The African Charter on Human Rights: Significance and Impact
The African Charter on Human Rights, adopted in 1981, holds profound significance for the advancement of human rights across the African continent. It represents a pivotal moment in the pursuit of justice, equality, and dignity for all African people. This charter sets forth a comprehensive framework for the protection and promotion of fundamental human rights, addressing a wide range of civil, political, economic, social, and cultural rights. The Charter acknowledges the unique historical, cultural, and social context of Africa, shaping a document tailored to the specific needs and aspirations of its people.
The Charter’s creation stemmed from a growing awareness among African nations of the need to solidify human rights protections within a distinctly African framework. Its development reflected a rejection of colonial legacies and an affirmation of the universality of human rights within the African context. The establishment of the African Commission on Human and Peoples’ Rights marked a critical step in the implementation and enforcement of the Charter. This body is tasked with monitoring state compliance, investigating human rights violations, and promoting human rights education and awareness.
The Core Principles of the African Charter on Human Rights
The African Charter on Human Rights outlines a broad spectrum of rights, encompassing civil and political rights, such as the right to life, liberty, and security of person, freedom of expression, and the right to participate in political processes. It also recognizes economic, social, and cultural rights, including the right to education, health, and work. Uniquely, the Charter also emphasizes the importance of peoples’ rights, including the right to self-determination, development, and a healthy environment.
Key Provisions and Their Impact on African Societies
The African Charter on Human Rights includes provisions relating to the rights of women, children, and vulnerable groups. The Charter explicitly prohibits discrimination based on race, ethnic origin, sex, religion, or political opinion. The Charter also calls for the abolition of all forms of slavery, torture, and cruel, inhuman, or degrading treatment.
 African Leaders Signing the African Charter on Human Rights
African Leaders Signing the African Charter on Human Rights
The African Charter has significantly impacted the development of human rights jurisprudence in Africa. It has served as a legal basis for challenging human rights violations and has influenced the development of national laws and policies. The Charter has also fostered a culture of human rights awareness and activism across the continent.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite its achievements, the African Charter faces several challenges. These include limited resources for the African Commission, weak enforcement mechanisms, and the lack of political will among some states to fully implement its provisions. Another challenge is the need to strengthen cooperation between the African Commission and national governments in promoting and protecting human rights.
african charter on human and peoples rights ratification
The future of the African Charter hinges on sustained efforts to enhance its implementation and effectiveness. This involves strengthening the capacity of the African Commission, promoting human rights education and training, and fostering greater engagement with civil society organizations. Strengthening regional and international partnerships is also crucial to supporting the implementation of the African Charter and advancing human rights across the continent.
 African Court on Human and Peoples' Rights in Session
African Court on Human and Peoples' Rights in Session
“The African Charter is not merely a document; it’s a living testament to the enduring pursuit of justice and dignity for all Africans,” says Dr. Aminata Sow, a renowned scholar of African law.
What is the role of the African Commission?
The African Commission monitors state compliance with the Charter, investigates human rights violations, and promotes human rights education.
How has the Charter influenced national laws?
The Charter has served as a model for national constitutions and legislation, promoting the incorporation of human rights principles into domestic legal frameworks.
“The Charter’s focus on peoples’ rights is a unique and valuable contribution to the global human rights discourse,” adds Professor Kwame Nkrumah, a leading expert on African human rights.
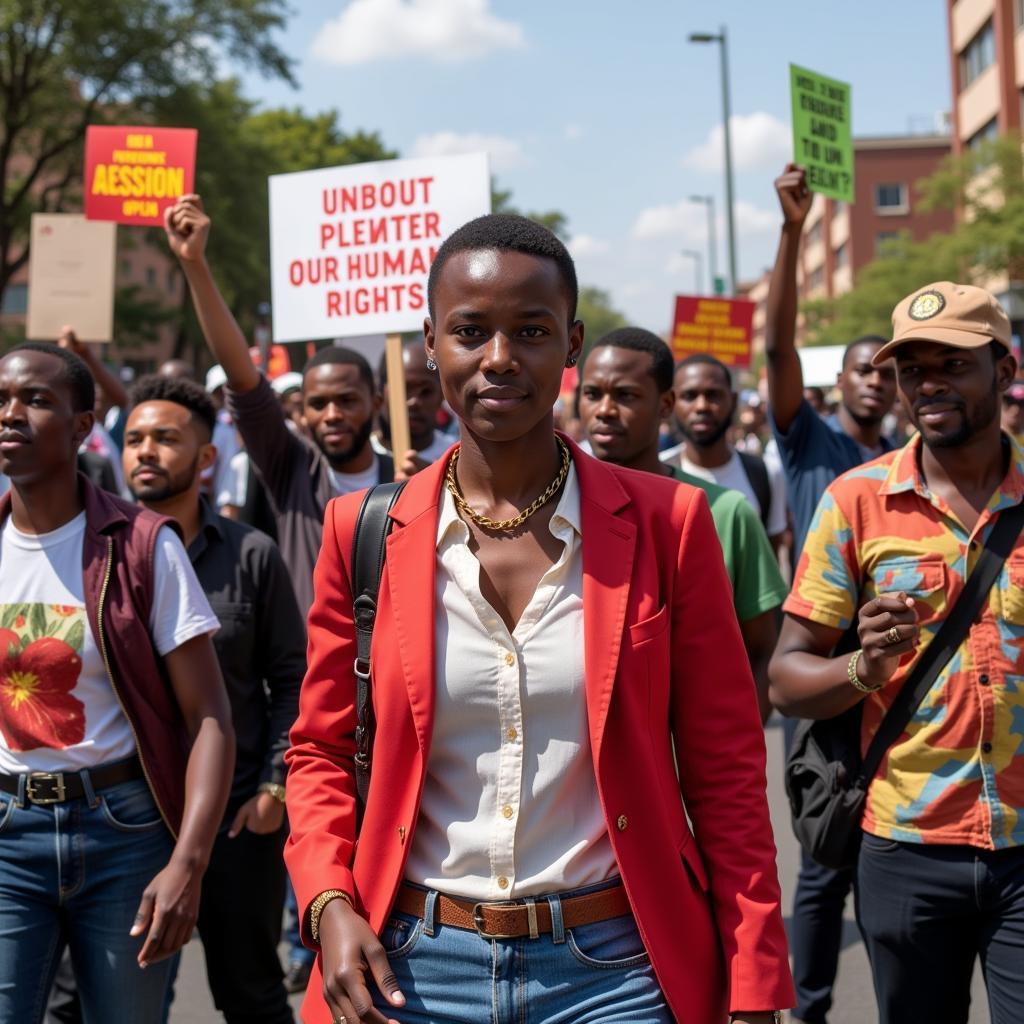 African Human Rights Activists Marching for Justice
African Human Rights Activists Marching for Justice
Conclusion
The African Charter on Human Rights signifies a landmark achievement in the pursuit of human rights for all Africans. While challenges remain, the Charter continues to serve as a vital instrument for promoting justice, equality, and human dignity across the continent. The African Charter on Human Rights is a critical tool for empowering individuals and communities to claim their rights and build a more just and equitable future for Africa.
FAQ
- What is the African Charter on Human Rights?
- When was the African Charter adopted?
- What are the key rights protected by the Charter?
- Who is responsible for enforcing the Charter?
- What are the current challenges facing the implementation of the Charter?
Situations where the African Charter is relevant:
- Cases of discrimination based on race, ethnicity, or gender.
- Violations of the right to freedom of expression or assembly.
- Instances of torture, cruel, inhuman, or degrading treatment.
- Denial of the right to education, health, or work.
- Situations impacting the rights of women, children, or vulnerable groups.
Further Exploration:
Explore other relevant topics on our website, such as african charter on prisoners right.
If you need any assistance, please contact us at +255768904061, email kaka.mag@gmail.com or visit us at Mbarali DC Mawindi, Kangaga, Tanzania. Our customer service team is available 24/7.
