African Grassland Shrubs: A Guide to These Hardy Plants
African Grassland Shrubs are a diverse group of plants that have adapted to survive the harsh conditions of the savannas and grasslands. These plants are an integral part of the African ecosystem, providing food and shelter for a wide range of animals. They are also a source of fascination for botanists and nature enthusiasts alike, showcasing a remarkable array of adaptations that allow them to thrive in this challenging environment.
This comprehensive guide explores the world of African grassland shrubs, delving into their unique characteristics, ecological importance, and some notable species.
Adapting to the African Grasslands: What Makes These Shrubs Unique?
African grassland shrubs face a unique set of challenges, from prolonged droughts to grazing herbivores and intense competition for resources. To survive, they have developed remarkable adaptations:
- Drought Tolerance: Many shrubs possess deep root systems that tap into underground water sources. Others have succulent leaves or stems that store water, allowing them to endure extended dry periods.
- Fire Resistance: Savannas are shaped by periodic fires. Some shrubs have thick bark that acts as insulation, while others sprout quickly after a fire, ensuring their survival.
- Defense Mechanisms: Thorns, spines, or bitter-tasting leaves are common defenses against hungry herbivores. Some shrubs even produce toxins that deter animals from browsing on them.
- Nutrient Efficiency: The soils of African grasslands can be nutrient-poor. These shrubs have adapted to thrive in these conditions, efficiently utilizing the limited nutrients available.
The Role of Shrubs in the Grassland Ecosystem
African grassland shrubs are far more than just plants; they are keystones of the ecosystem:
- Food Source: Shrubs provide a vital source of leaves, fruits, and seeds for a variety of herbivores, including giraffes, antelopes, and elephants.
- Shelter and Nesting: The dense foliage of shrubs offers crucial shelter from predators and the elements. Many bird species rely on shrubs for nesting sites.
- Soil Stabilization: Shrub roots help bind the soil, preventing erosion and promoting water retention, which benefits the entire ecosystem.
- Biodiversity Support: Shrubs contribute to the incredible biodiversity of African grasslands by creating microhabitats for insects, reptiles, and small mammals.
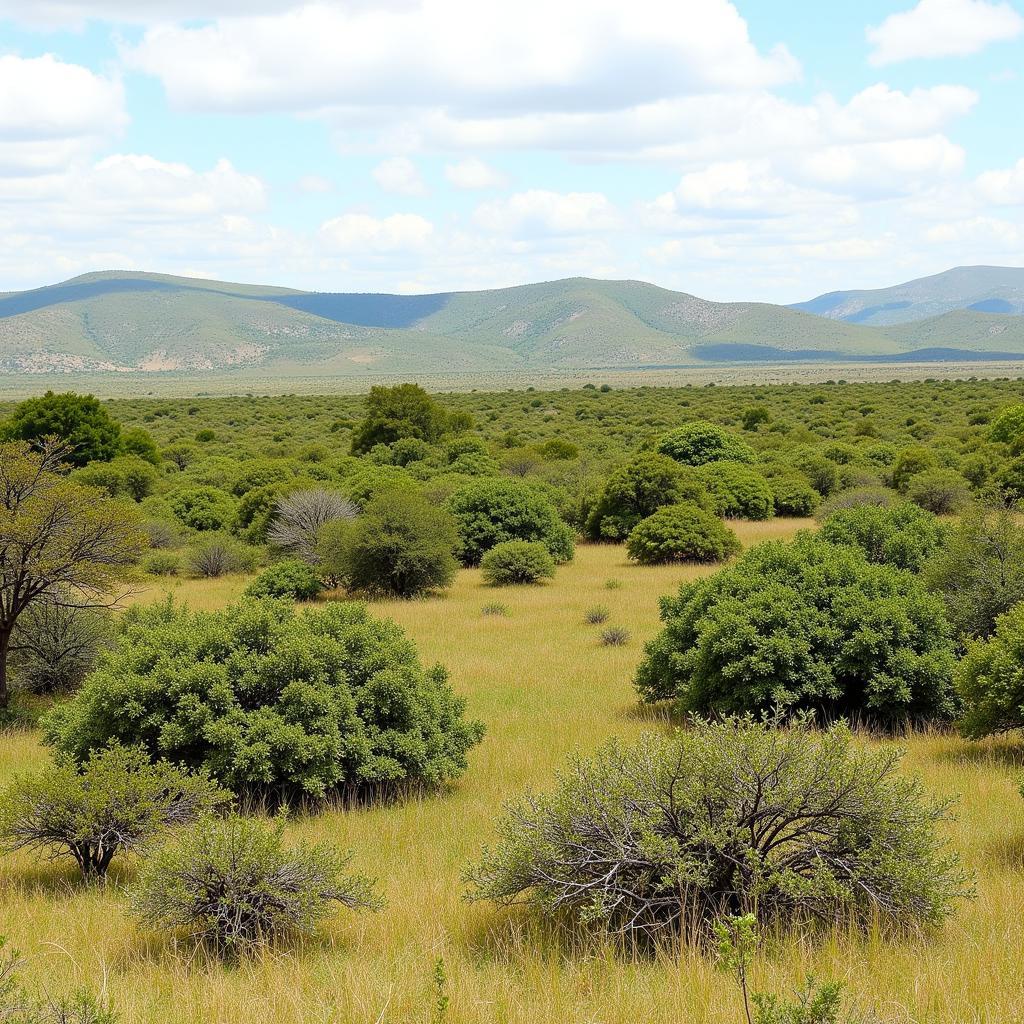 African Grassland Shrubs in Savanna
African Grassland Shrubs in Savanna
Exploring Notable African Grassland Shrubs
Acacia (Genus Acacia): Perhaps the most iconic of all African grassland shrubs, acacias are known for their umbrella-shaped canopies, thorns, and small, clustered flowers. They are a vital food source for many herbivores, and their gum is harvested for various uses. acacia african plants
Commiphora (Genus Commiphora): These shrubs and small trees are known for their fragrant resins, some of which are used in incense and perfumes (myrrh, for example). They often have peeling bark and twisted branches, adding to the unique beauty of the savanna.
Combretum (Genus Combretum): This genus is known for its diversity, encompassing a wide range of growth forms from small shrubs to large, climbing species. They produce distinctive fruits, often with four-winged structures, that are dispersed by the wind.
Grewia (Genus Grewia): Many Grewia species are important food sources for both people and animals. They produce small, berry-like fruits that are rich in vitamins and minerals. Some species are also used in traditional medicine.
Elephant Food (Elephantorrhiza elephantina): This shrub gets its name from its large, underground root system, which is a favorite food of elephants. It produces attractive, yellow flowers that attract a variety of pollinators.
The Future of African Grassland Shrubs
These remarkable plants face increasing pressures from habitat loss, climate change, and overgrazing. Conservation efforts are crucial to protect the biodiversity and ecological integrity of African grasslands. Sustainable land management practices, such as rotational grazing and controlled burning, can help ensure the survival of these vital plants for generations to come.
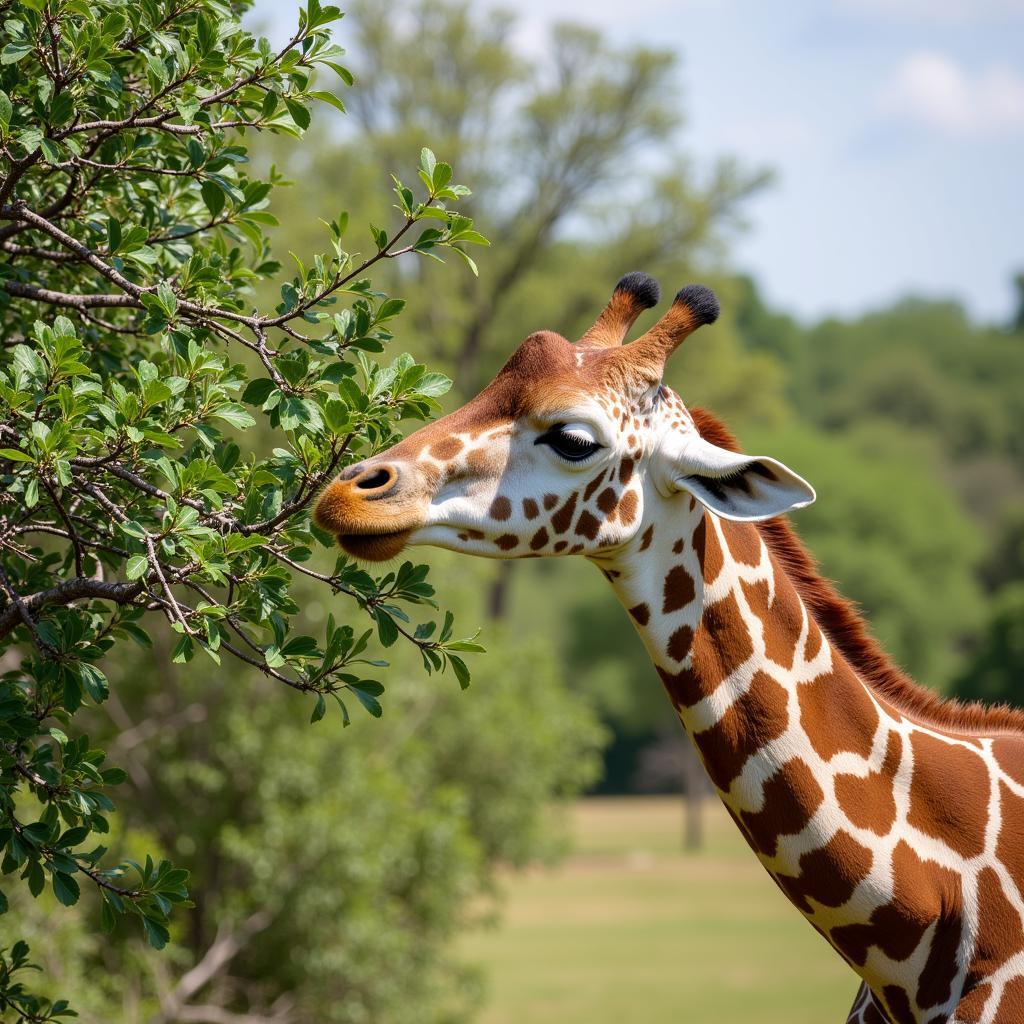 African Grassland Shrub and Giraffe
African Grassland Shrub and Giraffe
FAQs About African Grassland Shrubs
1. How do African grassland shrubs survive fires?
Many shrubs have adaptations like thick bark, underground root systems, or the ability to resprout quickly after a fire, ensuring their survival.
2. Why are thorns so common on African grassland shrubs?
Thorns are an effective defense mechanism against grazing herbivores, deterring them from consuming too much of the plant.
3. What is the ecological importance of African grassland shrubs?
They provide food and shelter for animals, stabilize the soil, contribute to biodiversity, and play a role in nutrient cycling.
4. Are any African grassland shrubs used by humans?
Yes, many species have medicinal uses, their fruits are edible, and some are used for fuel or construction materials.
5. How can I help conserve African grassland shrubs?
Supporting conservation organizations, promoting sustainable land management practices, and raising awareness about the importance of these ecosystems are all ways to contribute.
Delve Deeper into the African Savanna
- Discover the impressive african giraffe height and how it interacts with its environment.
- Learn about the resilient african wild ass and its adaptations for survival.
- Explore the african buffalo diet and its role in the grassland ecosystem.
- Uncover the secrets of african grassland shrubs thorny and their unique defenses.
Contact us at +255768904061, email us at kaka.mag@gmail.com, or visit us in Mbarali DC Mawindi, Kangaga, Tanzania for more information. Our team is available 24/7 to assist you.