Exploring the Majestic World of African Conifers
African Conifers, often overlooked amidst the continent’s diverse flora and fauna, represent a fascinating group of trees with unique ecological and cultural significance. These majestic evergreens, adapted to a range of climates from the Mediterranean coast to the high-altitude forests of East Africa, play a crucial role in their respective ecosystems. Let’s delve into the intriguing world of these ancient trees and discover their beauty and importance.
Unveiling the Diversity of African Conifers
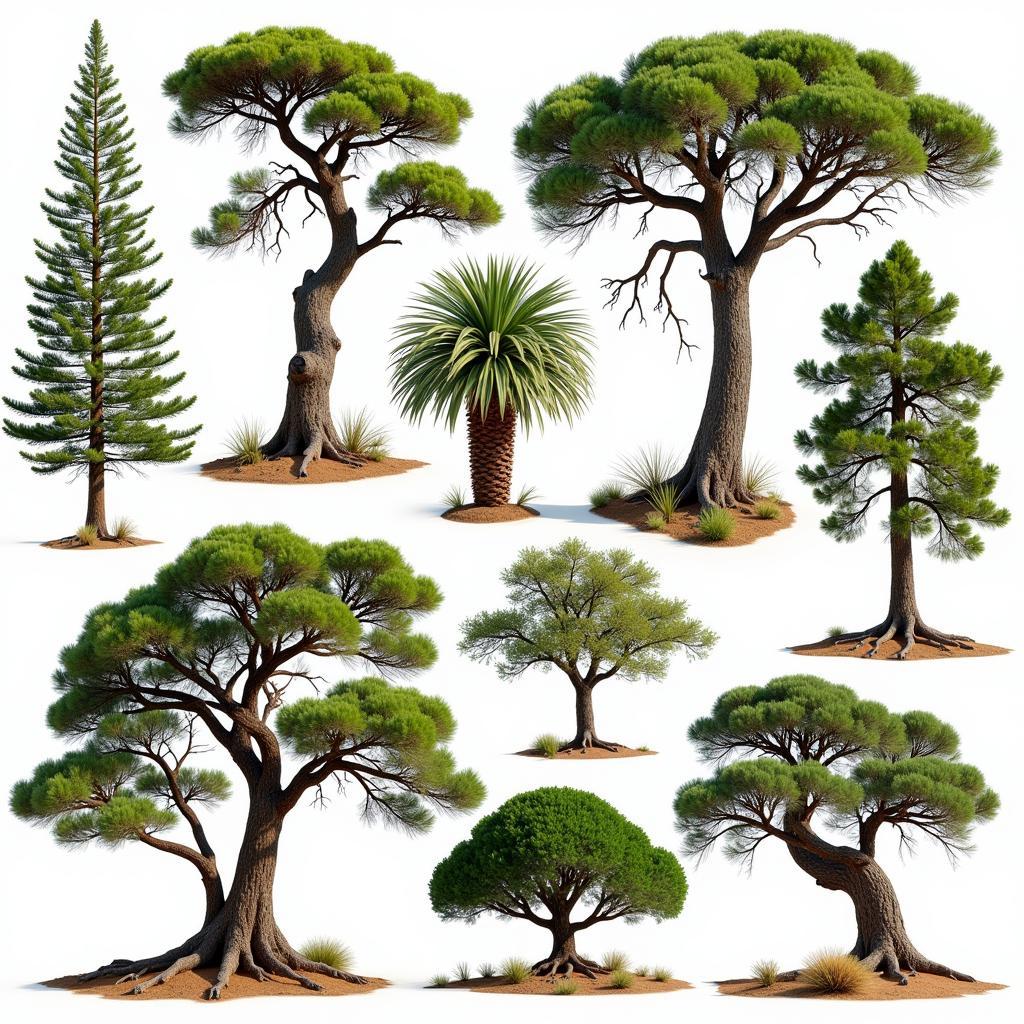 Diverse African Conifer Species Across the Continent
Diverse African Conifer Species Across the Continent
Africa boasts a surprising variety of conifer species, each uniquely adapted to its environment. While not as numerous as in other parts of the world, African conifers occupy distinct niches and contribute significantly to biodiversity. One notable example is the Afrocarpus falcatus, commonly known as the Outeniqua Yellowwood, a towering tree found in the southern regions of the continent. Its valuable timber has been prized for centuries, and its presence in ancient forests speaks to its resilience and longevity. Another noteworthy species is the Podocarpus latifolius, the Real Yellowwood, which thrives in the Afromontane forests of eastern Africa. This tree, with its distinctive yellow wood and dark green foliage, is often considered a symbol of strength and endurance.
The Ecological Role of African Conifers
African conifers play a vital role in maintaining the health and stability of their ecosystems. Their dense canopies provide habitat for a variety of bird species, while their seeds and cones offer a valuable food source for small mammals. They also contribute to soil stabilization, preventing erosion and maintaining water quality. The slow decomposition of their needle-like leaves enriches the soil, creating a favorable environment for other plant life.
Understanding the Unique Adaptations of African Conifers
Many African conifers have developed remarkable adaptations to survive in challenging environments. Some species, like the Widdringtonia cedarbergensis, or Clanwilliam Cedar, have adapted to fire-prone regions by developing thick bark that protects them from flames. Others, like certain Podocarpus species, have evolved specialized root systems that allow them to access water in dry and rocky terrains. These adaptations highlight the resilience and adaptability of these ancient trees.
Are African Conifers Threatened?
Unfortunately, several African conifer species face significant threats, primarily due to habitat loss and overexploitation. Deforestation for agriculture, logging, and urbanization has fragmented their natural habitats, putting pressure on their populations. Climate change also poses a significant threat, altering rainfall patterns and increasing the frequency and intensity of wildfires. Conservation efforts are crucial to protecting these unique trees and ensuring their survival for future generations.
The Cultural Significance of African Conifers
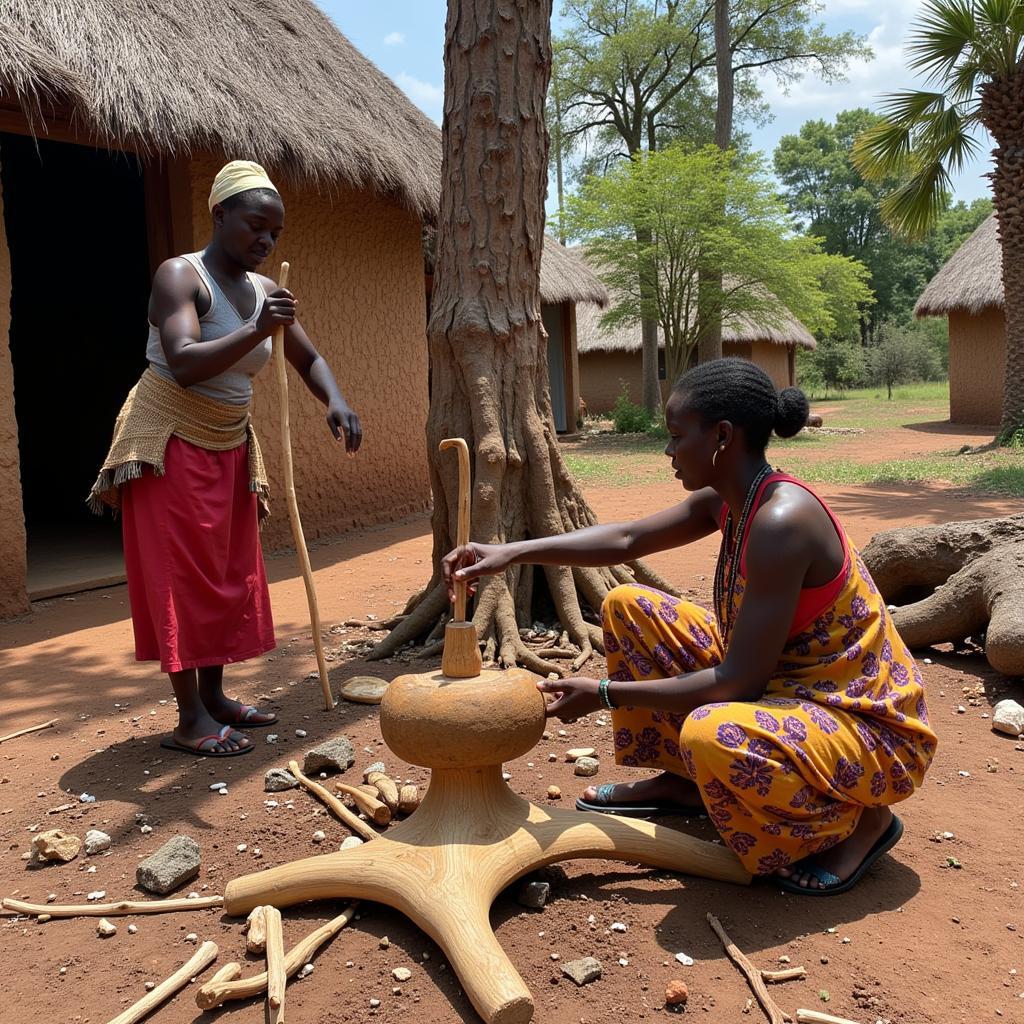 Cultural Significance of African Conifers in Local Communities
Cultural Significance of African Conifers in Local Communities
African conifers hold cultural significance for many communities across the continent. Their wood has been traditionally used for building houses, crafting furniture, and creating musical instruments. Some communities also attribute medicinal properties to the bark and leaves of certain species, using them in traditional remedies. The majestic presence of these trees often inspires folklore and traditional stories, further intertwining them with the cultural fabric of the region.
Dr. Abasi Okon, a renowned botanist specializing in African flora, notes, “The cultural significance of African conifers often goes unnoticed. These trees are more than just timber sources; they are integral to the history, traditions, and spiritual beliefs of many communities.” Similarly, Dr. Fatima Mohammedi, an ethnobotanist with years of experience studying African plant use, observes, “Understanding the traditional uses of these trees is essential for developing sustainable conservation strategies that respect both ecological and cultural values.” Echoing this sentiment, Professor Joseph Njoroge, a leading expert in African forest ecology, adds, “Protecting these trees isn’t just about preserving biodiversity; it’s about safeguarding cultural heritage.”
In conclusion, African conifers are a vital part of the continent’s rich biodiversity and cultural heritage. From their ecological importance to their traditional uses, these majestic trees deserve our attention and protection. By understanding their unique characteristics and the threats they face, we can work together to ensure their survival for generations to come.
Frequently Asked Questions:
- What is the tallest African conifer species?
- How are African conifers adapted to fire?
- What are the main threats to African conifers?
- How are African conifers used traditionally?
- Where can I find more information about African conifer conservation efforts?
- Are there any protected areas for African conifers?
- How can I contribute to African conifer conservation?
You may also want to read about the african fern pine tree.
For any support, please contact us at Phone Number: +255768904061, Email: kaka.mag@gmail.com or visit our address: Mbarali DC Mawindi, Kangaga, Tanzania. We have a 24/7 customer service team.