the eerie glow often observed in the eyes of nocturnal animals, including African cats.
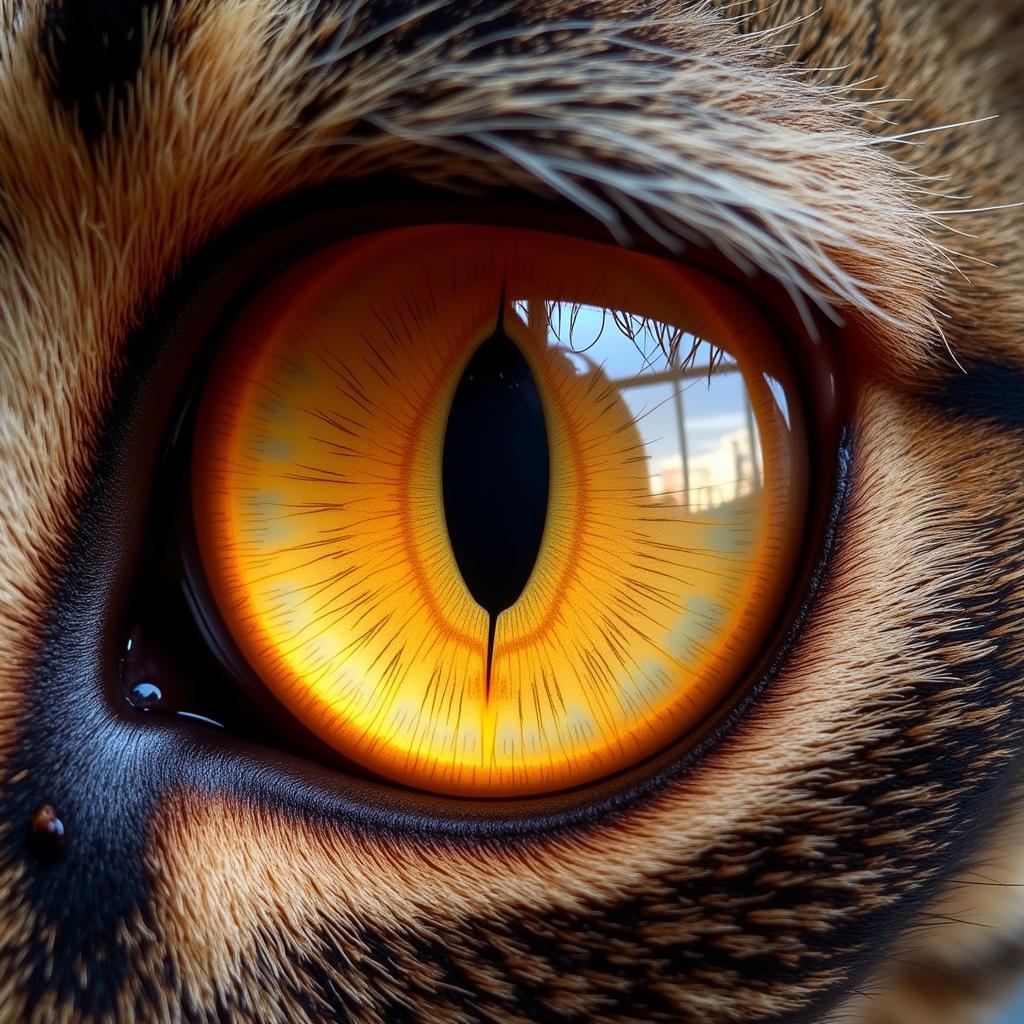 The Mechanics of Superior Night Vision in African Cats
The Mechanics of Superior Night Vision in African Cats
Beyond the Hunt: Navigating a Complex World
The benefits of the African cat eye extend beyond hunting and nocturnal vision. This unique adaptation plays a crucial role in various aspects of their lives. The enhanced depth perception provided by their elliptical pupils allows for precise distance estimation, critical for accurately judging leaps and pounces during hunting, as well as navigating complex terrains and tree canopies.
Moreover, the wider field of vision allows them to maintain a greater awareness of their surroundings, crucial for detecting potential threats and rivals in their often competitive environments. This enhanced peripheral vision provides an early warning system, crucial for survival in the wild.
African Cat Names: A Reflection of Their Eyes
It’s fascinating how the unique characteristics of African cats, particularly their eyes, have influenced their names in various cultures. For instance, the cheetah, renowned for its incredible speed, derives its name from the Sanskrit word “chitraka,” meaning “spotted,” a reference to its distinctive markings. However, some believe the name might also be linked to the cheetah’s keen eyesight, reflecting its ability to spot prey from afar.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Do all African cats have elliptical pupils?
While elliptical pupils are a common characteristic among African cats, there are exceptions. The lion, for instance, possesses round pupils. This difference is attributed to their hunting styles and the environments they inhabit.
2. Why do African cat eyes glow in the dark?
The glowing effect is due to the tapetum lucidum, a reflective layer behind the retina that reflects light back onto the photoreceptor cells, enhancing their night vision.
3. How far can African cats see?
While the exact distance varies depending on the species and environmental factors, African cats generally possess superior vision compared to humans. Lions, for example, can spot prey from a distance of up to two miles.
african grey parrot sounds and what they mean
Need More Information on African Wildlife?
Explore our website for captivating articles on the diverse fauna of Africa, including insights into their behavior, habitats, and the challenges they face in a changing world. From the intricate communication of African grey parrots to the breathtaking speed of the cheetah, we delve into the wonders of African wildlife.
For personalized assistance or inquiries, please don’t hesitate to contact our dedicated team at:
Phone: +255768904061
Email: kaka.mag@gmail.com
Address: Mbarali DC Mawindi, Kangaga, Tanzania.
Our customer service representatives are available 24/7 to assist you.