The Fascinating Life of Man in the African Forest
The African forest is a vibrant and diverse ecosystem, home to a wealth of plant and animal life, including a fascinating array of human communities. For centuries, people have thrived in these forests, adapting to the unique challenges and opportunities presented by this environment. This article delves into the rich tapestry of life for those who call the African forest home, exploring their unique traditions, cultural practices, and remarkable resilience.
A World of Rich Biodiversity
The African forest is a vast and intricate landscape, encompassing a range of ecological zones from dense rainforests to savanna woodlands. This diversity is mirrored in the human communities that inhabit these areas, with a wide variety of cultures, languages, and livelihoods. The forest provides sustenance, shelter, and spiritual connection for these communities, shaping their daily lives and traditions.
The Importance of Sustainability
The African forest is a treasure trove of resources, including valuable timber, medicinal plants, and wild animals. However, sustainable use is essential for preserving this fragile ecosystem and ensuring the well-being of its inhabitants. Indigenous communities have developed intricate systems of forest management, respecting the delicate balance of nature. They understand the importance of using resources wisely, ensuring their availability for future generations.
“The forest is our home, our provider, and our teacher. We must respect its rhythms and protect its secrets for generations to come,” says Chief Nyama, a renowned elder from the Baka community in the Congo Basin.
The Art and Rituals of Forest Dwellers
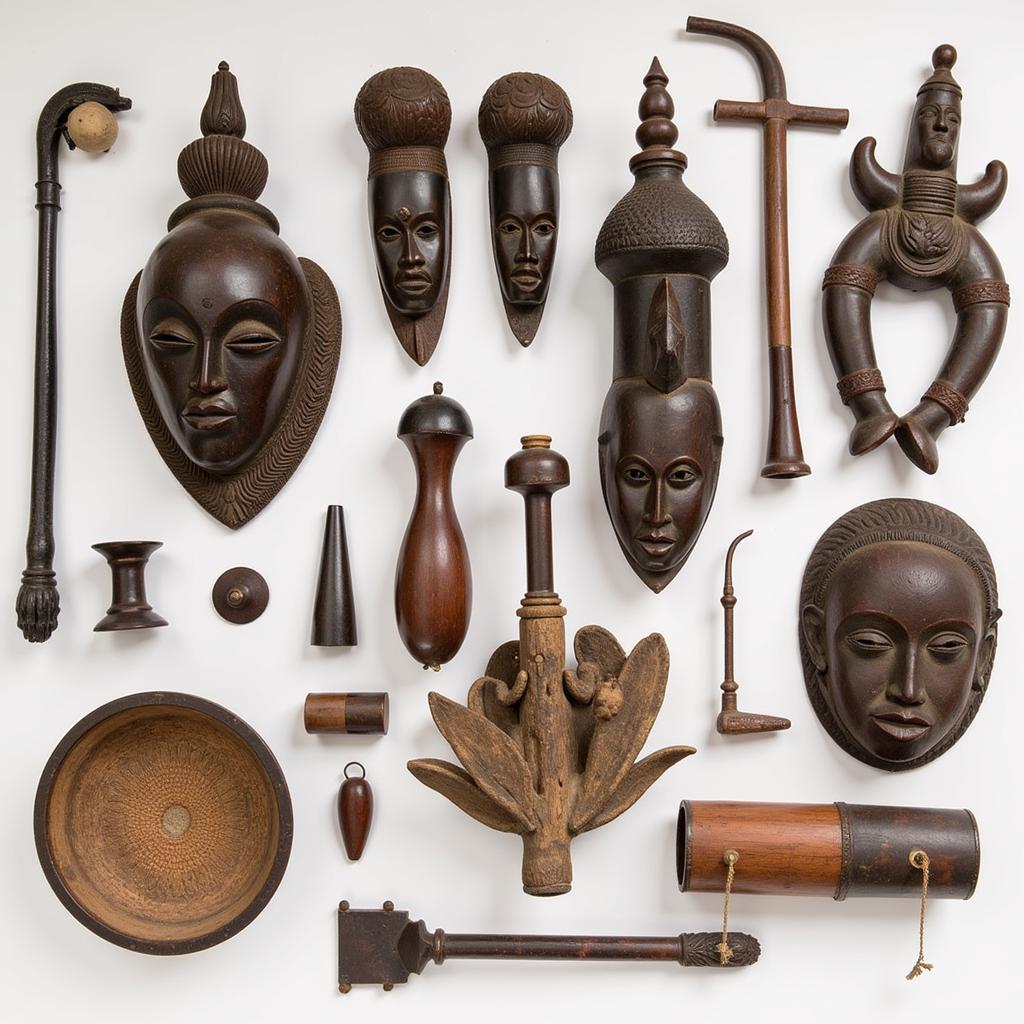
The African forest is a source of inspiration for art, music, and spirituality. Indigenous communities have developed unique forms of artistic expression, often using natural materials found in their surroundings. The intricate carvings, colorful masks, and evocative songs reflect their deep connection to the forest. These artistic traditions are not just expressions of beauty, but also serve as channels for communication, storytelling, and the preservation of their cultural heritage.
The Challenges of Modernity
Despite their deep connection to the forest, indigenous communities face challenges in the modern world. Deforestation, climate change, and the encroachment of commercial interests threaten their livelihoods and their traditional way of life. Many face displacement, poverty, and the loss of their cultural identity. However, they continue to fight for their rights and to protect the forest that sustains them.
The Power of Community
Despite these challenges, indigenous communities are resilient and adaptable. They have a strong sense of community and mutual support, enabling them to navigate difficult times and preserve their cultural heritage. Their traditional knowledge systems, passed down through generations, provide valuable insights into sustainable living, medicine, and forest management.
The Role of Conservation
Conservation efforts are increasingly focused on empowering indigenous communities to become stewards of their own lands. Community-based conservation initiatives are playing a vital role in protecting the forest, ensuring its continued health and the well-being of its inhabitants. These initiatives recognize the vital role that indigenous people play in safeguarding the environment.
The Future of Forest Communities
The future of African forest communities is intertwined with the fate of the forests themselves. Their well-being depends on preserving these vital ecosystems, while ensuring the rights and well-being of their inhabitants. By understanding their unique traditions, knowledge, and resilience, we can work together to create a future where the African forest continues to thrive, providing sustenance and cultural enrichment for generations to come.
FAQ
Q: What are some of the unique challenges faced by forest communities in Africa?
A: Forest communities face a variety of challenges, including deforestation, climate change, displacement from their lands, and the loss of their cultural heritage.
Q: How do indigenous communities contribute to forest conservation?
A: Indigenous communities have developed sustainable forest management practices and are actively involved in community-based conservation initiatives to protect their homelands.
Q: What are some examples of the art and rituals practiced by African forest communities?
A: They have a rich tradition of art, music, and ritual, often utilizing natural materials from the forest and expressing their deep connection to the natural world. Examples include elaborate carvings, colorful masks, and evocative songs.
Q: What role does community play in the lives of forest communities?
A: Forest communities have a strong sense of community, providing support, sharing resources, and preserving their cultural heritage.
Q: What is the importance of protecting the African forest for future generations?
A: The African forest is a vital ecosystem for biodiversity, climate regulation, and the livelihoods of indigenous communities. Protecting the forest ensures its continued health and the well-being of future generations.