African Elephant vs Indian Elephant Tusks: Unveiling the Differences
The majestic elephants of Africa and Asia, despite sharing the title of gentle giants, harbor distinct characteristics, especially when it comes to their tusks. The query “African elephant vs Indian elephant tusks” often arises, highlighting a point of fascination for many. Let’s delve into the captivating world of these ivory appendages, uncovering the evolutionary secrets and visual cues that set them apart.
Tusks: More Than Just Ivory
Before dissecting the differences, it’s essential to understand the significance of tusks in an elephant’s life. These elongated incisor teeth are more than just striking ornaments; they are tools for survival. Elephants employ these ivory extensions for a range of tasks, from digging for water and stripping bark to battling rivals and defending themselves.
The African Advantage: Size and Shape
The most noticeable difference between African and Indian elephant tusks lies in their size and shape. African elephants, both male and female, boast larger, more prominently curved tusks. These ivory swords can reach astonishing lengths, with the record-breaking tusk measuring over 10 feet long!
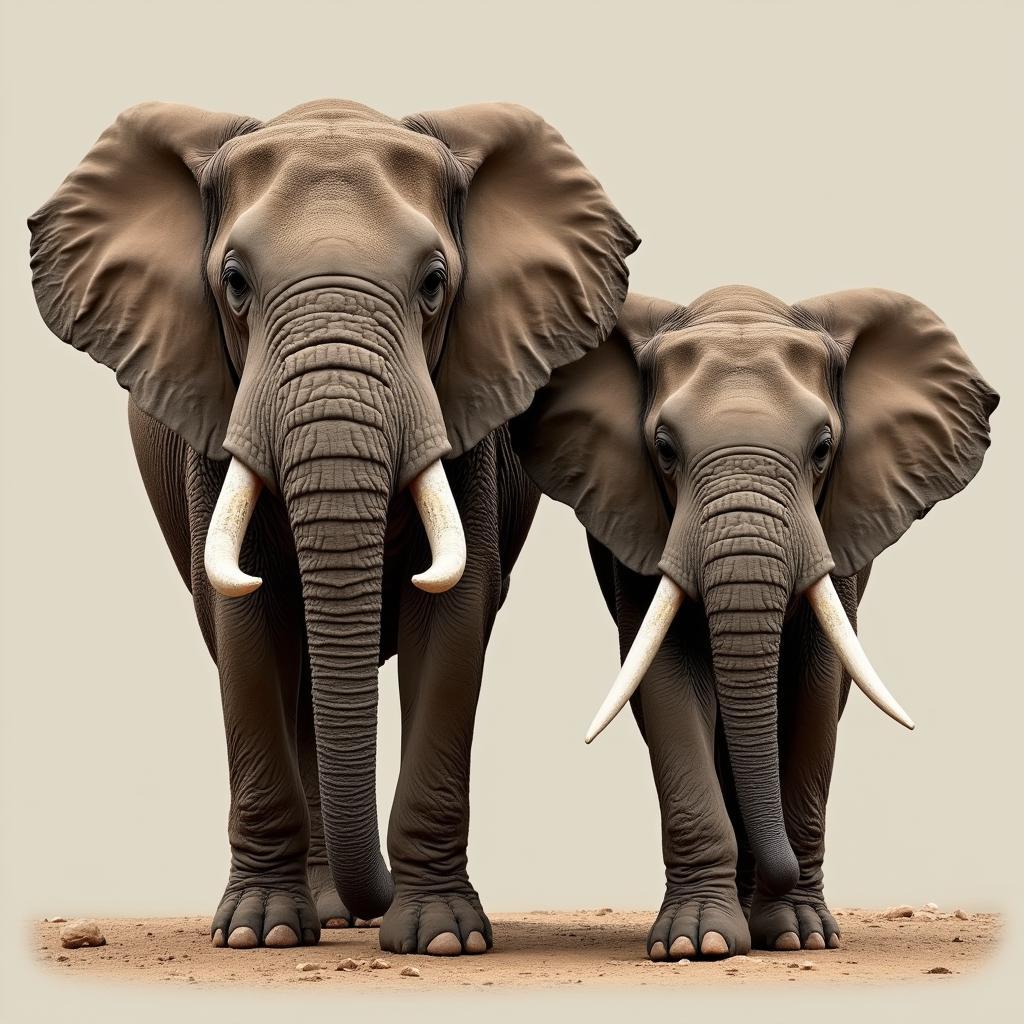 Male and Female African Elephants with Tusks
Male and Female African Elephants with Tusks
Indian Elephants: A Subtler Display
In contrast, Indian elephants exhibit a more subdued tusk presence. Generally, only male Indian elephants develop prominent tusks, while females possess smaller, barely visible tusks called “tushes.” Moreover, their tusks are shorter and straighter, lacking the dramatic curve seen in their African counterparts.
Evolutionary Tales Etched in Ivory
Why do these differences exist? The answer lies in the distinct evolutionary pressures faced by these elephants in their respective habitats. The African savanna, with its open grasslands and fierce competition, favored the evolution of larger, more formidable tusks for defense and resource acquisition.
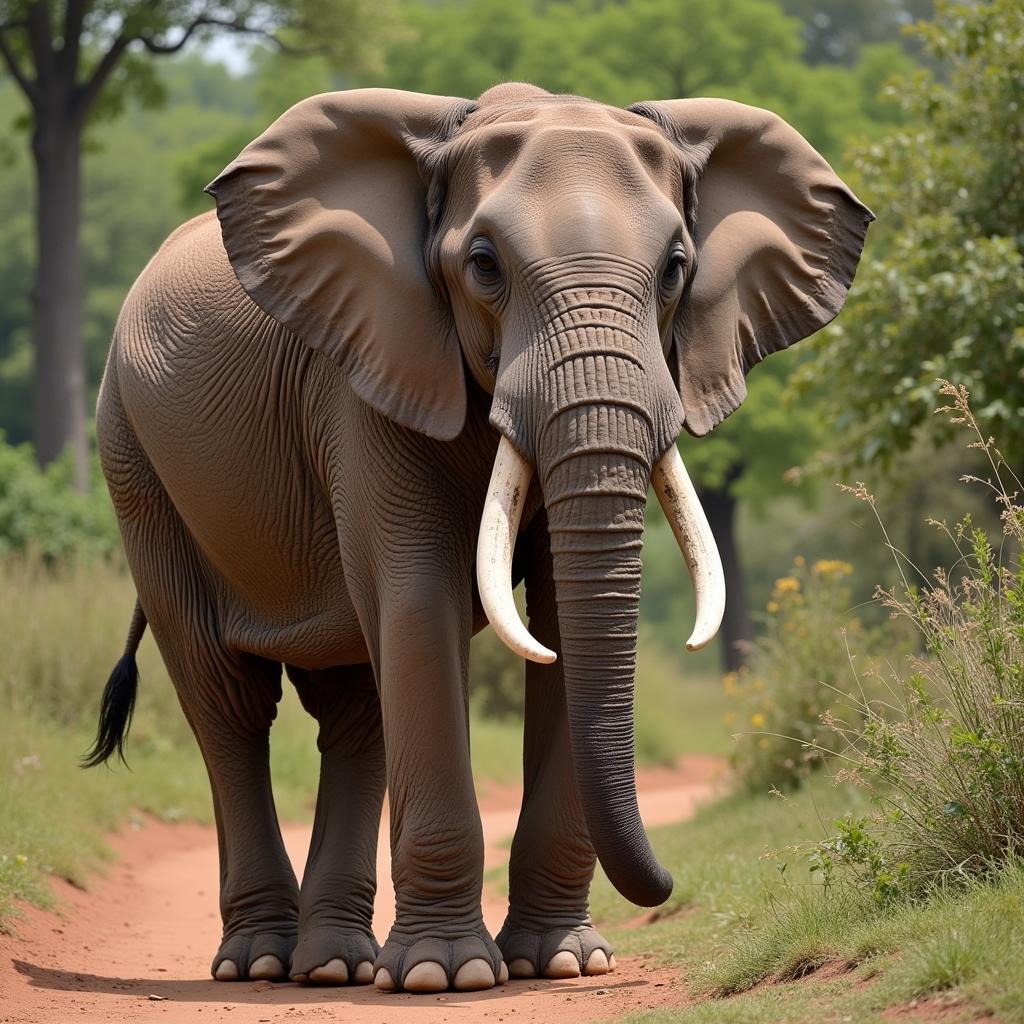 Indian Elephant with Tusks
Indian Elephant with Tusks
Meanwhile, the dense forests of India presented different challenges, demanding more agility and maneuverability. Smaller, straighter tusks proved more advantageous in these environments, allowing Indian elephants to navigate through thick vegetation with ease.
Beyond the Surface: Internal Structure and Composition
While the external differences are readily apparent, African and Indian elephant tusks also exhibit subtle variations in their internal structure and composition. These differences, though less obvious to the naked eye, contribute to the unique characteristics of each type of ivory.
Conservation Concerns: Protecting the Giants
Tragically, the beauty and allure of elephant tusks have fueled a cruel and unsustainable ivory trade, pushing these magnificent creatures toward the brink of extinction. Understanding the differences between African and Indian elephant tusks is not just an academic pursuit; it plays a crucial role in combating poaching and promoting conservation efforts.
By recognizing the unique features of each type of ivory, authorities can better identify the origin of illegal ivory, track poaching hotspots, and implement targeted measures to protect these gentle giants for generations to come.