African Cheetah Translocation: A New Hope for the Fastest Land Animal
African Cheetah Translocation is a complex and controversial conservation strategy aimed at bolstering dwindling cheetah populations across the continent and beyond. It involves capturing wild cheetahs from established source populations and relocating them to new, carefully selected habitats where cheetahs have either disappeared or exist in critically low numbers. This process, while promising, carries significant challenges and requires meticulous planning and ongoing monitoring to ensure success. african cheetah translocation ias
Understanding the Need for African Cheetah Translocation
The cheetah, the world’s fastest land animal, faces a dire situation. Habitat loss, human-wildlife conflict, and prey depletion have dramatically reduced their numbers. Translocation offers a potential solution by establishing new populations and increasing genetic diversity, which is crucial for long-term survival. This approach isn’t just about moving cheetahs; it’s about giving them a second chance in areas where they can thrive.
Why is genetic diversity so important? A limited gene pool makes a population vulnerable to diseases and environmental changes. Translocation helps introduce new genes, strengthening the overall health and resilience of the cheetah population.
The Challenges of African Cheetah Translocation
While translocation holds promise, it’s not without its challenges. Introducing cheetahs to a new environment requires careful consideration of numerous factors, including prey availability, the presence of other predators like lions and hyenas, and the potential for conflict with local communities.
One major challenge is ensuring that the released cheetahs can adapt to their new surroundings and establish territories. Monitoring their movements and behaviors post-release is crucial to understanding their adjustment and identifying any potential problems.
Dr. Asani Ndidi, a wildlife biologist specializing in cheetah conservation in East Africa, emphasizes the complexity of the process: “Translocation isn’t simply moving cheetahs from point A to point B. It requires in-depth ecological studies, careful selection of individuals, and ongoing monitoring to minimize risks and maximize the chances of success.”
Where are Cheetahs Being Translocated in Africa?
Several African countries are actively involved in cheetah translocation projects. Southern Africa, particularly South Africa, has played a significant role as a source population for cheetahs. Countries like Malawi, Mozambique, and Zambia have received cheetahs in efforts to re-establish or bolster their existing populations. african cheetah reintroduction Each translocation project is tailored to the specific needs and ecological conditions of the receiving area.
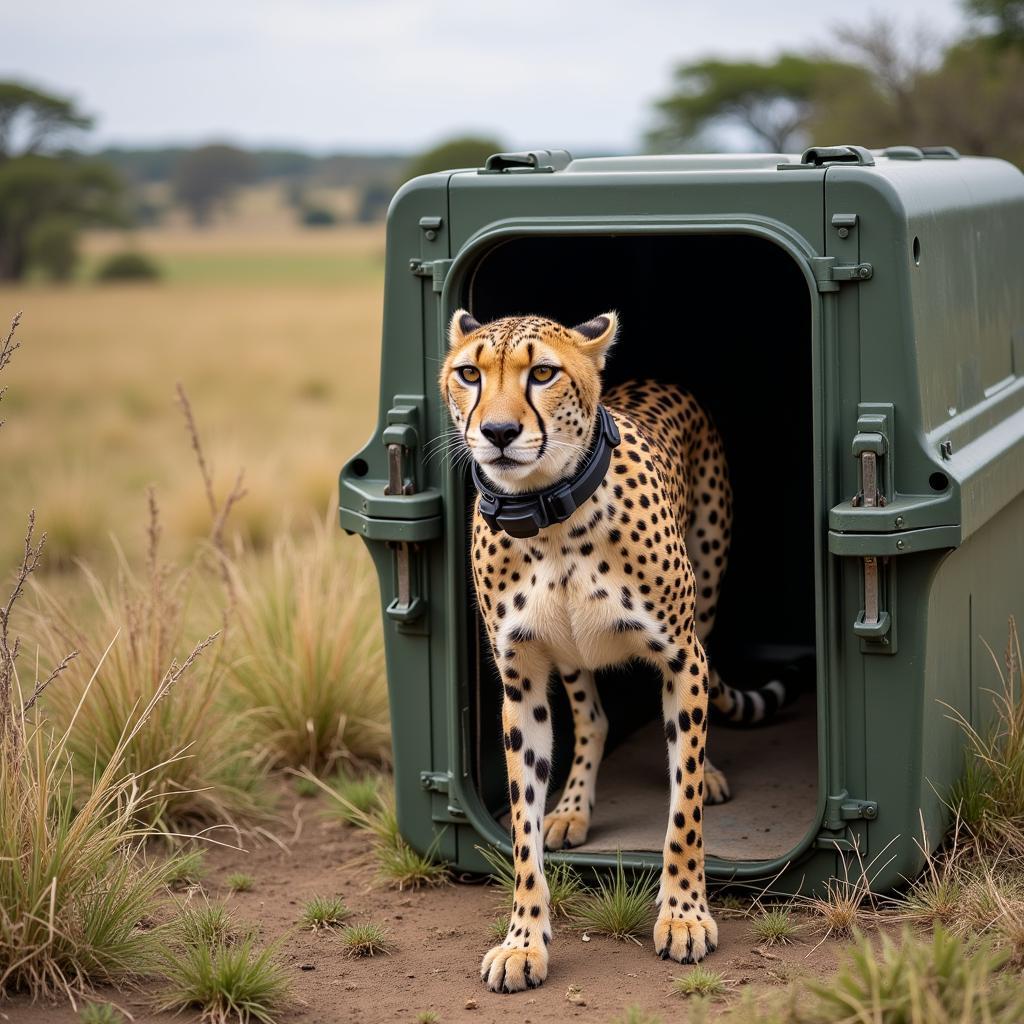 Cheetah Released into New Habitat
Cheetah Released into New Habitat
The Global Perspective: African Cheetahs to India
The concept of African cheetah translocation has also extended beyond the continent, with a notable example being the reintroduction of cheetahs to India. After being declared extinct in India in 1952, african cheetahs to indian jungles were brought from Namibia in a historic translocation effort. This ambitious project highlights the global reach of cheetah conservation initiatives and the potential for international collaboration in saving this iconic species. african cheetah in india
Why is African Cheetah Translocation Important?
What is the significance of these translocations? They are vital for the survival of the cheetah, representing a proactive approach to conservation. By expanding the cheetah’s range and creating genetically diverse populations, we increase the species’ resilience against extinction.
Professor Femi Alabi, a leading expert on African wildlife conservation, explains, “African cheetah translocation is a crucial tool in our arsenal against extinction. It represents a proactive, collaborative effort to safeguard this magnificent species for future generations.”
Conclusion: A Future for the Cheetah Through African Cheetah Translocation
African cheetah translocation is a complex but vital conservation strategy. It provides a glimmer of hope for the future of the cheetah by establishing new populations, boosting genetic diversity, and expanding the species’ range. While challenges remain, ongoing research, careful planning, and dedicated conservation efforts are key to ensuring the long-term success of these initiatives. By working together, we can give this magnificent creature a fighting chance in the wild.
FAQ
- What is African cheetah translocation? Relocating cheetahs to new habitats to help the species survive.
- Why is it necessary? To create new populations and improve genetic diversity.
- What are the challenges? Habitat suitability, predator presence, community relations.
- Where are cheetahs being translocated? Various African countries and even India.
- How can I support cheetah conservation efforts? Donate to reputable organizations, spread awareness.
- Is translocation always successful? No, it requires careful planning and monitoring.
- What is the long-term goal? To ensure the survival of the cheetah in the wild.
Common Scenarios
-
Scenario: A community is concerned about cheetahs being translocated near their livestock.
-
Solution: Open communication and education about cheetah behavior and mitigation strategies.
-
Scenario: Translocated cheetahs are struggling to find prey in their new environment.
-
Solution: Supplemental feeding and habitat management to support their adaptation.
Further Reading and Resources
Check out these related articles for more information: african genetic bottleneck
Call to Action
For support with cheetah conservation or related inquiries, contact us:
Phone: +255768904061
Email: kaka.mag@gmail.com
Address: Mbarali DC Mawindi, Kangaga, Tanzania
Our customer service team is available 24/7.