African Life During the 1900s: A Century of Change
The early 1900s in Africa marked a period of immense change, with colonial powers tightening their grip on the continent while indigenous cultures and societies continued to evolve. This era witnessed the rise of nationalism, the development of new economic systems, and the birth of modern African cities. Join us as we delve into the fascinating tapestry of African Life during this pivotal century.
Colonial Rule and Resistance
The 1900s were marked by the intensification of colonial rule across Africa. European powers carved up the continent into colonies, exploiting its vast resources and imposing their political and social structures. This period saw the introduction of new administrative systems, the development of infrastructure, and the exploitation of Africa’s natural resources, such as rubber, diamonds, and gold.
“The colonial period was a time of both destruction and creation,” says Dr. Aminata Diallo, a historian specializing in African colonial history. “While it brought about some advancements in areas like infrastructure and education, it also caused immense social upheaval and exploitation.”
However, colonial rule faced resistance from Africans who fought for their independence and cultural preservation. The early 1900s saw the emergence of nationalist movements across the continent, fueled by the desire for self-determination. These movements organized protests, boycotts, and armed resistance, demonstrating the resilience of African societies in the face of colonial oppression.
Economic Transformation and Urbanization
The colonial period brought about significant changes to the African economy, shifting from traditional subsistence agriculture to cash crop production for the global market. The introduction of new crops like cotton and cocoa led to the expansion of commercial agriculture, but it also created dependencies on European markets and led to inequalities in land ownership.
“Colonial economic policies often benefited European interests over those of Africans,” explains Dr. Samuel Mwanza, an economist focusing on African development. “The emphasis on cash crops led to neglect of food production, contributing to food insecurity in some regions.”
The colonial period also witnessed the rise of urbanization in Africa, as people migrated from rural areas to urban centers seeking employment in mines, factories, and government offices. This led to the development of new cities like Lagos, Accra, and Nairobi, which became centers of trade, commerce, and cultural exchange.
The Rise of African Culture and Identity
Despite the challenges posed by colonial rule, African cultures and identities flourished during the 1900s. Traditional arts and crafts continued to thrive, adapting to new materials and contexts. Oral traditions, music, and dance played a vital role in preserving African heritage and transmitting knowledge across generations.
“The 1900s saw a conscious effort by Africans to reclaim and celebrate their cultural heritage,” shares Dr. Abena Mensah, an anthropologist studying African cultural expressions. “The arts became a powerful tool for expressing resistance and asserting cultural identity.”
The emergence of pan-African movements and organizations like the African National Congress (ANC) in South Africa and the National Union of Nigerian Students (NUNS) in Nigeria further fostered a sense of shared African identity. These movements promoted the idea of African unity and worked towards the liberation of the continent from colonial rule.
The Path to Independence
The post-World War II era saw the rise of anti-colonial movements across the globe, including in Africa. The struggle for independence gained momentum, leading to the decolonization of most African countries between the 1950s and the 1970s. The 1900s saw the emergence of iconic figures like Nelson Mandela, Kwame Nkrumah, and Jomo Kenyatta, who led the fight for freedom and self-determination.
“The decolonization of Africa was a major turning point in the history of the continent,” emphasizes Dr. Omar Ibrahim, a political scientist specializing in African politics. “It opened up opportunities for Africans to build independent nations and pursue their own destinies.”
A Legacy of Change
The 1900s in Africa were a century of immense change, marked by both the challenges of colonialism and the resilience of African societies. This era laid the foundation for the development of independent African nations, the emergence of new economic systems, and the flourishing of diverse cultures and identities. As we move forward, understanding the legacy of this pivotal century remains crucial for shaping the future of Africa.
FAQ
Q1. What were the key factors that led to the rise of nationalism in Africa during the 1900s?
The rise of nationalism in Africa was driven by a range of factors, including the desire for self-determination, the experience of colonial oppression, the influence of pan-African movements, and the growing awareness of shared African identity.
Q2. How did colonial rule impact the African economy in the 1900s?
Colonial rule brought about significant economic transformation in Africa, shifting from traditional subsistence agriculture to cash crop production for the global market. This led to the expansion of commercial agriculture but also created dependencies on European markets and inequalities in land ownership.
Q3. What were some of the major challenges faced by African societies during the colonial period?
African societies faced numerous challenges during the colonial period, including political oppression, social upheaval, economic exploitation, and the erosion of traditional cultures.
Q4. How did African cultures and identities adapt and evolve during the 1900s?
African cultures and identities continued to thrive despite the challenges posed by colonial rule. Traditional arts and crafts adapted to new materials and contexts, while oral traditions, music, and dance played a crucial role in preserving heritage.
Q5. What are some examples of African nationalist movements that emerged during the 1900s?
Some notable African nationalist movements that emerged during the 1900s include the African National Congress (ANC) in South Africa, the National Union of Nigerian Students (NUNS) in Nigeria, and the Kenya African National Union (KANU) in Kenya.
Q6. What were some of the key figures who led the fight for independence in Africa?
Iconic figures who led the fight for independence in Africa include Nelson Mandela, Kwame Nkrumah, Jomo Kenyatta, Julius Nyerere, and Leopold Sedar Senghor.
Q7. How did the decolonization of Africa impact the continent’s development?
The decolonization of Africa was a major turning point, opening up opportunities for Africans to build independent nations, pursue their own destinies, and shape their economic and political future.
 African life during the colonial era
African life during the colonial era
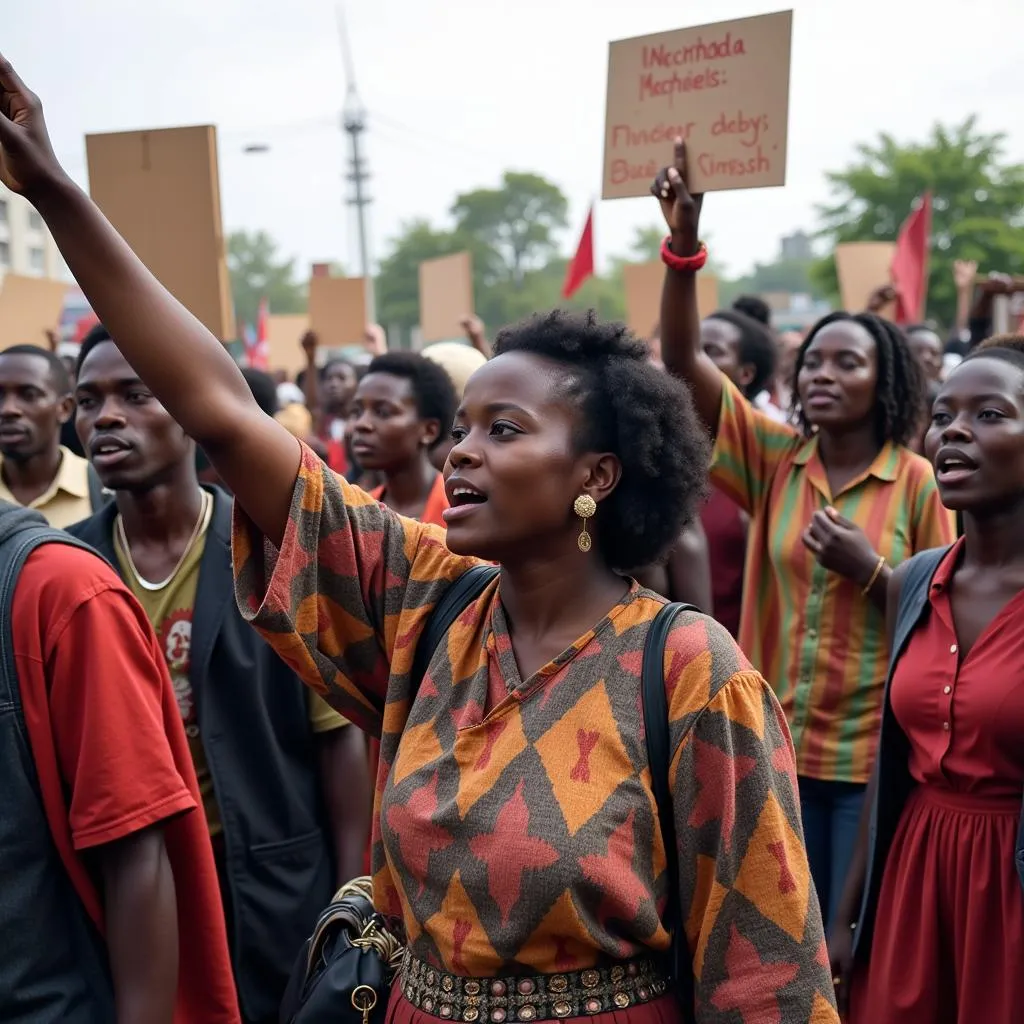 African nationalist movements
African nationalist movements
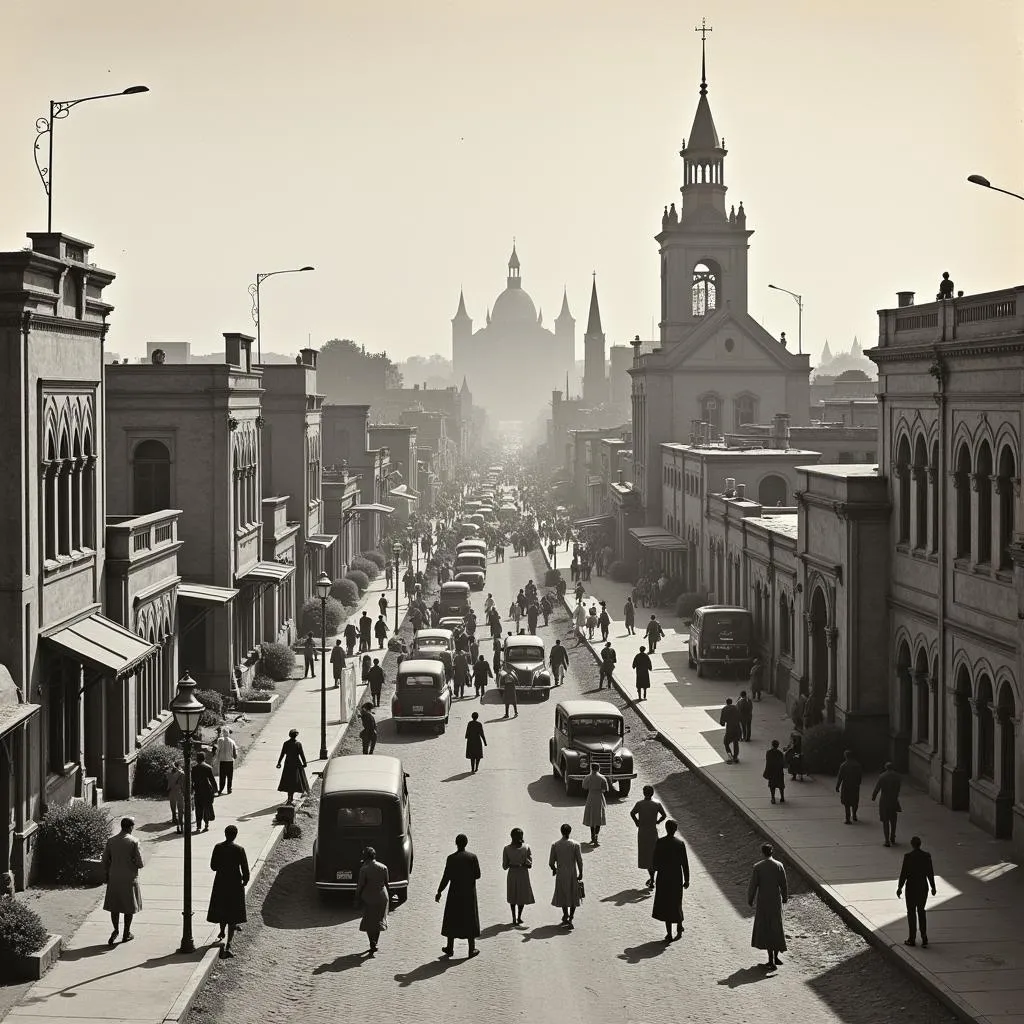 African urbanization in the 1900s
African urbanization in the 1900s
The 1900s in Africa were a century of both challenges and triumphs. While colonial rule brought about profound changes and injustices, it also sparked the development of modern Africa and the emergence of strong national identities. By understanding this complex and fascinating era, we can gain valuable insights into the history and trajectory of the continent, paving the way for a more equitable and prosperous future for all Africans.