African Dwarf Frog and Betta Lock: A Guide to Peaceful Coexistence
The captivating world of freshwater aquariums often sees the African dwarf frog and betta fish sharing the same aquatic haven. While these two species can co-exist, the term “African Dwarf Frog And Betta Lock” hints at a potential problem: bettas sometimes mistake these tiny amphibians for food or rivals. This comprehensive guide delves into the dynamics of keeping African dwarf frogs and bettas together, emphasizing how to create a harmonious environment for both.
Understanding the African Dwarf Frog and Betta
Before introducing these fascinating creatures into a shared tank, it’s crucial to understand their individual needs and behaviors.
African Dwarf Frog: The Peaceful Aquatic Dweller
Originating from the Congo Basin in Africa, the African dwarf frog (Hymenochirus boettgeri) is a fully aquatic species, spending its entire life underwater. Unlike their land-dwelling counterparts, these frogs don’t possess a protruding tongue for catching prey. Here’s a closer look:
- Size: Adults reach a maximum size of 3 inches.
- Temperament: Peaceful and social, they thrive in groups.
- Diet: Carnivorous, preferring live or frozen foods like bloodworms and brine shrimp.
Betta Fish: The Splendid but Territorial Fighter
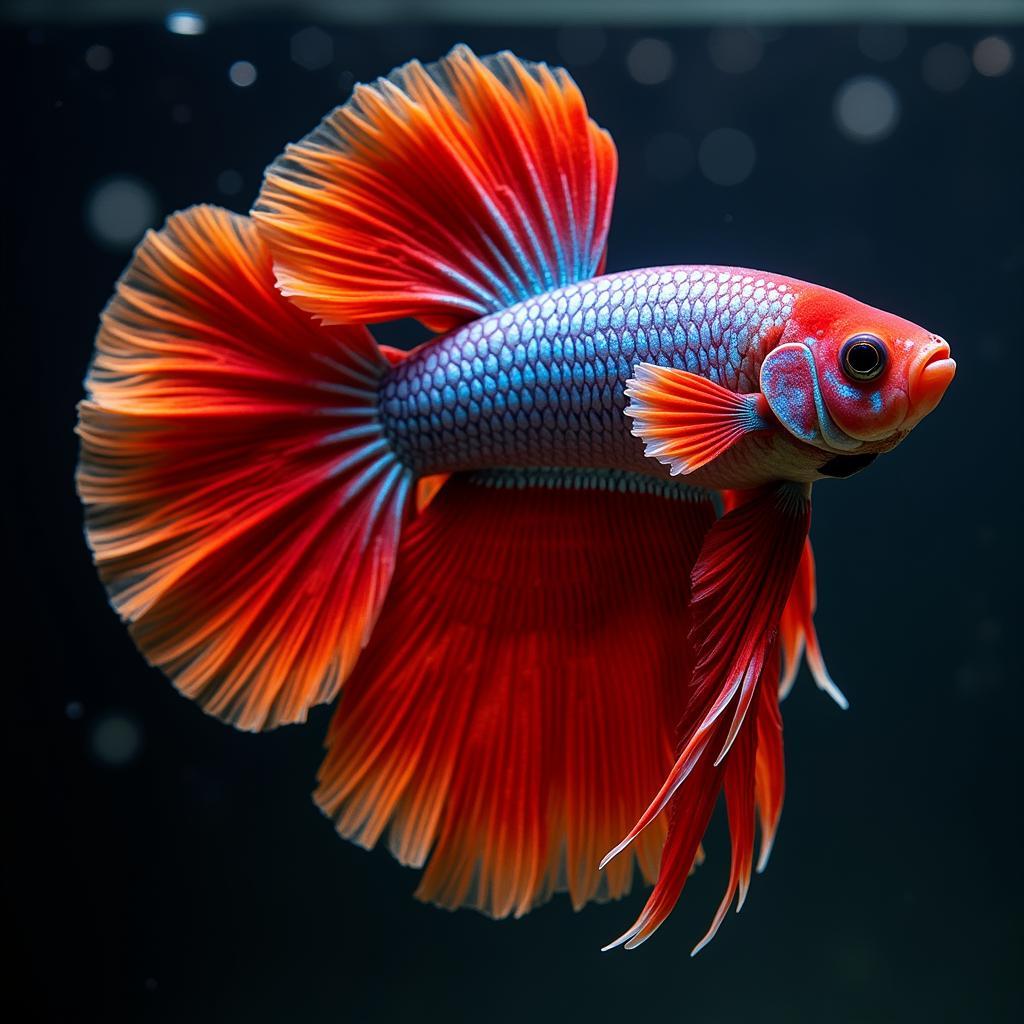 Male Siamese fighting fish with fanned-out fins.
Male Siamese fighting fish with fanned-out fins.
The betta fish (Betta splendens), also known as the Siamese fighting fish, hails from the Mekong basin in Southeast Asia. Renowned for their vibrant colors and flowing fins, bettas are sadly associated with aggression, especially amongst males:
- Size: Males can grow up to 3 inches, with females being slightly smaller.
- Temperament: Can be territorial and aggressive, particularly males towards other males or species they perceive as rivals.
- Diet: Carnivorous, requiring a diet rich in protein from sources like betta pellets and bloodworms.
Can African Dwarf Frogs and Bettas Live Together?
Yes, African dwarf frogs and bettas can coexist peacefully in the same aquarium with careful planning and consideration of their specific needs.
Factors to Consider for Cohabitation:
- Tank Size: A larger tank (at least 10 gallons) is crucial for successful cohabitation. This allows for establishing territories and reducing the chances of encounters that could lead to aggression.
- Aquascaping: Provide plenty of hiding spots for both species using plants, caves, rocks, and driftwood. This helps create a sense of security and reduces stress.
- Water Parameters: Maintain water parameters suitable for both species. Aim for a temperature between 78-82°F (25-28°C), a pH of 6.5-7.5, and low levels of ammonia, nitrite, and nitrates.
- Feeding: Feed both the betta and the frogs adequately to prevent the betta from mistaking the frog for food. Offer a varied diet of high-quality betta pellets, bloodworms, brine shrimp, and other suitable foods.
Preventing and Addressing “Betta Lock”
“Betta lock” refers to a potentially dangerous situation where a betta fish latches onto an African dwarf frog, mistaking it for food or a rival.
Prevention is Key:
- Choose Tank Mates Wisely: Opt for a female betta or a less aggressive male betta variety.
- Introduce the Frog First: Allow the frog to establish itself in the tank before introducing the betta.
- Monitor Closely: Keep a watchful eye on their interactions, especially during the initial days after introduction.
- Separate if Needed: Have a backup plan ready, such as a separate tank or divider, in case the betta shows persistent aggression towards the frog.
Creating a Thriving Habitat
A well-maintained aquarium is crucial for the health and well-being of both species.
- Regular Water Changes: Perform weekly water changes of 25-50% to maintain water quality and remove waste products.
- Filtration: Use a filter suitable for the tank size to keep the water clean and oxygenated.
- Lighting: Provide moderate lighting for 8-10 hours a day, mimicking their natural environment.
Conclusion
While keeping African dwarf frogs and bettas together requires thoughtful planning and careful observation, it can be a rewarding experience. By understanding their unique needs and following the guidelines outlined in this guide, you can create a harmonious and enriching aquatic environment where both species can thrive. Remember, a well-planned and maintained tank is the key to successful cohabitation and the enjoyment of these captivating creatures.