African Elephant Info: All You Need to Know
African elephants are iconic giants that roam the savannas, forests, and deserts of Africa. These magnificent creatures are the largest land mammals on Earth and are known for their intelligence, social complexity, and unique physical features.
Types of African Elephants
There are two main species of African elephants: the African forest elephant and the African savanna elephant.
African Forest Elephant
The African forest elephant (Loxodonta cyclotis) is smaller than its savanna cousin and has straighter tusks and rounder ears. They are critically endangered and primarily found in the dense rainforests of Central Africa. These elephants play a crucial role in maintaining the health of the rainforest ecosystem by creating clearings and dispersing seeds.
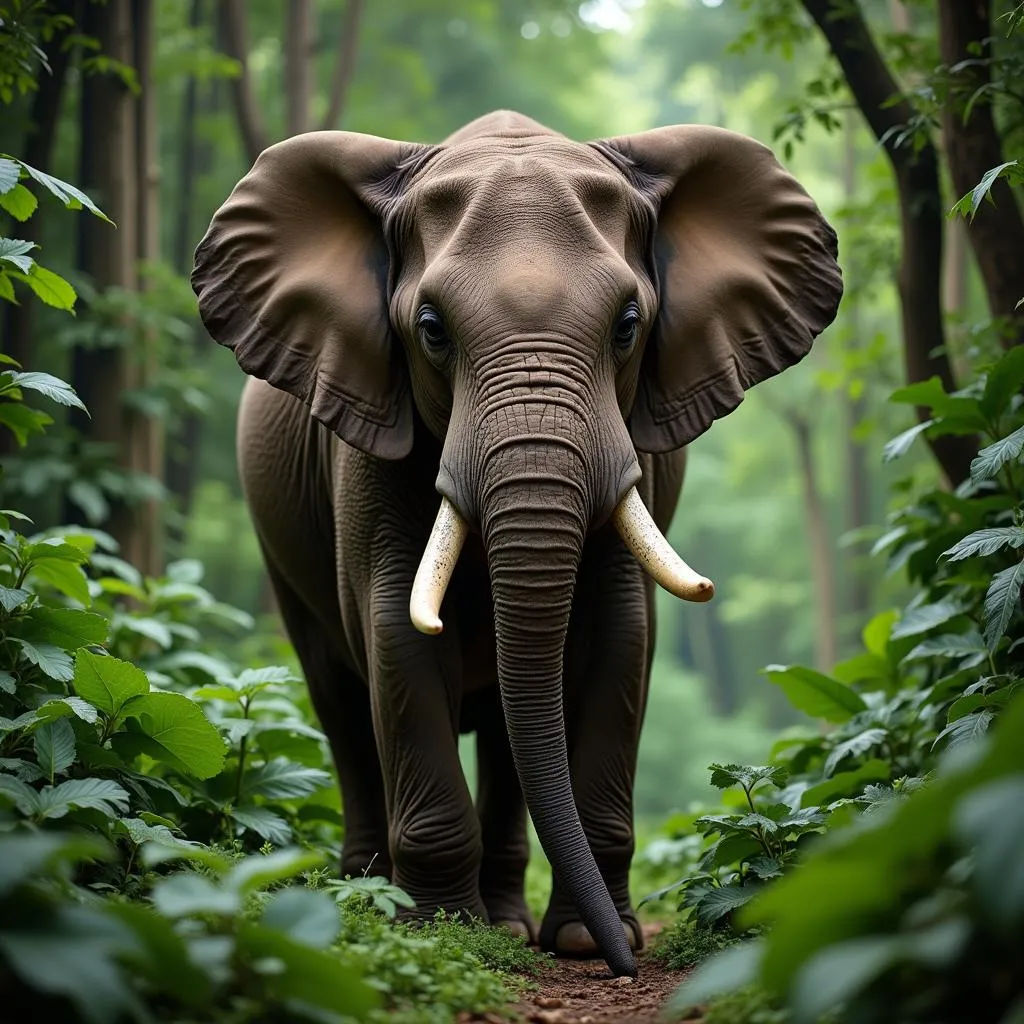 African Forest Elephant in its Natural Habitat
African Forest Elephant in its Natural Habitat
African Savanna Elephant
The African savanna elephant (Loxodonta africana) is the larger of the two species and is characterized by its curved tusks and large, fan-shaped ears. They are classified as endangered and are found in a wider range of habitats across sub-Saharan Africa, including grasslands, woodlands, and deserts. Savanna elephants are highly social animals that live in complex herds led by a matriarch, the oldest and most experienced female.
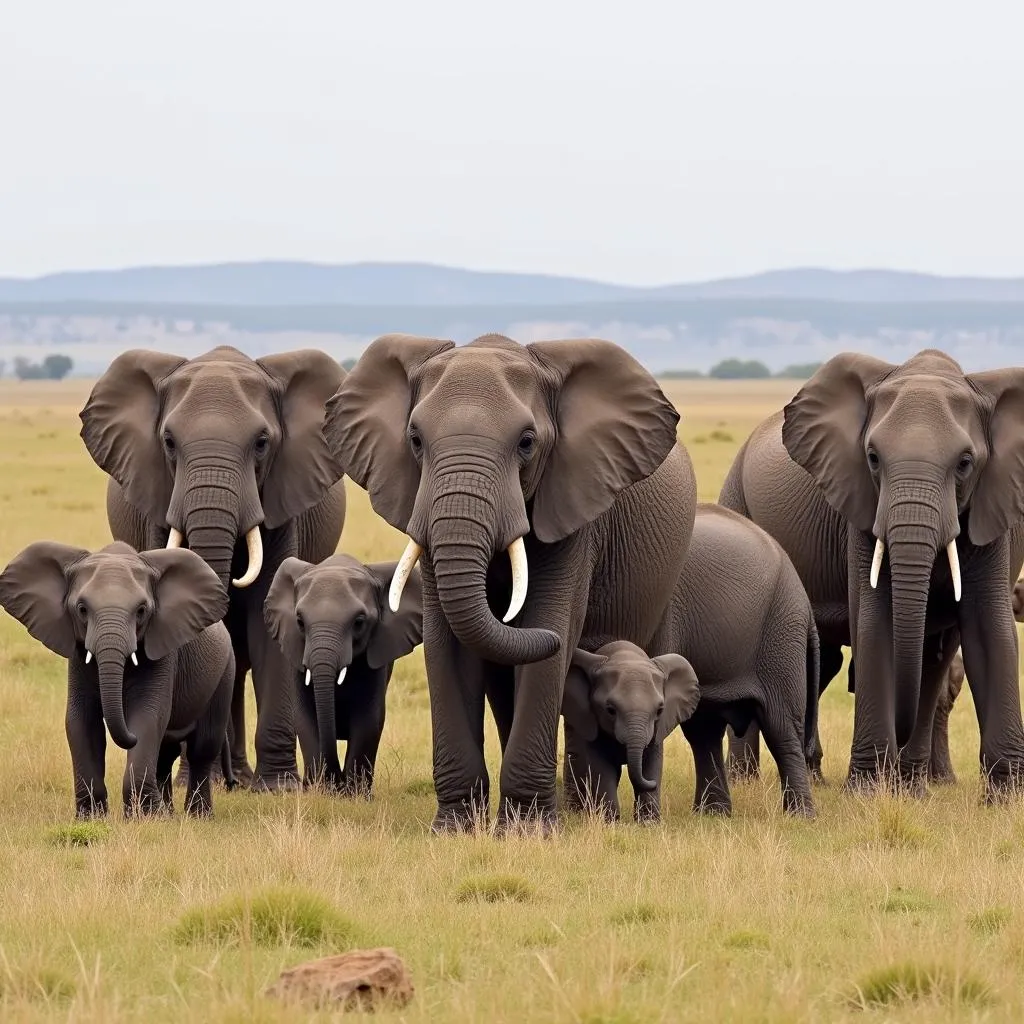 Herd of African Savanna Elephants
Herd of African Savanna Elephants
Physical Characteristics
African elephants share several distinctive physical characteristics:
- Tusks: Both male and female African elephants have tusks, which are elongated incisor teeth that continue to grow throughout their lives. Tusks are used for a variety of purposes, including digging, foraging, defense, and display.
- Trunk: The elephant’s trunk is a remarkable organ that is a fusion of the nose and upper lip. It is incredibly strong and dexterous, capable of picking up a single blade of grass or ripping bark off a tree.
- Ears: The large, fan-shaped ears of African elephants help to regulate their body temperature by radiating heat.
- Size: African savanna elephants can grow up to 13 feet tall at the shoulder and weigh up to 6 tons, making them the largest land animals on Earth.
Diet and Behavior
African elephants are herbivores and consume a wide variety of vegetation, including grasses, leaves, bark, and fruit. They are known to spend up to 16 hours a day feeding and can consume up to 600 pounds of food daily.
Elephants are highly social animals that live in complex herds led by a matriarch. These herds can range in size from a few individuals to several hundred. Communication between elephants is complex and involves a variety of vocalizations, including trumpets, rumbles, and roars.
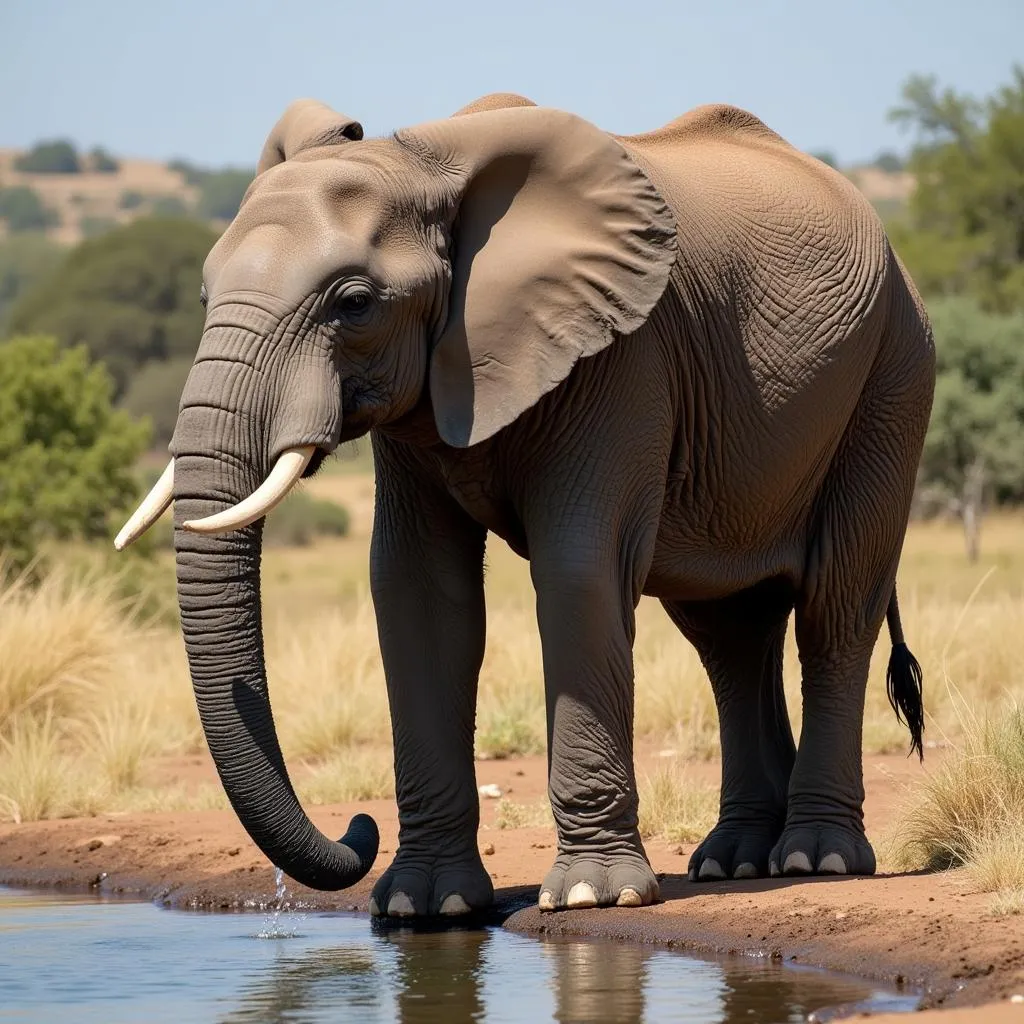 African Elephant Drinking Water
African Elephant Drinking Water
Conservation Status and Threats
Both species of African elephants are facing significant threats to their survival, primarily due to human activities.
- Poaching: The illegal ivory trade continues to be a major threat to African elephants. Despite international efforts to ban the trade, elephants are still poached for their tusks, which are highly valued in some parts of the world.
- Habitat loss: As human populations grow, elephant habitat is being lost to agriculture, logging, and mining. This leads to fragmentation and degradation of elephant populations, making it harder for them to survive.
- Human-elephant conflict: As elephant ranges overlap with human settlements, conflict can arise over access to resources such as water and crops. This can lead to elephants being killed or injured by humans.
Conservation Efforts
There are a number of organizations and initiatives working to conserve African elephants:
- Protected areas: National parks and reserves provide a safe haven for elephants and other wildlife.
- Anti-poaching efforts: Rangers and law enforcement agencies work to combat poaching and illegal wildlife trade.
- Community-based conservation: Engaging local communities in elephant conservation efforts is crucial for the long-term success of these initiatives.
- Education and awareness: Raising awareness about the importance of elephant conservation is essential for changing attitudes and behaviors.
The Importance of African Elephants
African elephants play a crucial role in their ecosystems and are considered keystone species. They help to maintain the health of savannas and forests by creating clearings, digging waterholes, and dispersing seeds. The loss of elephants would have a devastating impact on the African ecosystem.
In addition to their ecological importance, African elephants also hold cultural and economic significance. They are revered in many African cultures and are a major draw for tourism.
Conclusion
African elephants are magnificent creatures that face a number of challenges to their survival. By understanding the threats they face and supporting conservation efforts, we can help ensure that these iconic giants continue to roam the African continent for generations to come. The future of African elephants depends on our collective action.
FAQ
1. How long do African elephants live?
African elephants have an average lifespan of 60-70 years in the wild.
2. How much do African elephants weigh?
African savanna elephants can weigh up to 6 tons, while African forest elephants are smaller, weighing up to 3 tons.
3. What is the main difference between African and Asian elephants?
African elephants have larger ears and concave backs, while Asian elephants have smaller ears and convex backs. African elephants also have two “fingers” at the tip of their trunks, while Asian elephants have only one.
4. How many African elephants are left in the wild?
There are estimated to be around 415,000 African elephants left in the wild.
5. How can I help protect African elephants?
You can help protect African elephants by supporting organizations working on elephant conservation, raising awareness about the issue, and making informed choices as a consumer, such as avoiding products made from ivory.
Need More African Elephant Info?
Check out these related articles on our website:
For any further assistance or inquiries, please contact us at:
Phone Number: +255768904061
Email: kaka.mag@gmail.com
Address: Mbarali DC Mawindi, Kangaga, Tanzania.
Our customer service team is available 24/7.