African Elephant Facts: Everything You Need to Know from National Geographic
The African elephant, a majestic creature that roams the savannas and forests of Africa, is an iconic symbol of the continent’s rich biodiversity. These gentle giants are the largest land mammals on Earth, and their presence has been a defining feature of African ecosystems for millions of years. In this article, we’ll delve into the fascinating world of African elephants, exploring their physical characteristics, social behavior, and the challenges they face in an ever-changing world.
The Physical Prowess of African Elephants
African elephants are renowned for their massive size and distinctive features. They are divided into two species: the African bush elephant (Loxodonta africana) and the African forest elephant (Loxodonta cyclotis).
African Bush Elephant:
- Size: Adults can reach up to 13 feet tall and weigh up to 13,000 pounds.
- Tusks: Males typically have long, curved tusks, which are actually modified incisor teeth.
- Ears: Large, fan-shaped ears that help to regulate body temperature.
African Forest Elephant:
- Size: Smaller than their bush counterparts, with adults typically reaching up to 8 feet tall and weighing up to 6,000 pounds.
- Tusks: Usually smaller than those of bush elephants.
- Ears: Smaller and rounder compared to bush elephants.
 African Elephant Physical Features
African Elephant Physical Features
Social Life and Family Bonds
African elephants are highly social animals and live in matriarchal herds led by the oldest and most experienced female. These herds can consist of several generations of related females, their young, and sometimes a few adult males.
The Matriarch’s Role
The matriarch is the decision-maker and leader of the herd. She has a vast knowledge of the terrain, water sources, and food resources, ensuring the well-being of the entire group. She is responsible for guiding the herd to safe locations, protecting them from predators, and teaching young elephants valuable survival skills.
Communication and Intelligence
Elephants communicate through a variety of vocalizations, including trumpets, roars, and infrasound. These low-frequency sounds can travel long distances and play a crucial role in maintaining social cohesion and alerting the herd to danger. Moreover, elephants are known for their exceptional intelligence and problem-solving abilities.
African Elephant Conservation
Despite their iconic status, African elephants are facing a severe threat from habitat loss, poaching, and human conflict.
Habitat Loss and Fragmentation
As human populations continue to expand, elephant habitats are shrinking due to deforestation, agriculture, and urbanization. This fragmentation of their natural range limits their ability to find food, water, and safe breeding grounds.
Poaching for Ivory
The illegal ivory trade has led to a dramatic decline in elephant populations. Poaching for tusks is a cruel and unsustainable practice that has left many elephants orphaned and has pushed several populations to the brink of extinction.
Human-Elephant Conflict
As human settlements encroach upon elephant territories, there are increasing instances of conflict between people and elephants. This can lead to crop damage, property destruction, and even human fatalities.
What You Can Do to Help
You can contribute to the conservation of African elephants by supporting organizations that work to protect these animals. Boycott products made from ivory, educate others about the threats facing elephants, and advocate for stronger conservation policies.
Expert Insight
“African elephants are a vital part of the ecosystem, playing a key role in seed dispersal, maintaining forest structure, and shaping the landscape. Their decline is a warning sign that we need to do more to protect our planet’s biodiversity.” – Dr. Emily Grace, Wildlife Conservationist.
FAQ
1. What is the difference between African forest elephants and African bush elephants?
African forest elephants are smaller, have smaller ears, and live in forested areas. African bush elephants are larger, have larger ears, and live in open savannas.
2. How long do African elephants live?
African elephants can live up to 70 years in the wild.
3. Do elephants mourn their dead?
There is evidence to suggest that elephants display behaviors indicative of grief, such as touching the remains of dead individuals and staying near the body for prolonged periods.
4. What is the gestation period for an African elephant?
The gestation period for an African elephant is 22 months, the longest of any land mammal.
5. Are African elephants endangered?
Both the African forest elephant and the African bush elephant are listed as endangered by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN).
6. What are some organizations working to conserve African elephants?
Several organizations are dedicated to protecting African elephants, including the World Wildlife Fund (WWF), the African Wildlife Foundation (AWF), and the International Fund for Animal Welfare (IFAW).
7. Can I visit elephants in the wild?
Responsible eco-tourism programs allow visitors to see elephants in their natural habitat while minimizing the impact on the animals and their environment. However, it is important to choose reputable operators who prioritize animal welfare and conservation.
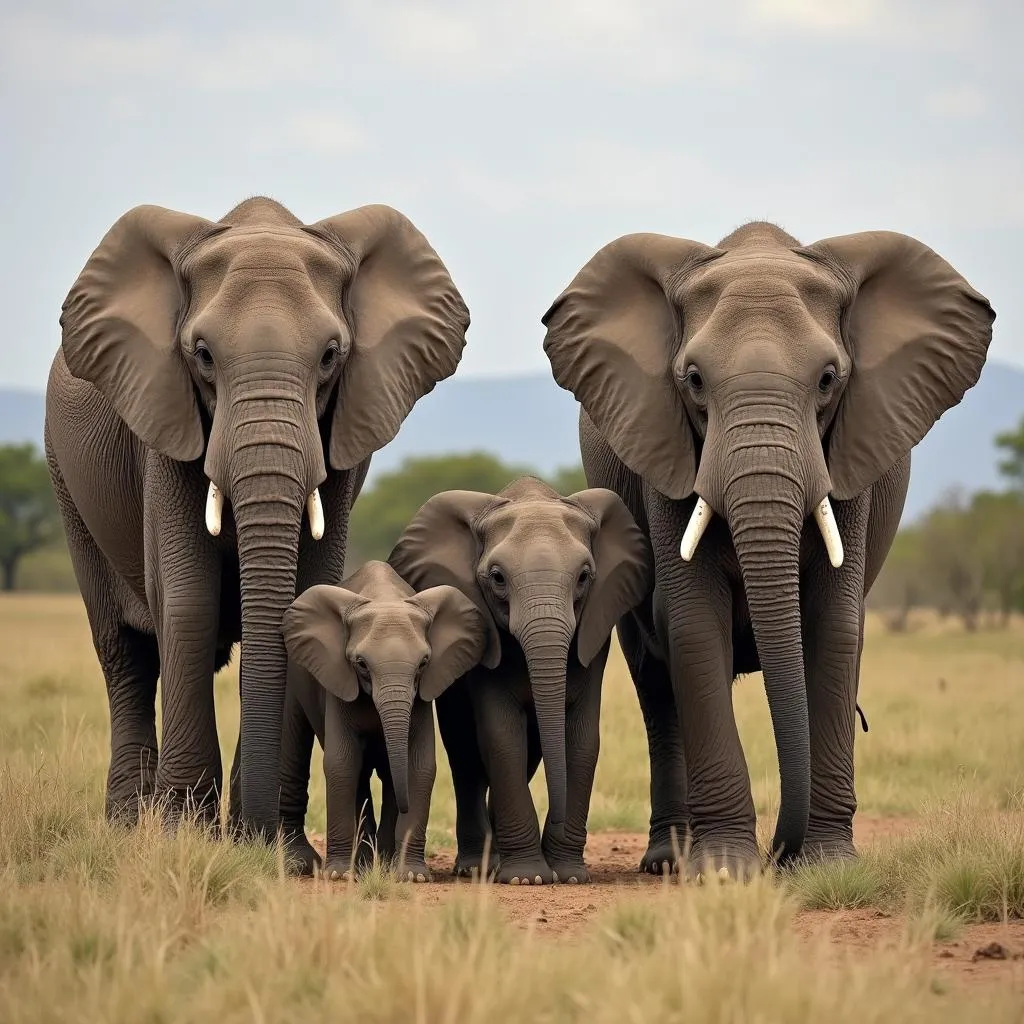 African Elephant Herd
African Elephant Herd
Exploring Further
Want to learn more about African elephants? Here are some additional resources:
- National Geographic’s “African Elephants” page: [Link to National Geographic website]
- WWF’s “African Elephants” page: [Link to WWF website]
- AWF’s “Elephant Conservation” page: [Link to AWF website]
Call to Action
We all have a role to play in protecting African elephants and their future. Join the efforts of conservation organizations by donating, volunteering, or simply raising awareness. By working together, we can help ensure that these magnificent creatures continue to roam the African landscape for generations to come.
If you need help with supporting African elephant conservation or have any questions, please contact us at:
Phone: +255768904061
Email: kaka.mag@gmail.com
Address: Mbarali DC Mawindi, Kangaga, Tanzania.
Our dedicated customer service team is available 24/7 to assist you.