African Forest Elephant Population: A Conservation Crisis
The African Forest Elephant Population, a vital component of the continent’s biodiversity, faces a dire situation. These gentle giants, smaller than their savanna counterparts, play a crucial role in maintaining the health of Central African forests. However, habitat loss, human-wildlife conflict, and the persistent threat of poaching have driven their numbers to critically low levels.
Understanding the Forest Elephant’s Plight
Unlike the iconic savanna elephants that roam the vast African plains, forest elephants are uniquely adapted to dense rainforest habitats. Their smaller size and straighter tusks allow them to navigate the undergrowth, while their specialized diet of fruits, leaves, and bark makes them crucial seed dispersers, shaping the forest ecosystem.
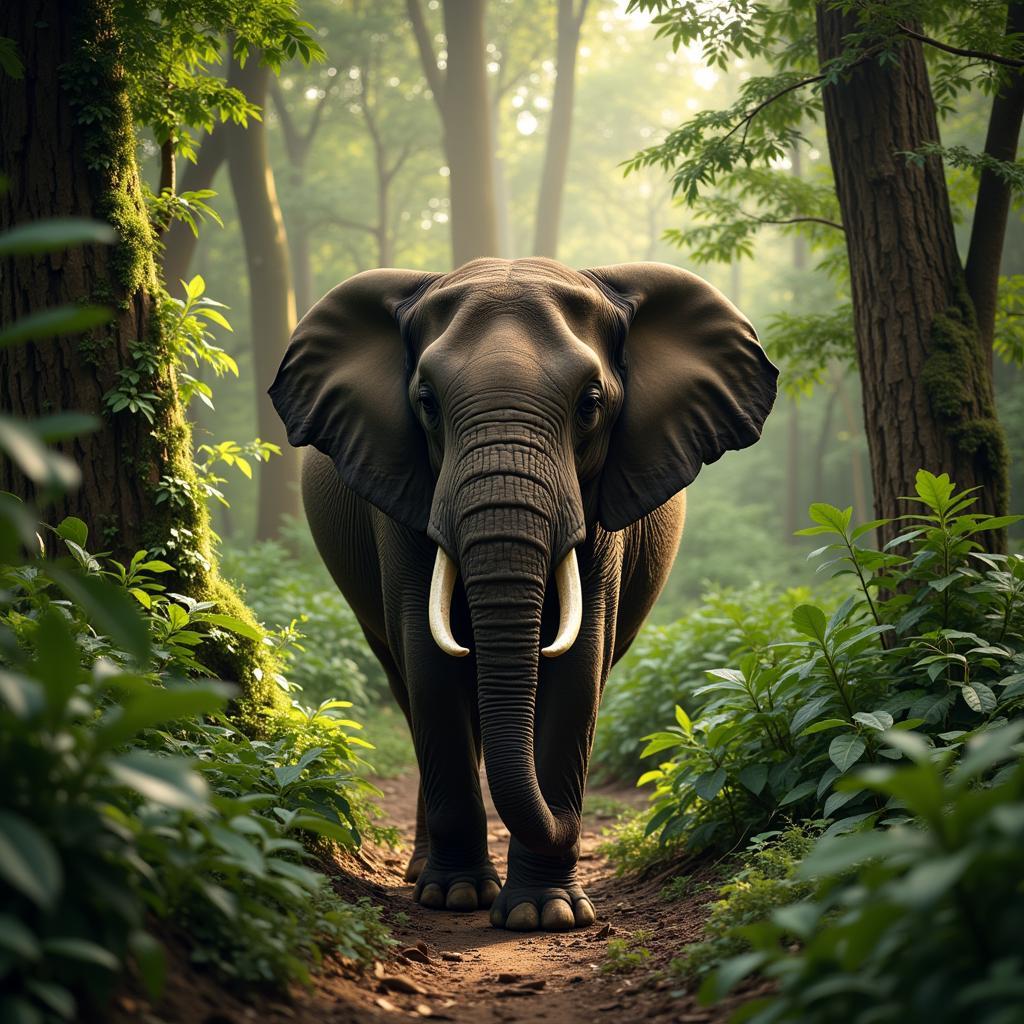 African Forest Elephant Navigating Dense Rainforest
African Forest Elephant Navigating Dense Rainforest
However, these magnificent creatures are facing an unprecedented crisis. Decades of deforestation, driven by logging, mining, and agricultural expansion, have fragmented their habitat, isolating populations and making them more vulnerable to threats. This habitat loss also increases the likelihood of human-elephant conflict as elephants are pushed closer to human settlements in search of food and resources.
Poaching: A Dire Threat to Survival
While habitat loss poses a significant threat, poaching for ivory remains the most immediate danger to African forest elephant populations. The illegal wildlife trade, fueled by demand for ivory, has decimated elephant numbers across Africa, and forest elephants are particularly susceptible due to their slow reproductive rates and the remoteness of their habitat.
The ivory trade not only robs us of these intelligent and social animals but also has devastating ecological consequences. Forest elephants are considered keystone species, meaning their presence is crucial for the survival of numerous other plant and animal species. Their loss can trigger a cascade of negative impacts throughout the ecosystem.
Conservation Efforts and the Future of Forest Elephants
Despite the challenges, there is hope for the African forest elephant. Dedicated individuals, organizations, and governments are working tirelessly to protect these animals and their habitat. Anti-poaching patrols, community conservation initiatives, and efforts to curb the illegal ivory trade are all playing a role in safeguarding their future.
Conservation efforts also focus on mitigating human-elephant conflict through measures like establishing wildlife corridors, promoting sustainable land-use practices, and educating communities about elephant behavior and importance. By addressing both the immediate threats and the underlying drivers of decline, we can ensure a future where African forest elephants continue to thrive in their rainforest homes.
Conclusion
The plight of the African forest elephant is a stark reminder of the interconnectedness of our planet’s ecosystems and the urgent need for conservation action. Protecting these magnificent creatures requires a multifaceted approach that addresses habitat loss, combats poaching, and promotes human-wildlife coexistence. By working together, we can ensure that future generations have the opportunity to marvel at the wonder of African forest elephants in the wild.