The Majestic African Forest Elephant: Guardian of the Tropical Rainforest
The African forest elephant, a denizen of the dense tropical rainforests of Central Africa, plays a vital role in maintaining the health and biodiversity of these complex ecosystems. Often overshadowed by their larger savanna cousins, these elephants are uniquely adapted to their forested homes.
A World Within the Trees: The African Forest Elephant’s Habitat
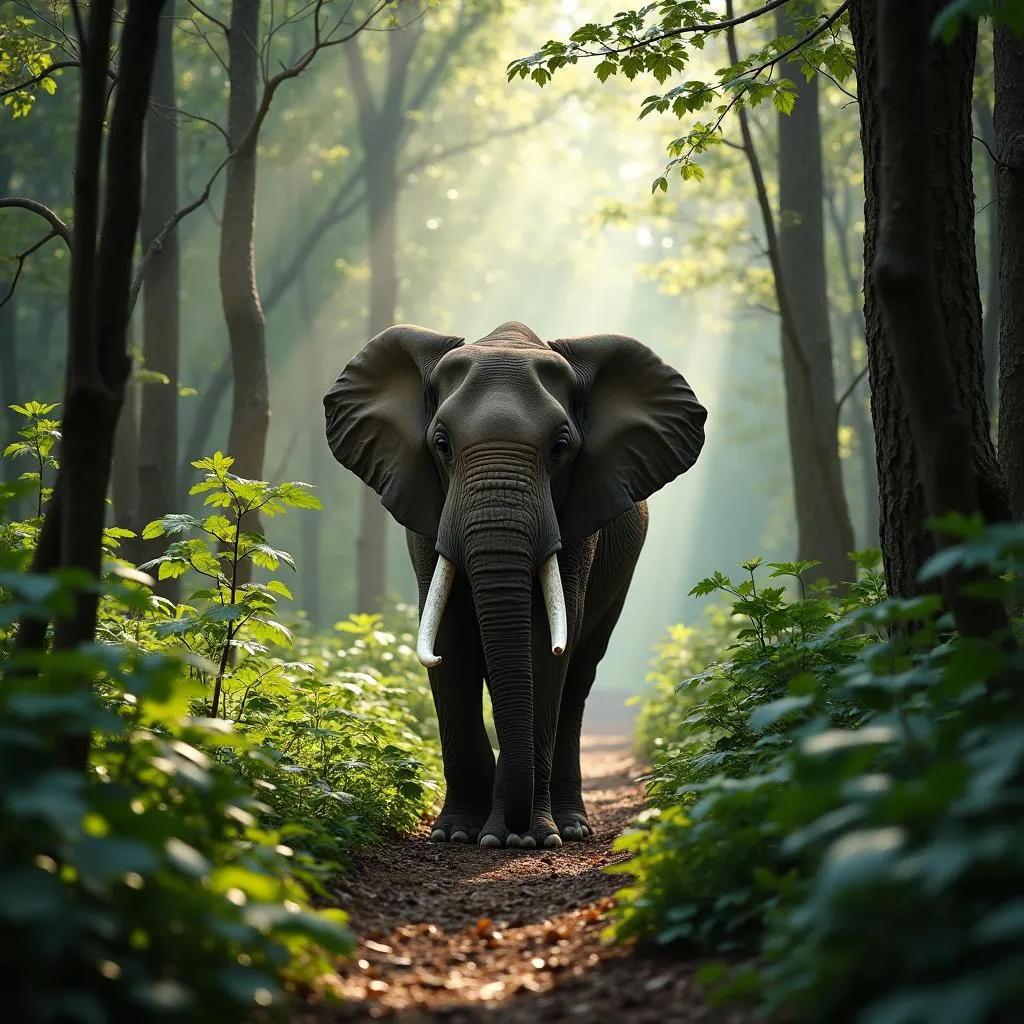 African Forest Elephant in Rainforest Habitat
African Forest Elephant in Rainforest Habitat
Imagine a world of towering trees, their canopies forming a thick emerald ceiling above the forest floor. This is the domain of the African forest elephant. These elephants are found in the tropical rainforests of countries like Gabon, the Democratic Republic of Congo, and Cameroon. These forests are characterized by high rainfall, humidity, and an incredible diversity of plant and animal life. Unlike the open savannas, the rainforest presents a world of limited visibility and a maze of dense vegetation.
Navigating a Green Labyrinth: Adaptations for Forest Life
African forest elephants are smaller than their savanna counterparts, with straighter tusks and rounded ears. These adaptations are crucial for navigating the dense rainforest undergrowth. Their smaller size allows them to move more easily through the tightly packed trees, while their straighter tusks are perfect for clearing paths and digging for food. Their rounded ears, unlike the large fan-shaped ears of savanna elephants, are less prone to snagging on branches.
Architects of the Ecosystem: The Forest Elephant’s Impact
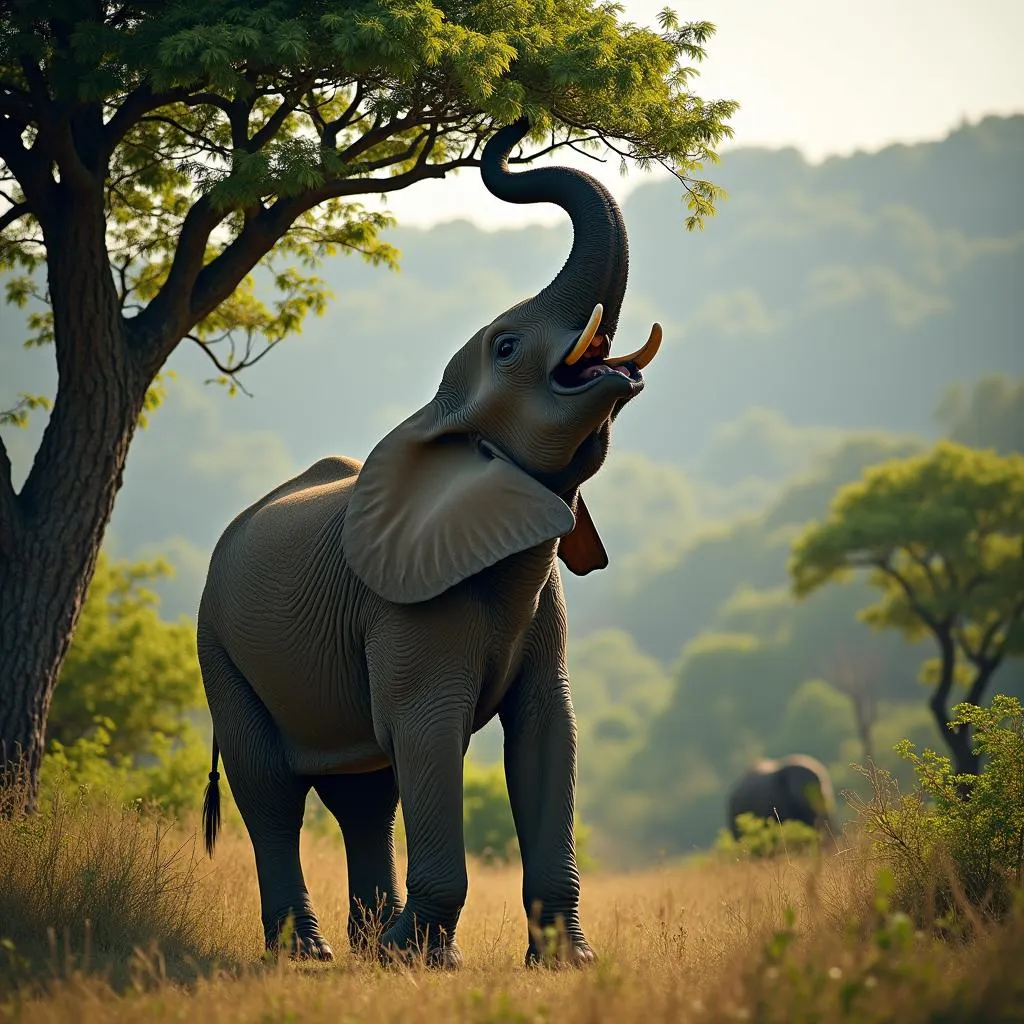 African Forest Elephant Feeding on Fruit
African Forest Elephant Feeding on Fruit
African forest elephants are true ecosystem engineers. Their feeding habits, which include stripping bark from trees, digging for roots and minerals, and consuming large amounts of fruit, play a crucial role in shaping the forest structure. By creating clearings in the dense undergrowth, they open up the forest floor to sunlight, fostering the growth of new plants and creating habitats for other animals. Their dung, rich in nutrients and often containing undigested seeds, acts as a natural fertilizer and seed disperser, contributing to the incredible biodiversity of these forests.
Seed Dispersal Superstars: The African Fruit Tree Connection
African forest elephants have a particularly important relationship with African fruit trees. Many rainforest tree species rely heavily on these elephants to disperse their seeds. The elephants consume large quantities of fruit, and the seeds pass through their digestive system unharmed. As they travel, they deposit these seeds across the forest floor in their dung, effectively planting the next generation of trees.
Threats to a Gentle Giant: Protecting the Forest Elephant
Unfortunately, these gentle giants are facing a growing number of threats. Poaching for their ivory remains a significant problem, and habitat loss due to deforestation for agriculture, logging, and mining is fragmenting their populations. This fragmentation isolates elephant groups, disrupting their social structures and genetic diversity.
Conservation Efforts: A Glimmer of Hope
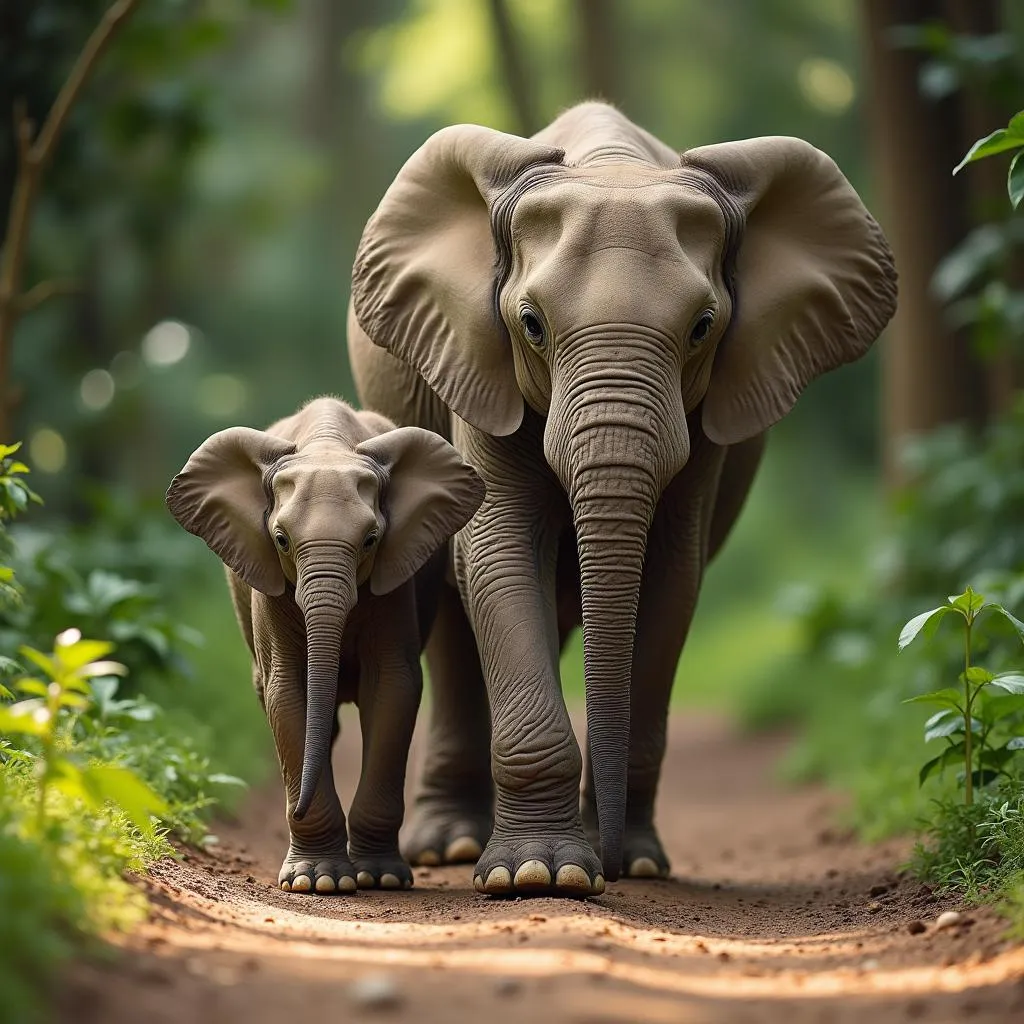 African Forest Elephant Calf with its Mother
African Forest Elephant Calf with its Mother
Despite these challenges, there is hope for the African forest elephant. Conservation organizations are working tirelessly to protect these animals and their habitat. Anti-poaching patrols, community-based conservation initiatives, and the creation of protected areas are all playing a part in safeguarding the future of these magnificent creatures.
The Future of the Rainforest: Why We Need Forest Elephants
Protecting African forest elephants is not just about saving a single species; it is about preserving the health and integrity of entire ecosystems. These elephants are keystone species, playing a vital role in maintaining the balance of the rainforest. By protecting them, we are protecting the incredible biodiversity of these forests and ensuring the well-being of countless other species that depend on them.