Navigating the Complexities: Understanding “African Countries Illegal”
The search term “African Countries Illegal” presents a curious case. It suggests a quest for information about activities, entities, or situations deemed illegal within various African nations. While the term itself might be broad, it opens the door to exploring a range of crucial topics, from wildlife trafficking and resource exploitation to human rights violations and political corruption.
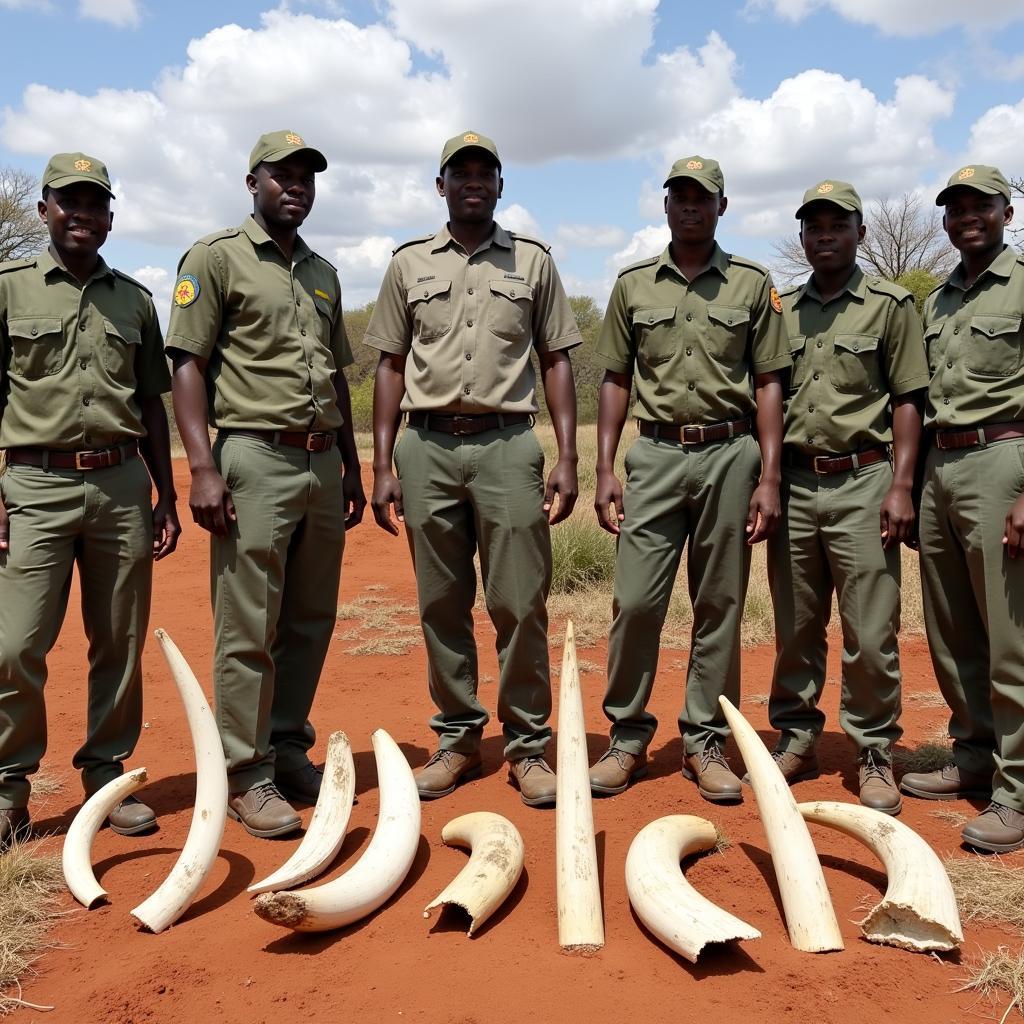 Illegal Wildlife Trade in Africa
Illegal Wildlife Trade in Africa
Unpacking the Search: What People Are Really Looking For
The ambiguity of “African countries illegal” requires us to delve deeper into user intent. Are individuals seeking information on:
- Specific Illegal Activities: Such as poaching endangered species, illegal mining operations, or human trafficking networks?
- Legal Systems and Enforcement: Are they interested in understanding the legal frameworks in place within different African countries and how effectively these laws are enforced?
- International Implications: Do they want to learn about international laws and agreements that address illegal activities impacting African countries, like the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES)?
- Corruption and Governance: Is their search driven by a desire to understand how corruption and weak governance contribute to the prevalence of certain illegal activities in some African nations?
By considering these potential interpretations, we can begin to construct content that is both informative and relevant to the individuals using this search term.
Wildlife Trafficking: A Grave Threat to Africa’s Natural Heritage
One of the most pressing issues captured by the term “African countries illegal” is the devastating illegal wildlife trade. This illicit industry, driven by demand for rare animal parts and exotic pets, poses a significant threat to numerous species across the continent.
- Elephants and Rhinos: These iconic animals are poached for their tusks and horns, which are highly valued in some cultures.
- Pangolins: Holding the unfortunate title of the most trafficked mammal in the world, pangolins are targeted for their scales and meat.
- African Grey Parrots: Prized for their intelligence and ability to mimic human speech, these birds are often captured illegally for the pet trade.
The consequences of this illegal trade are far-reaching, impacting not only biodiversity but also local communities, economies, and security.
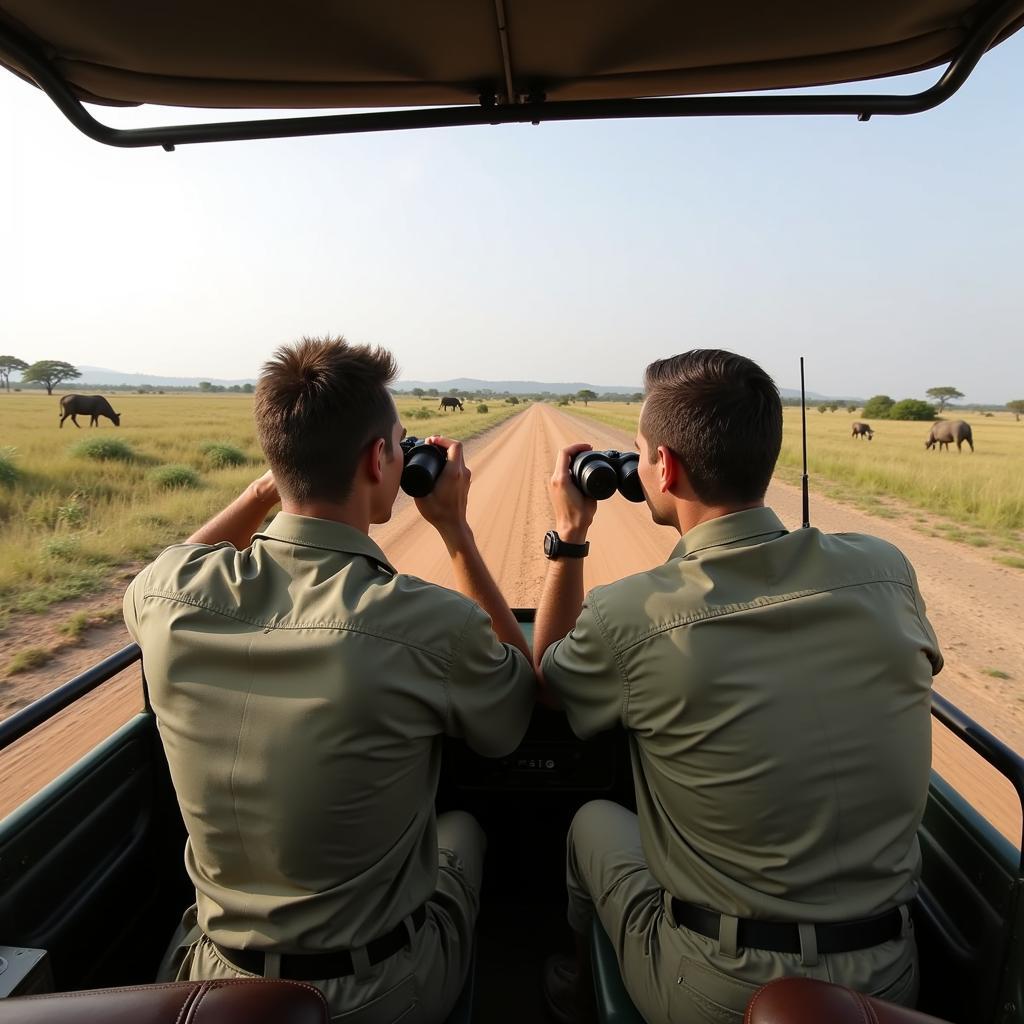 African Park Rangers on Anti-Poaching Patrol
African Park Rangers on Anti-Poaching Patrol
Resource Exploitation: Plundering Africa’s Riches
The illegal extraction and trade of natural resources represent another critical facet of “African countries illegal.” This exploitation takes various forms, including:
- Illegal Mining: From gold and diamonds to coltan (used in electronics), the lure of valuable minerals fuels illegal mining operations that often operate with little regard for environmental regulations or worker safety.
- Illegal Logging: The demand for timber, particularly from valuable hardwoods, drives the illegal felling of trees, contributing to deforestation, habitat loss, and climate change.
- Illegal Fishing: Foreign fishing vessels operating without licenses or exceeding quotas deplete fish stocks, harming local communities reliant on fishing for their livelihoods.
These illegal activities not only deprive African nations of their rightful revenue but also lead to environmental degradation and social unrest.
Human Trafficking and Exploitation: A Dark Side of “African Countries Illegal”
The term “African countries illegal” also encompasses the grim realities of human trafficking and exploitation. These human rights violations manifest in various ways:
- Forced Labor: Individuals, often vulnerable migrants seeking a better life, are tricked or coerced into working in exploitative conditions with little to no pay.
- Sexual Exploitation: Women and children are particularly vulnerable to being trafficked for the purpose of sexual exploitation, forced into prostitution against their will.
- Child Soldiery: In conflict zones, children are sometimes forcibly recruited or manipulated into joining armed groups, subjected to unimaginable horrors.
Addressing these issues requires a multi-faceted approach, including strengthening law enforcement, improving border controls, raising awareness, and providing support to victims.
Combating “African Countries Illegal”: A Collective Effort
Tackling the complex web of illegal activities plaguing some African nations demands a united front.
- Strengthening Governance and Rule of Law: Addressing corruption and promoting good governance are crucial steps in creating an environment where illegal activities are less likely to thrive.
- Empowering Local Communities: Engaging with communities affected by these illegal activities, providing education and alternative livelihood opportunities, is essential for long-term success.
- International Cooperation: Collaborative efforts between African nations and the international community, including sharing intelligence, providing technical assistance, and harmonizing legal frameworks, are vital to combating transnational criminal networks.
Conclusion: Moving Beyond the Search Term
While “African countries illegal” might seem like a simplistic phrase, it shines a light on a complex tapestry of challenges. By understanding the nuances of this search term and exploring the issues it encompasses, we can foster greater awareness and contribute to meaningful solutions that promote justice, sustainability, and the well-being of all Africans.