Exploring the Heart of Africa: Unveiling the Beauty and Diversity of African Forests
The African continent evokes images of vast savannas teeming with wildlife, but beyond these iconic landscapes lies a world of lush and diverse forests. These forests, often referred to as the “lungs of Africa,” are not only crucial for the planet’s health but also hold immense cultural, ecological, and economic significance. From the dense rainforests of the Congo Basin to the ancient woodlands of the Atlas Mountains, African forests are a testament to the continent’s rich biodiversity and natural heritage.
A Tapestry of Life: Unveiling the Diversity of African Forests
African forests are far from monolithic, encompassing a wide range of ecosystems, each with its unique characteristics and inhabitants. The Congo Basin, home to the second-largest rainforest on Earth, boasts an astonishing array of plant and animal life, including gorillas, forest elephants, and okapi.
Further north, the Guinean Forests of West Africa are known for their high levels of endemism, meaning that many species found there exist nowhere else on the planet. These forests are also home to chimpanzees, pygmy hippos, and a variety of primates.
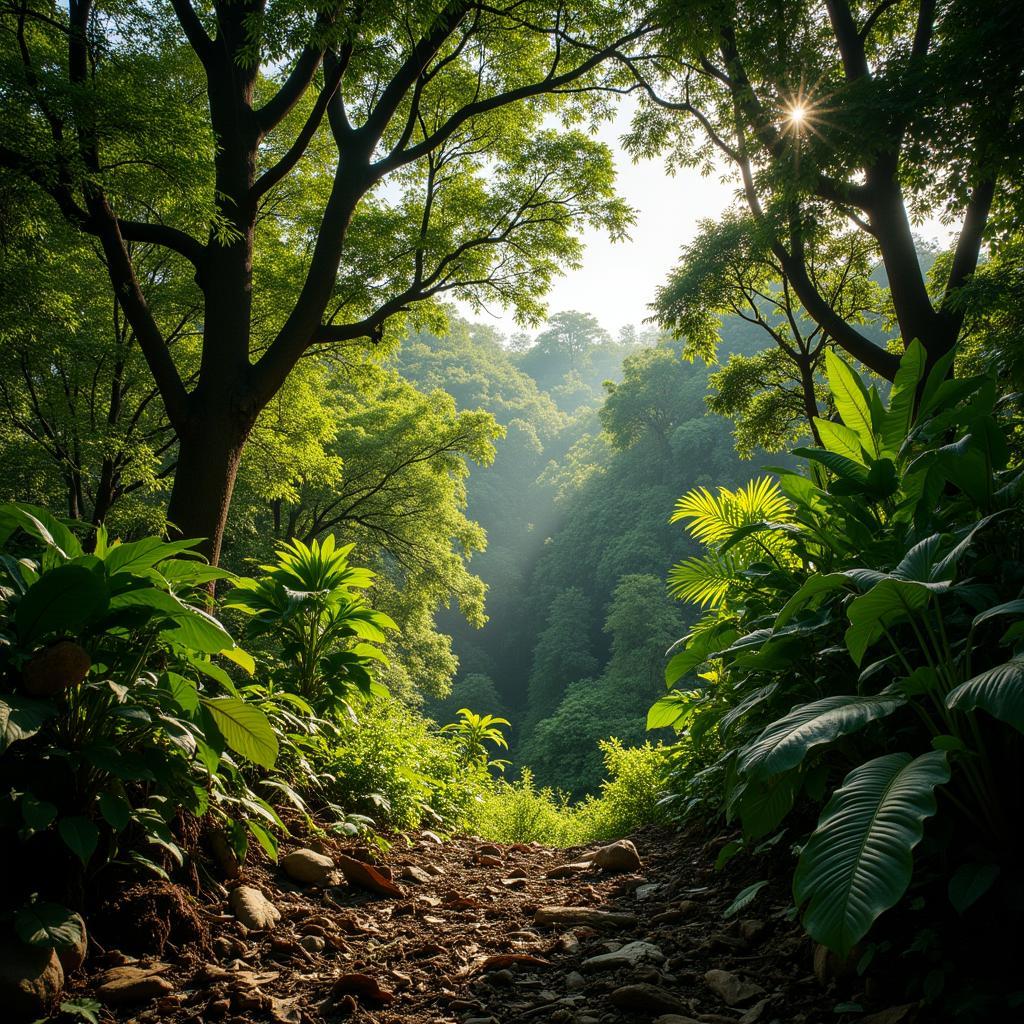 Guinean Forest Canopy
Guinean Forest Canopy
Along the eastern coast of the continent, the Eastern Afromontane forests, stretching from Ethiopia to South Africa, are characterized by their high altitude and unique plant life, including ancient cycads and tree ferns. These forests provide vital water resources and are home to a variety of endemic birds and mammals.
Guardians of Culture and Tradition: The Cultural Significance of African Forests
For centuries, African forests have been intricately woven into the cultural fabric of the continent. They are often revered as sacred spaces, home to spirits and ancestors. Traditional beliefs and practices are closely tied to the natural world, with forests providing sustenance, medicine, and materials for building and crafting.
Many communities living in and around forests have developed sustainable practices that allow them to benefit from the forest’s resources without causing harm. For example, the practice of agroforestry, where trees are integrated into farming systems, promotes biodiversity and helps to maintain soil fertility.
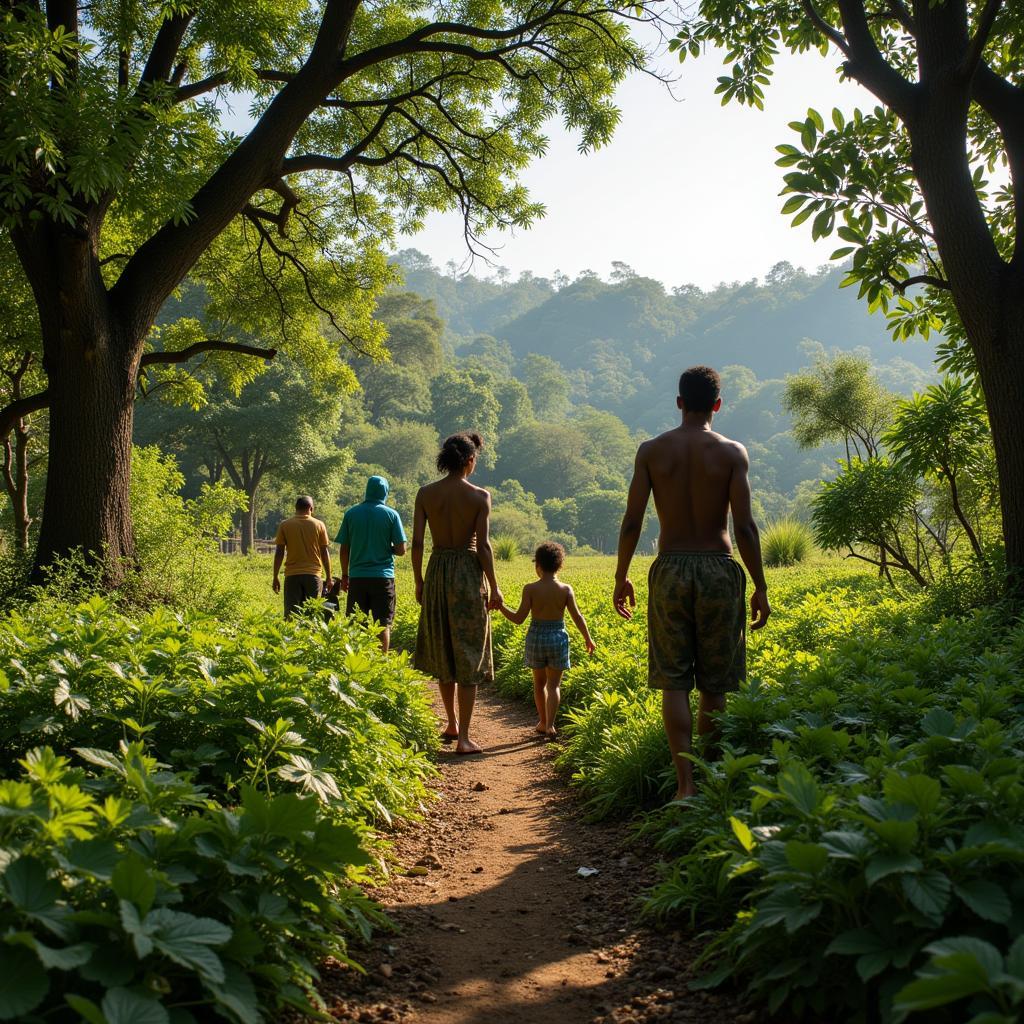 African Forest Community
African Forest Community
Facing the Future: The Challenges and Opportunities of Conserving African Forests
Despite their ecological and cultural importance, African forests face numerous threats, including deforestation, habitat loss, and climate change. The demand for timber, land for agriculture, and resources such as minerals and oil is putting increasing pressure on these fragile ecosystems.
However, there is hope. Across the continent, individuals, communities, and governments are working to protect and restore forests. Initiatives such as community forestry, sustainable forest management, and ecotourism are proving to be effective in promoting conservation and providing economic opportunities for local communities.
By recognizing the immense value of African forests and working together to address the threats they face, we can ensure that these vital ecosystems continue to thrive for generations to come.