The Truth About African Elephant Lifespan in Captivity
The African elephant, a symbol of strength and wisdom, roams the savannas of Africa with an expected lifespan that often surpasses that of humans. However, when it comes to African Elephant Lifespan In Captivity, the story takes a different turn.
Exploring the Lifespan Disparity
While African elephants in their natural habitat can live well into their 60s and 70s, their counterparts in captivity often face a shorter lifespan. Studies have shown a concerning trend: African elephants in zoos and other captive environments tend to live shorter lives compared to their wild relatives. This stark difference raises important questions about the well-being and longevity of these magnificent creatures when they are removed from their natural environments.
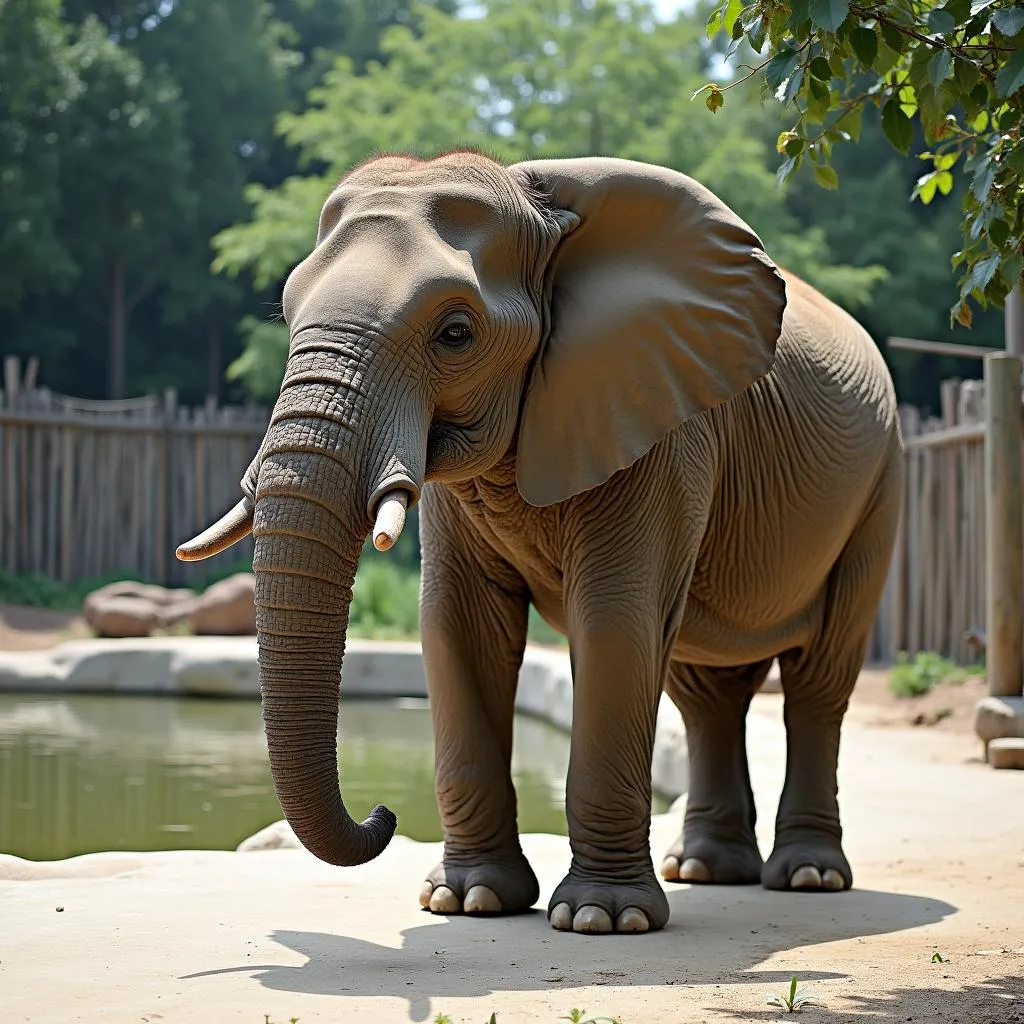 An African elephant standing in a zoo enclosure.
An African elephant standing in a zoo enclosure.
Factors Impacting Lifespan in Captivity
There are several factors that contribute to the reduced lifespan of African elephants in captivity. Some of these factors include:
- Limited Space and Lack of Exercise: Zoo enclosures, no matter how large, can never truly replicate the vast landscapes that elephants are accustomed to in the wild. This restriction in movement can lead to obesity, foot problems, and other health issues that can shorten their lifespan.
- Dietary Differences: In the wild, African elephants have a diverse diet consisting of a wide variety of plants, fruits, and bark. In captivity, their diet is often limited to hay, fruits, and vegetables, which may not provide all the necessary nutrients.
- Social Isolation and Stress: African elephants are highly social animals that live in complex herds with strong family bonds. In captivity, they may be separated from their families or forced to live in smaller, less stimulating social groups. This social isolation can lead to stress, depression, and other behavioral problems that can impact their health.
- Exposure to Diseases: Captive elephants can be more susceptible to certain diseases, such as tuberculosis and herpesvirus, which can be fatal.
Comparing Wild and Captive Environments
The table below highlights the key differences between the lives of African elephants in the wild and in captivity:
| Factor | Wild | Captivity |
|---|---|---|
| Lifespan | 60-70 years | 30-40 years |
| Diet | Diverse, including plants, fruits, bark | Limited, often consisting of hay, fruits, vegetables |
| Space | Vast savannas and forests | Restricted enclosures |
| Social Groups | Large, complex herds | Smaller, less stimulating groups |
| Exercise | Constant roaming and foraging | Limited movement |
Ethical Considerations
The significant difference in African elephant lifespan in captivity raises ethical concerns about keeping these intelligent and social animals in zoos. It is crucial for zoos and other captive facilities to prioritize the welfare of their elephants by providing them with spacious enclosures, enriching environments, and opportunities for social interaction.
Conservation Efforts and the Future
While the challenges facing African elephants in captivity are undeniable, there is hope for the future. Many zoos and conservation organizations are working to improve the lives of captive elephants by creating larger, more natural enclosures and implementing enrichment programs. Additionally, there is a growing focus on in-situ conservation efforts aimed at protecting elephant populations in their natural habitats.
Conclusion
The African elephant lifespan in captivity is a complex issue with ethical and conservation implications. While zoos can play a role in educating the public and supporting conservation efforts, it is essential to ensure that the welfare of these magnificent creatures is always paramount. By understanding the challenges faced by captive elephants and supporting efforts to improve their lives, we can work towards a future where all African elephants, whether in the wild or in captivity, can thrive.
FAQ
-
Why do African elephants live longer in the wild?
In the wild, elephants have access to vast spaces, a natural diet, and complex social structures that contribute to their physical and mental well-being. -
What can zoos do to improve the lives of captive elephants?
Zoos can provide larger enclosures, enrichment programs, and opportunities for social interaction to better mimic the conditions elephants experience in the wild. -
How can I help protect African elephants?
You can support organizations working on elephant conservation, educate yourself and others about the issues facing elephants, and advocate for responsible tourism practices. -
Is it ethical to keep elephants in captivity?
This is a complex question with no easy answer. It’s important to consider the individual needs of each animal and ensure their welfare is prioritized. -
What is the future for African elephants in captivity?
The future of African elephants in captivity depends on the commitment of zoos and conservation organizations to prioritize their well-being and support efforts to protect wild populations.
Need More Information?
For further information on African elephants and conservation efforts, please visit our website or contact us:
Phone: +255768904061
Email: kaka.mag@gmail.com
Address: Mbarali DC Mawindi, Kangaga, Tanzania
We have a 24/7 customer service team available to assist you.