The Fascinating World of the African Clawed Frog
The African Clawed Frog, a peculiar amphibian native to Sub-Saharan Africa, has captivated scientists and hobbyists alike. These aquatic creatures, with their unique clawed feet and smooth, slippery skin, have a story far richer than their unassuming appearance might suggest. Let’s delve into the intriguing world of the Xenopus laevis and explore its biology, role in scientific research, and the responsibilities that come with keeping them as pets.
As an important african clawed frog model organisms, these creatures have contributed significantly to our understanding of developmental biology and human health. They are remarkably adaptable, thriving in a variety of aquatic environments, and their relatively simple care requirements make them a popular choice for both experienced and novice aquarium enthusiasts. But before you consider adding one to your collection, it’s crucial to understand their specific needs and the potential impact they can have on local ecosystems.
Understanding the African Clawed Frog: Biology and Behavior
African clawed frogs, scientifically known as Xenopus laevis, are fully aquatic frogs. They lack tongues and instead use their clawed forelimbs to sweep food into their mouths. Their flattened bodies and streamlined shape allow them to navigate their watery homes with ease. Interestingly, they rely primarily on their highly sensitive lateral line system to detect vibrations and locate prey, as their eyesight is relatively poor. They are carnivorous, feeding on insects, small crustaceans, and even other frogs.
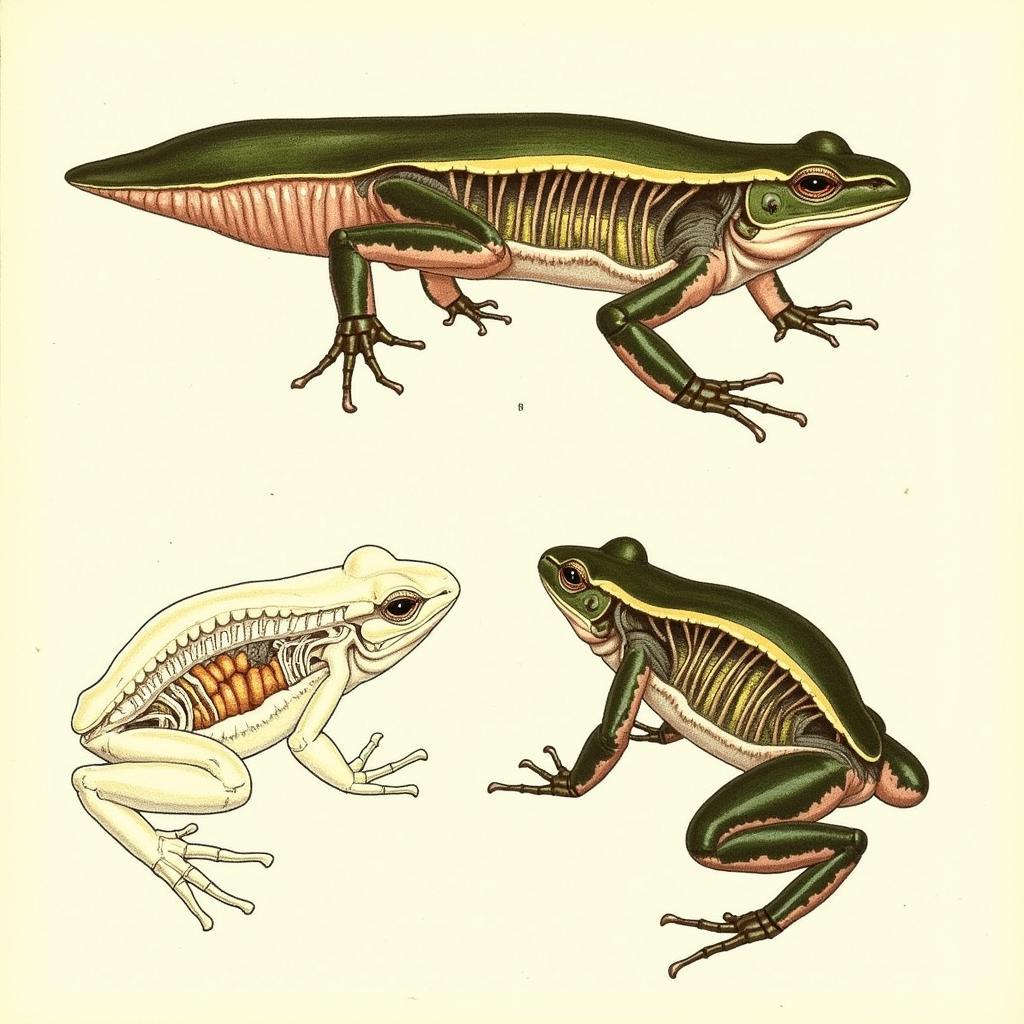 African Clawed Frog Anatomy: External Features and Internal Organs
African Clawed Frog Anatomy: External Features and Internal Organs
Their unique reproductive cycle adds another layer of intrigue to these fascinating creatures. Unlike many other frog species, African clawed frogs do not undergo metamorphosis in the typical sense. Instead, they transition directly from tadpoles to adults while remaining fully aquatic. Females can lay hundreds of eggs at a time, which attach to aquatic vegetation. The tadpoles then hatch and begin their journey to adulthood.
The African Clawed Frog in Science: A Model Organism
The African clawed frog has played a pivotal role in scientific research for over a century. Their hardiness, ease of breeding, and large, easily manipulated eggs have made them ideal african clawed frog model organisms for studying embryonic development, cell biology, and genetics.
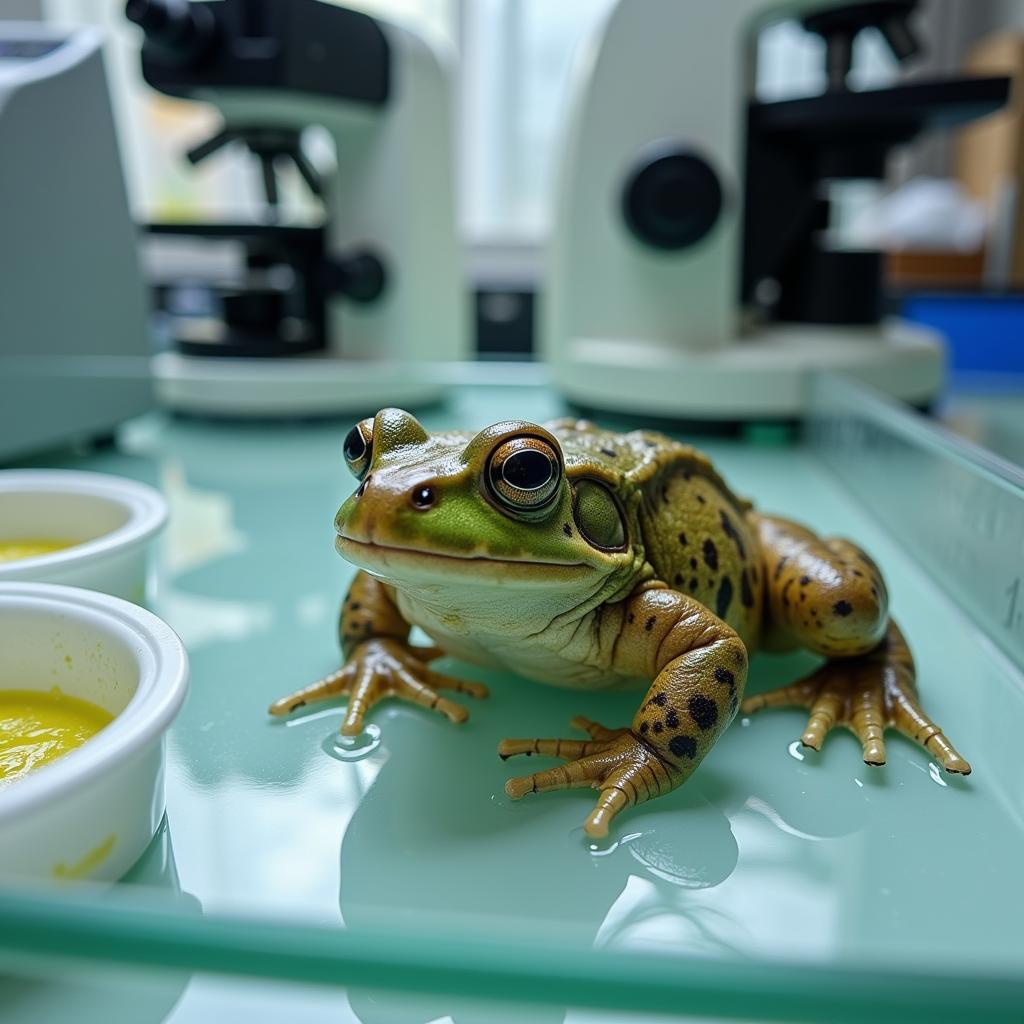 African Clawed Frog in a Laboratory Setting for Research
African Clawed Frog in a Laboratory Setting for Research
From early pregnancy tests to groundbreaking research in cloning, the African clawed frog has contributed significantly to scientific advancements. Their use in research continues to this day, providing valuable insights into human health and disease.
Caring for African Clawed Frogs: A Pet Owner’s Guide
While they may seem low-maintenance, keeping African clawed frogs requires specific considerations. Understanding their african clawed frog eating habits and potential african clawed frog not eating problems is crucial for their well-being. A properly set up aquarium with adequate filtration, appropriate water parameters, and a balanced diet is essential for their health and longevity. Overfeeding can lead to obesity and other health issues, so it’s important to monitor their food intake. Researching african clawed frog price and availability can help you find a reputable source for these fascinating pets.
The Importance of Responsible Ownership
It’s crucial to acknowledge the potential ecological impact of owning African clawed frogs. In some regions, escaped or released African clawed frogs have become invasive species, outcompeting native amphibians and disrupting ecosystems. Understanding the potential consequences of irresponsible ownership is vital. Knowing about african clawed frog eggs and their reproductive capacity can help prevent unwanted breeding and potential release into the wild.
Conclusion
The African clawed frog, with its unique characteristics and scientific significance, is a truly remarkable creature. From its contributions to medical research to its intriguing biology, the Xenopus laevis offers a glimpse into the wonders of the natural world. By understanding their needs and embracing responsible ownership, we can appreciate these fascinating amphibians while safeguarding our environment. Remember, the African clawed frog is more than just a pet; it’s a living testament to the interconnectedness of life on Earth.
FAQ
- What do African clawed frogs eat?
- How big do African clawed frogs get?
- How long do African clawed frogs live?
- Can African clawed frogs live with other fish?
- What kind of tank setup do African clawed frogs need?
- Are African clawed frogs good pets for beginners?
- How can I tell if my African clawed frog is sick?
For further assistance, please contact us at Phone: +255768904061, Email: kaka.mag@gmail.com, or visit us at Mbarali DC Mawindi, Kangaga, Tanzania. We have a 24/7 customer service team.


