African Free Trade Zone Members: A Continent United by Trade
The African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA) is a landmark achievement in the pursuit of intra-African trade and economic integration. This ambitious trade agreement brings together African Free Trade Zone Members with the goal of creating a single market for goods and services across the continent. With a market of over 1.3 billion people and a combined GDP of over $3.4 trillion, the AfCFTA has the potential to be a game-changer for Africa’s economic development.
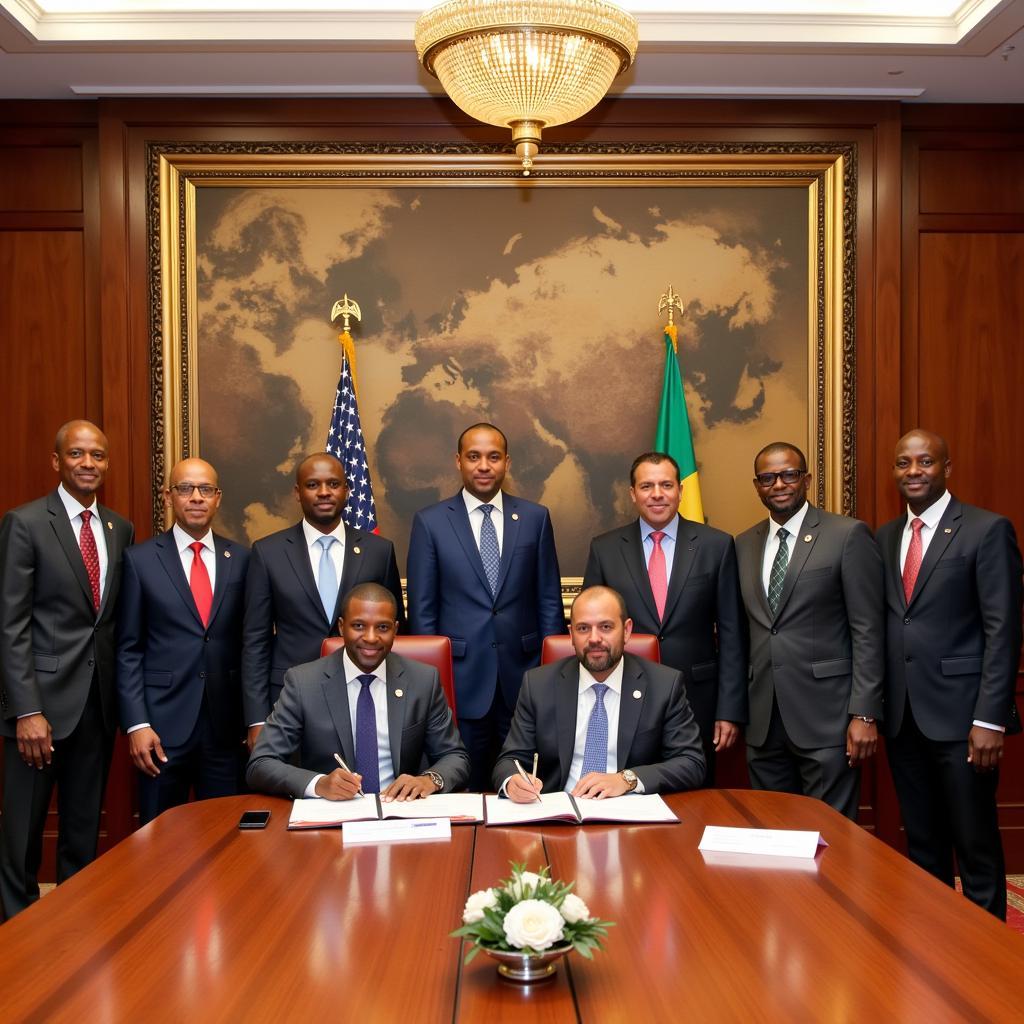 African leaders signing the AfCFTA agreement
African leaders signing the AfCFTA agreement
Understanding the African Free Trade Zone Members
The AfCFTA encompasses all 55 African Union member states, with Eritrea being the only exception as of 2023. The agreement aims to eliminate tariffs on 90% of goods traded between member countries, reduce non-tariff barriers, and create a more conducive environment for cross-border investment.
Key Objectives of the AfCFTA
The AfCFTA has several key objectives, including:
- Boosting intra-African trade: By eliminating tariffs and reducing non-tariff barriers, the AfCFTA aims to significantly increase trade among African countries.
- Promoting industrialization and value addition: The agreement encourages the development of regional value chains and promotes industrialization by fostering a more competitive business environment.
- Creating jobs and economic opportunities: Increased trade and investment are expected to create much-needed jobs and economic opportunities, particularly for Africa’s burgeoning youth population.
- Enhancing Africa’s competitiveness in the global market: By fostering a larger and more integrated market, the AfCFTA seeks to enhance Africa’s competitiveness in the global economy.
Benefits and Opportunities for African Free Trade Zone Members
The AfCFTA presents numerous benefits and opportunities for its member states:
- Increased market access: Businesses gain access to a much larger market of over 1.3 billion consumers, opening up new avenues for growth and expansion.
- Reduced trade costs: The elimination of tariffs and streamlining of customs procedures reduces the cost of doing business across borders.
- Enhanced investment attractiveness: The larger and more integrated market makes Africa a more attractive destination for foreign direct investment.
- Job creation and economic diversification: The AfCFTA is expected to create millions of jobs and foster economic diversification by promoting industrialization and value addition.
Challenges and the Road Ahead
While the AfCFTA holds immense promise, there are also challenges that need to be addressed:
- Infrastructure gaps: Inadequate infrastructure, such as roads, railways, and ports, can hinder the smooth flow of goods and services.
- Non-tariff barriers: Addressing non-tariff barriers, such as cumbersome customs procedures and bureaucratic regulations, is crucial for facilitating trade.
- Capacity constraints: Building the capacity of businesses and institutions to take advantage of the opportunities presented by the AfCFTA is essential.
Conclusion
The African Continental Free Trade Area marks a significant step towards a more integrated and prosperous Africa. By breaking down trade barriers and fostering closer economic cooperation, African free trade zone members are creating a brighter future for the continent and its people. The AfCFTA has the potential to unlock Africa’s economic potential and drive sustainable development for generations to come.
african economic community home page
FAQs
1. What is the current status of the AfCFTA?
The AfCFTA entered into force in 2019 and trading under the agreement commenced in January 2021. Implementation is ongoing, with member states working to address tariff reductions, non-tariff barriers, and other aspects of the agreement.
2. Which countries are not part of the AfCFTA?
As of 2023, Eritrea is the only African Union member state that has not yet signed the AfCFTA agreement.
3. What are the key sectors expected to benefit from the AfCFTA?
Several sectors are expected to benefit significantly from the AfCFTA, including agriculture, manufacturing, tourism, and services.
4. How will the AfCFTA impact small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs)?
The AfCFTA is expected to benefit SMEs by providing them with access to a larger market, reducing trade costs, and fostering greater competition.
5. What role can technology play in the success of the AfCFTA?
Technology can play a crucial role in facilitating trade, improving logistics, enhancing market information systems, and promoting financial inclusion.
Need Assistance?
Contact us at:
Phone Number: +255768904061
Email: kaka.mag@gmail.com
Address: Mbarali DC Mawindi, Kangaga, Tanzania.
We have a 24/7 customer support team ready to assist you.