Navigating the Landscape of African Data Privacy Laws
The digital age has brought with it an explosion of data, and Africa, with its burgeoning tech scene, is no exception. As more and more personal information is collected and processed, the need for robust data privacy laws becomes paramount. This raises the question: what does the current landscape of African Data Privacy Laws look like?
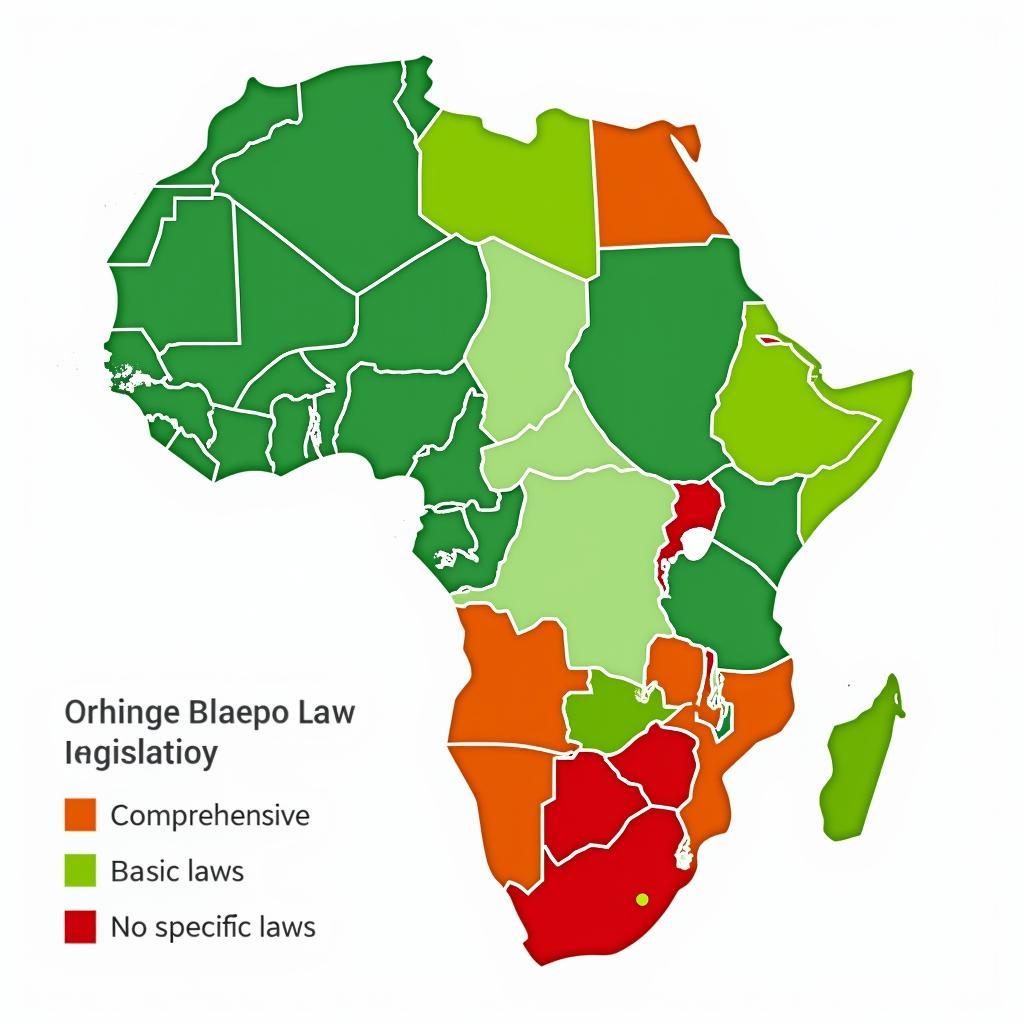 Map of Africa Highlighting Countries with Data Protection Laws
Map of Africa Highlighting Countries with Data Protection Laws
A Continent in Transition: The Patchwork of Data Protection
Africa’s journey towards comprehensive data protection is characterized by progress and challenges. While a growing number of African countries are enacting data privacy legislation, a significant gap still exists. This patchwork of laws can pose a challenge for businesses operating across borders.
One of the key drivers for data privacy laws in Africa is the need to foster trust in the digital economy. Robust data protection regimes can boost investor confidence and promote cross-border data flows, ultimately contributing to economic growth.
Key Legislation Shaping the African Data Privacy Landscape
Several key pieces of legislation have been instrumental in shaping the African data privacy landscape:
-
The African Union Convention on Cyber Security & Personal Data Protection (Malabo Convention): This convention, adopted in 2014, provides a continental framework for data protection. It covers a wide range of issues, including the collection, processing, storage, and transfer of personal data.
-
Nigeria’s Data Protection Regulation (NDPR): Inspired by the EU’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), NDPR is one of the most comprehensive data privacy laws on the continent. It establishes the rights of data subjects and the obligations of data controllers and processors.
-
South Africa’s Protection of Personal Information Act (POPIA): POPIA shares similarities with the GDPR and aims to protect the personal information of individuals. It introduces strict rules for the processing of personal information and establishes an Information Regulator to oversee compliance.
Challenges and Opportunities in Implementing Data Privacy Laws
Despite the progress made, several challenges remain in implementing data privacy laws in Africa:
-
Lack of Awareness: Raising awareness among businesses and individuals about their rights and obligations under the new laws is crucial for effective implementation.
-
Limited Resources: Enforcement agencies often face resource constraints, which can hinder their ability to effectively monitor compliance and impose penalties.
-
Harmonization of Laws: The lack of harmonization between different national data protection laws can create legal uncertainty for businesses operating across borders.
However, these challenges also present opportunities:
-
Capacity Building: Investing in capacity building for government officials, legal professionals, and businesses is essential to ensure effective implementation and enforcement.
-
Regional Cooperation: Strengthening regional cooperation and harmonizing data protection laws can help create a more conducive environment for businesses and boost cross-border data flows.
What Does the Future Hold for African Data Privacy?
The future of data privacy in Africa is likely to be shaped by several key trends:
-
Increased Digitization: The rapid pace of digitization across the continent will continue to drive the need for robust data protection measures.
-
Growing Focus on Data Sovereignty: African nations are increasingly asserting their right to control the flow of data across their borders, leading to the emergence of data localization requirements.
-
The Rise of New Technologies: Technologies like artificial intelligence (AI) and blockchain will create new challenges and opportunities in the field of data privacy, requiring innovative solutions and regulatory frameworks.
African Data Privacy: A Journey Towards a More Secure Digital Future
The journey towards comprehensive data privacy in Africa is ongoing. However, by addressing the challenges and seizing the opportunities, African nations can create a more secure and trustworthy digital environment for their citizens and businesses alike.
Frequently Asked Questions About African Data Privacy Laws:
1. What are the penalties for non-compliance with data privacy laws in Africa?
Penalties vary across different countries and can include fines, imprisonment, or both.
2. Do I need to appoint a Data Protection Officer (DPO) if my business operates in Africa?
This depends on the specific requirements of the data protection law in the country where you operate.
3. Can I transfer personal data from Africa to other countries?
Yes, but there are restrictions. Most African data privacy laws have provisions regulating the transfer of personal data to other countries, especially those deemed to have inadequate data protection levels.
4. How can I learn more about data privacy laws in a specific African country?
You can consult with legal professionals specializing in data privacy in the relevant country or refer to the websites of data protection authorities.
5. What is the role of data subjects in African data privacy laws?
Data subjects have rights such as access to their data, correction of inaccurate data, and the right to object to processing.
For further assistance regarding African data privacy laws, feel free to reach out to us. You can contact us at:
Phone Number: +255768904061
Email: kaka.mag@gmail.com
Address: Mbarali DC Mawindi, Kangaga, Tanzania.
Our dedicated customer support team is available 24/7 to address your queries.