African Elephant Adaptations for Kids
African elephants, the largest land animals on Earth, have some amazing adaptations that help them survive in the harsh African environments. These adaptations, developed over millions of years, allow them to thrive in diverse habitats, from savannas and forests to deserts and swamps. Let’s explore some of these incredible features that make African elephants so unique.
Trunks: A Multi-Purpose Tool
The trunk is perhaps the most recognizable and versatile adaptation of the African elephant. It’s a fusion of the nose and upper lip, forming a powerful and dexterous tool. Elephants use their trunks for a variety of tasks, from breathing and smelling to drinking, eating, and communicating. They can pick up objects as small as a single blade of grass or as large as a fallen tree branch. Imagine having a nose that could do all that!
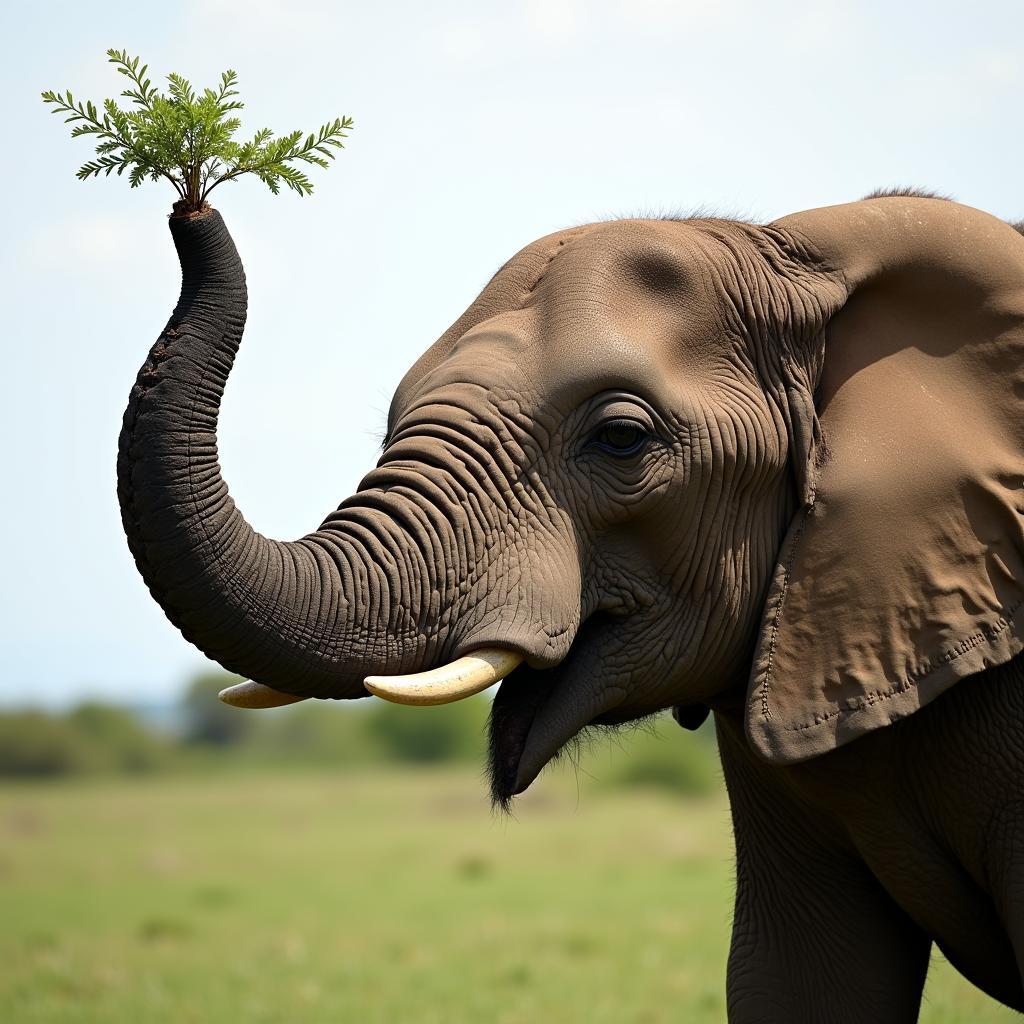 African Elephant Using its Trunk
African Elephant Using its Trunk
How Does the Trunk Help with Eating and Drinking?
Elephants use their trunks like a giant straw to suck up water. They can then squirt the water into their mouths or over their bodies for a refreshing shower. When it comes to food, the trunk acts like a hand, grasping leaves, fruits, and grasses. For larger branches, they can use their tusks to break them down into smaller, manageable pieces.
Big Ears: Keeping Cool in the Heat
African elephants possess enormous ears, another key adaptation for surviving in hot climates. These large ears act like radiators, helping them regulate their body temperature. The ears are filled with blood vessels close to the surface. When the elephant flaps its ears, the blood cools down, and this cooler blood circulates throughout the body, helping to lower its overall temperature. Isn’t that clever?
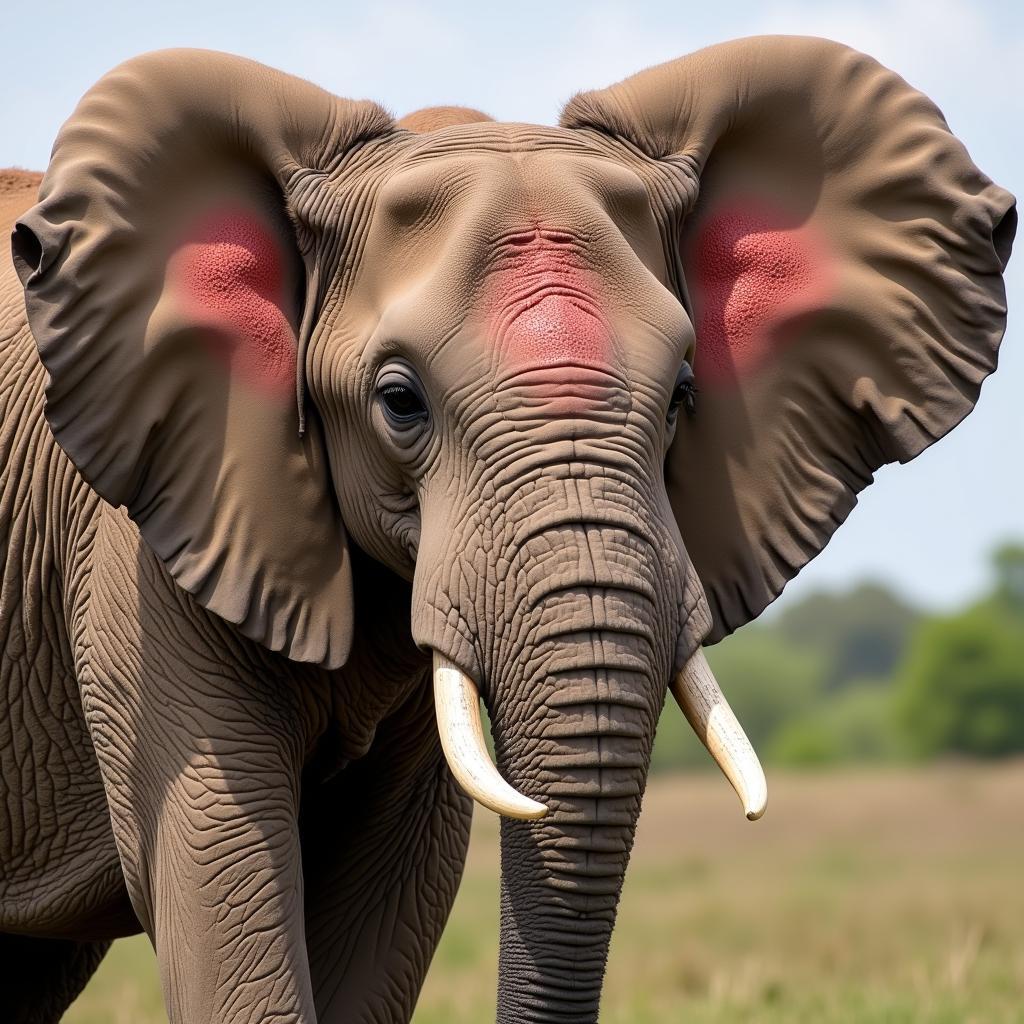 African Elephant Flapping its Ears to Cool Down
African Elephant Flapping its Ears to Cool Down
How Big Are an Elephant’s Ears?
An adult African elephant’s ear can be up to six feet wide! That’s about the same height as an average adult human. Think about how much surface area that provides for cooling. You can learn more about the size and dimensions of different elephant species at african forest elephant height.
Tusks: More Than Just Decorations
Both male and female African elephants have tusks, which are elongated incisor teeth. Tusks serve several purposes. They are used for digging for roots and water, stripping bark from trees, and for defense against predators. Sadly, these magnificent tusks have also made them a target for poachers.
Why are Tusks Important for Survival?
Tusks are essential tools for elephants, helping them access vital resources like water and food. They also play a crucial role in social interactions and dominance displays. You can learn more about elephants and their natural habitat by watching an african jungle life documentary.
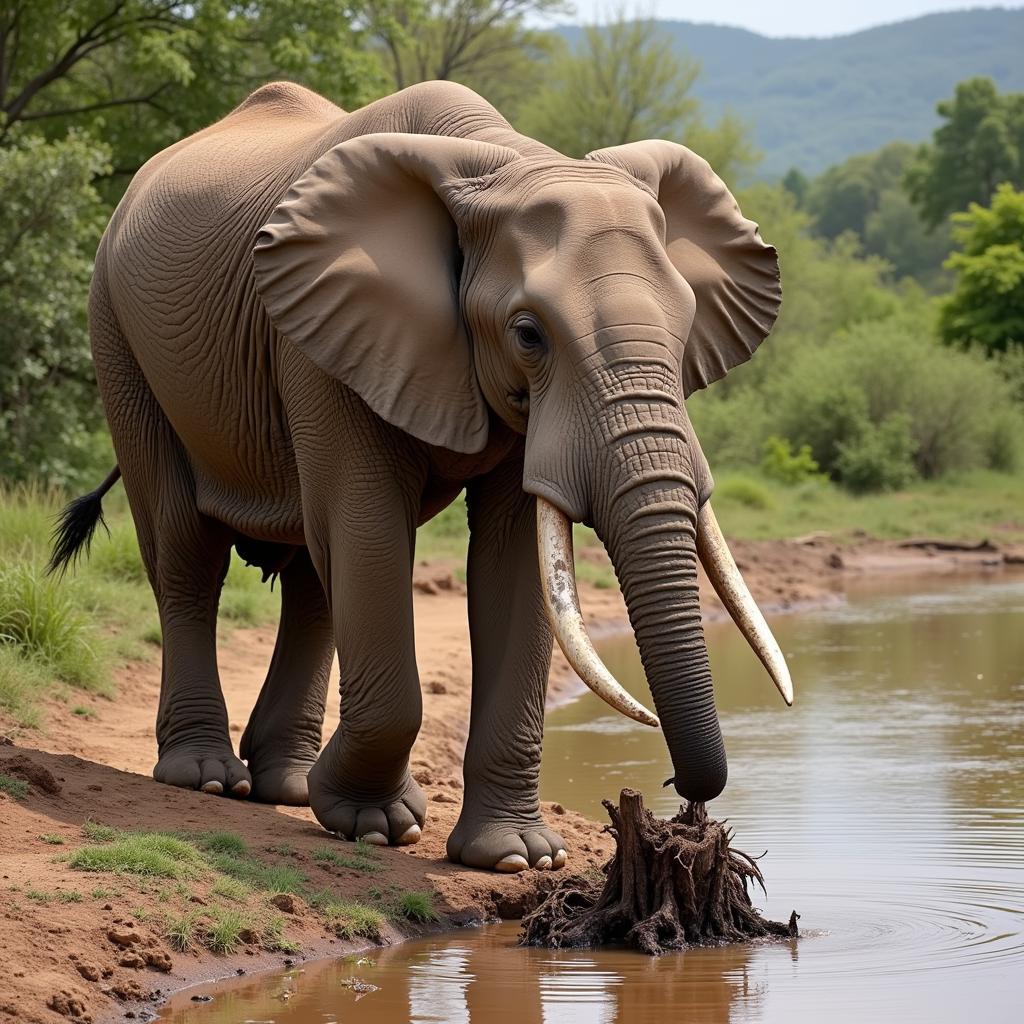 African Elephant Using Tusks to Dig
African Elephant Using Tusks to Dig
Thick Skin: Protection from the Elements
African elephants have thick, gray skin that protects them from the sun, insects, and even minor injuries. While the skin is tough, it’s also surprisingly sensitive. Elephants often take dust baths to protect their skin from the sun and insects. The dust acts as a natural sunscreen and insect repellent.
What other adaptations do African elephants have?
African elephants have strong legs and large feet, enabling them to travel long distances in search of food and water. Their digestive system is adapted to process large quantities of plant matter, and their social structure, based on matriarchal herds, provides protection and support for the young. For a wider perspective on the African landscape and its inhabitants, explore the african landscape. If you’re interested in observing elephants and other animals in action, you can find some fascinating videos showcasing african animals hunting video. You can also browse an african animals alphabetical list to learn more about the diverse fauna of Africa.
Dr. Anika Patel, a renowned wildlife biologist specializing in African elephants, notes, “The trunk is arguably the most remarkable adaptation, allowing elephants to perform a wide range of tasks crucial for their survival.” Another expert, Dr. Jabari Otieno, adds, “The large ears are not just for show; they are vital for thermoregulation in the intense African heat.” Dr. Fatima Mbaye, a leading conservationist, emphasizes, “Protecting elephants is crucial, not just for their own sake but for the health of the entire ecosystem.”
In conclusion, African elephants demonstrate a remarkable suite of adaptations that enable them to thrive in the diverse and challenging environments of Africa. From their versatile trunks and massive ears to their powerful tusks and thick skin, each adaptation plays a crucial role in their survival. Learning about these adaptations helps us appreciate these incredible animals and understand the importance of protecting them for future generations.
FAQ
-
What do African elephants eat? African elephants are herbivores, primarily eating grasses, leaves, fruits, and bark.
-
How long do African elephants live? African elephants can live up to 70 years in the wild.
-
How much do African elephants weigh? Adult African elephants can weigh up to 6 tons.
-
How tall are African elephants? African elephants can reach heights of up to 13 feet.
-
How fast can African elephants run? African elephants can run up to 25 miles per hour.
-
What are the main threats to African elephants? Poaching for ivory and habitat loss are the biggest threats to African elephants.
-
How can I help protect African elephants? Supporting conservation organizations and raising awareness about the threats facing elephants are important steps in protecting these magnificent animals.
Need support? Contact us 24/7: Phone: +255768904061, Email: kaka.mag@gmail.com or visit us at Mbarali DC Mawindi, Kangaga, Tanzania.