Understanding the African Elephant Range
The African Elephant Range has seen significant changes over the centuries, shaped by both natural factors and human impact. This article delves into the complexities of where these magnificent creatures roam, exploring the challenges they face and the conservation efforts underway to secure their future. We’ll explore the geographical distribution of African elephants, examining the factors influencing their range and the ongoing efforts to protect these iconic animals.
The African elephant, the largest land mammal on Earth, occupies a vast but shrinking territory across the African continent. Understanding the dynamics of the African elephant range is crucial for effective conservation strategies. Factors such as habitat loss, human-wildlife conflict, and the illegal ivory trade have all contributed to the decline in elephant populations and their range contraction. Yet, pockets of resilience exist, highlighting the importance of continued conservation efforts. Let’s delve deeper into the intricacies of the African elephant range and the ongoing battle to protect these majestic creatures. For a visual representation of this, check out the African elephant range map.
Factors Influencing African Elephant Range
Historically, African elephants roamed across much of the continent. However, their range has been drastically reduced due to several key factors. Habitat loss, driven by expanding human settlements, agriculture, and infrastructure development, is a primary threat. As human populations grow and land gets converted for other uses, elephants lose crucial foraging grounds and migratory routes. This often leads to increased human-wildlife conflict as elephants venture closer to human settlements in search of food and water.
Another significant factor impacting the African elephant range is poaching for ivory. Despite international bans, the illegal ivory trade continues to threaten elephant populations across Africa. This criminal activity not only decimates elephant herds but also disrupts their social structures and long-term survival. Climate change, with its associated droughts and altered rainfall patterns, also plays a role, impacting water availability and vegetation, essential resources for elephant survival.
The Impact of Human-Wildlife Conflict
As elephant habitats shrink, interactions between elephants and humans become increasingly frequent and often lead to conflict. Crop raiding by elephants, while essential for their survival, can devastate local farmers’ livelihoods. Similarly, elephants can pose a threat to human safety when they venture into villages or towns. Addressing these complex issues requires innovative solutions that both protect elephants and support the needs of local communities.
 African Elephant Habitat Loss Due to Human Encroachment
African Elephant Habitat Loss Due to Human Encroachment
Conservation Efforts and Their Impact on the African Elephant Range
Numerous organizations and governments are working tirelessly to protect African elephants and their shrinking range. These efforts include establishing protected areas, strengthening anti-poaching patrols, and working with local communities to develop sustainable solutions to human-wildlife conflict. Community-based conservation programs empower local people to become stewards of their natural resources, fostering a sense of ownership and responsibility for elephant conservation.
Investing in research and monitoring is also crucial. Understanding elephant movement patterns, population dynamics, and the impact of environmental changes helps to inform effective conservation strategies. Collaborative efforts between governments, NGOs, and local communities are essential for achieving long-term success in securing the future of African elephants. See how the elephants are distributed across Africa with this African elephant distribution map.
The Role of Technology in Elephant Conservation
Technological advancements are playing an increasingly important role in elephant conservation. GPS tracking collars allow researchers to monitor elephant movements, providing valuable insights into their behavior and habitat use. Drone technology is also being employed for anti-poaching patrols, covering vast areas more efficiently than traditional methods. These innovations, combined with on-the-ground efforts, offer hope for the future of African elephants.
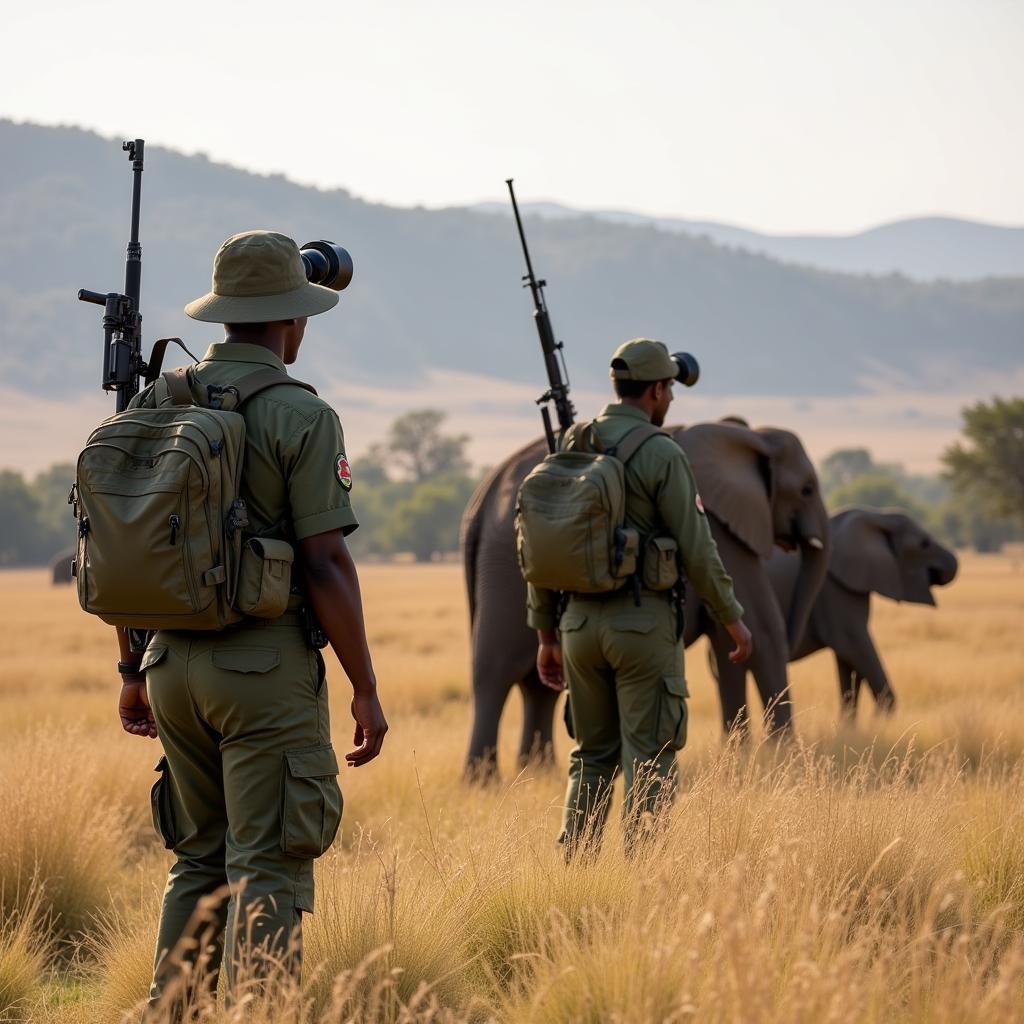 Rangers Patrolling and Protecting African Elephants
Rangers Patrolling and Protecting African Elephants
The Future of the African Elephant Range
The future of the African elephant range depends on continued and strengthened conservation efforts. Addressing the root causes of habitat loss, combating poaching, and mitigating human-wildlife conflict are crucial for securing the long-term survival of these magnificent animals. Supporting community-based conservation initiatives and investing in research and innovation are essential for ensuring that future generations can continue to marvel at the presence of African elephants in the wild. Explore the range specifically for the African bush elephant range to understand the nuances between the different species. Perhaps you’d like to look at an African giraffe sculpture or browse our extensive African animals list A-Z.
Conclusion
The African elephant range, while facing significant pressures, remains a testament to the resilience of these incredible animals. By understanding the complexities of their distribution and the threats they face, we can work together to ensure their survival for generations to come. The African elephant range is not just a geographical area; it is a symbol of our commitment to preserving biodiversity and the wonders of the natural world.
FAQs
- What countries do African elephants live in? African elephants are found in a number of countries across sub-Saharan Africa.
- What is the biggest threat to African elephants? Habitat loss and poaching are the biggest threats.
- How many African elephants are left in the wild? Estimates suggest around 400,000.
- What is being done to protect African elephants? Conservation efforts include anti-poaching patrols and habitat preservation.
- How can I help protect African elephants? Supporting conservation organizations and spreading awareness are great ways to help.
- What is the difference between African bush elephants and African forest elephants? Bush elephants are larger and live in savannas, while forest elephants are smaller and inhabit forests.
- What do African elephants eat? They are herbivores, consuming grasses, leaves, bark, and fruits.
Other questions you might have:
- How does climate change affect African elephant populations?
- What are the social structures of elephant herds?
- How do elephants communicate with each other?
Further reading:
You can find more information about African wildlife on our website, including articles on:
- The impact of tourism on elephant conservation
- The role of local communities in protecting elephants
- The latest research on elephant behavior and ecology
Need support? Contact us 24/7:
Phone: +255768904061
Email: [email protected]
Address: Mbarali DC Mawindi, Kangaga, Tanzania.