African Heidelbergensis: A Journey Through Early Human Evolution in Africa
The study of human evolution is a fascinating journey that takes us deep into the past, exploring the origins of our species and the complex processes that shaped us. Among the key milestones in this journey is the discovery of Homo heidelbergensis, an ancient human species that inhabited Europe, Asia, and, importantly, Africa. This article delves into the intriguing world of African Homo heidelbergensis, exploring its significance in human evolution, its unique characteristics, and its potential impact on our understanding of early human history.
Unlocking the Secrets of African Heidelbergensis
African Homo heidelbergensis represents a pivotal stage in human evolution, bridging the gap between earlier hominins like Homo erectus and later archaic humans like Neanderthals and Denisovans. While European and Asian Homo heidelbergensis have been extensively studied, African Homo heidelbergensis remains shrouded in mystery, with limited fossil evidence and ongoing research efforts.
*The importance of studying African Homo heidelbergensis* lies in its potential to shed light on the evolutionary pathways that led to modern humans, particularly in Africa. This region is considered the cradle of humankind, and uncovering the details of Homo heidelbergensis* presence in Africa could offer valuable insights into the early stages of our own species’ development.
Distinctive Features of African Heidelbergensis
While the fossil record of African Homo heidelbergensis is limited, several key features distinguish this species from other early hominins:
- Larger Brain Size: Compared to their predecessors, Homo heidelbergensis in Africa possessed larger brain capacities, indicating advanced cognitive abilities.
- Sophisticated Tool Use: Evidence suggests that African Homo heidelbergensis used a diverse range of tools, including hand axes and spears, for hunting and other tasks.
- Potential for Symbolic Thought: While the evidence is still debated, there are hints that African Homo heidelbergensis might have possessed some form of symbolic thinking, perhaps through rudimentary art or other forms of expression.
These characteristics suggest that African Homo heidelbergensis was a complex and adaptable species, capable of navigating challenging environments and employing sophisticated technologies.
What is the Evidence for African Heidelbergensis?
The evidence for African Homo heidelbergensis is sparse and fragmented. This is partly due to the challenging nature of fossil preservation in Africa’s diverse environments. Some key sites that have yielded evidence of African Homo heidelbergensis include:
- Bodo, Ethiopia: This site revealed a partial skull dating back to 600,000 years ago, showcasing a large braincase and distinctive features.
- Kabwe, Zambia: The Kabwe cranium, discovered in 1921, is another significant find, dating back to around 300,000 years ago. This skull exhibits a combination of primitive and advanced features, contributing to the ongoing debate about the classification of African Homo heidelbergensis.
These limited discoveries highlight the need for continued exploration and research in Africa to uncover more evidence of African Homo heidelbergensis and its significance in human evolution.
African Heidelbergensis and the Human Lineage
The exact relationship between African Homo heidelbergensis and our own species, Homo sapiens, is a complex and debated topic. Some scientists suggest that Homo heidelbergensis was a direct ancestor of Homo sapiens, while others view it as a sister species, diverging from the human lineage around 500,000 years ago.
The discovery of Homo naledi in South Africa, a species with a combination of primitive and modern traits, further complicates the picture, adding another layer of complexity to the early human family tree.
“The study of African Homo heidelbergensis is like piecing together a complex puzzle,” says Professor Dr. Njeri Kuria, a renowned paleoanthropologist at the University of Nairobi. “Every new discovery provides more pieces, but we’re still working to understand the full picture.”
The African Heidelbergensis Enigma
The mystery of African Homo heidelbergensis extends beyond its evolutionary connection to our species. Researchers are also trying to unravel its cultural practices and behavior. Did they use fire for cooking and warmth? Did they have complex social structures? Did they engage in symbolic behavior?
These questions remain unanswered, but each new discovery brings us closer to understanding the intricacies of this fascinating ancient human species.
Looking Forward: Uncovering the Hidden History
The study of African Homo heidelbergensis is an ongoing journey of discovery. As researchers continue to explore Africa’s rich paleontological landscape, we can expect to uncover more clues about this pivotal species, shedding light on its evolution, behavior, and impact on the human lineage.
Future research efforts will focus on:
- Expanding the Fossil Record: Discoveries of new fossils in Africa will be crucial for a more complete understanding of African Homo heidelbergensis.
- Advanced Dating Techniques: Using advanced dating methods will allow researchers to refine the timeline of African Homo heidelbergensis and its interactions with other hominin species.
- Archaeological Investigations: Detailed analyses of stone tools, remains of campsites, and other archaeological evidence will provide insights into the cultural practices and behavior of African Homo heidelbergensis.
These endeavors will help us unravel the mysteries of this fascinating chapter in human history and gain a deeper understanding of our own evolutionary journey.
FAQs
Q1: When did African Homo heidelbergensis exist?
African Homo heidelbergensis is thought to have lived between 600,000 and 300,000 years ago.
Q2: What are the most significant fossil discoveries of African Homo heidelbergensis?
The Bodo skull in Ethiopia and the Kabwe cranium in Zambia are among the most significant fossil discoveries of African Homo heidelbergensis.
Q3: How did African Homo heidelbergensis compare to other hominins?
African Homo heidelbergensis exhibited larger brain sizes, more advanced tool use, and potentially symbolic thought compared to earlier hominins like Homo erectus.
Q4: What is the relationship between African Homo heidelbergensis and Homo sapiens?
The exact relationship between African Homo heidelbergensis and our species is still being debated. It could be an ancestor or a sister species.
Q5: What are some key areas of research for future studies of African Homo heidelbergensis?
Expanding the fossil record, refining dating techniques, and conducting archaeological investigations are crucial areas of research for future studies of African Homo heidelbergensis.
Q6: What is the importance of studying African Homo heidelbergensis?
Studying African Homo heidelbergensis helps us understand the evolutionary pathways that led to modern humans and provides valuable insights into the early stages of human development in Africa.
Q7: How do you find out more about African Homo heidelbergensis?
Stay updated with the latest research and discoveries through scientific journals, documentaries, and educational websites dedicated to paleoanthropology and human evolution.
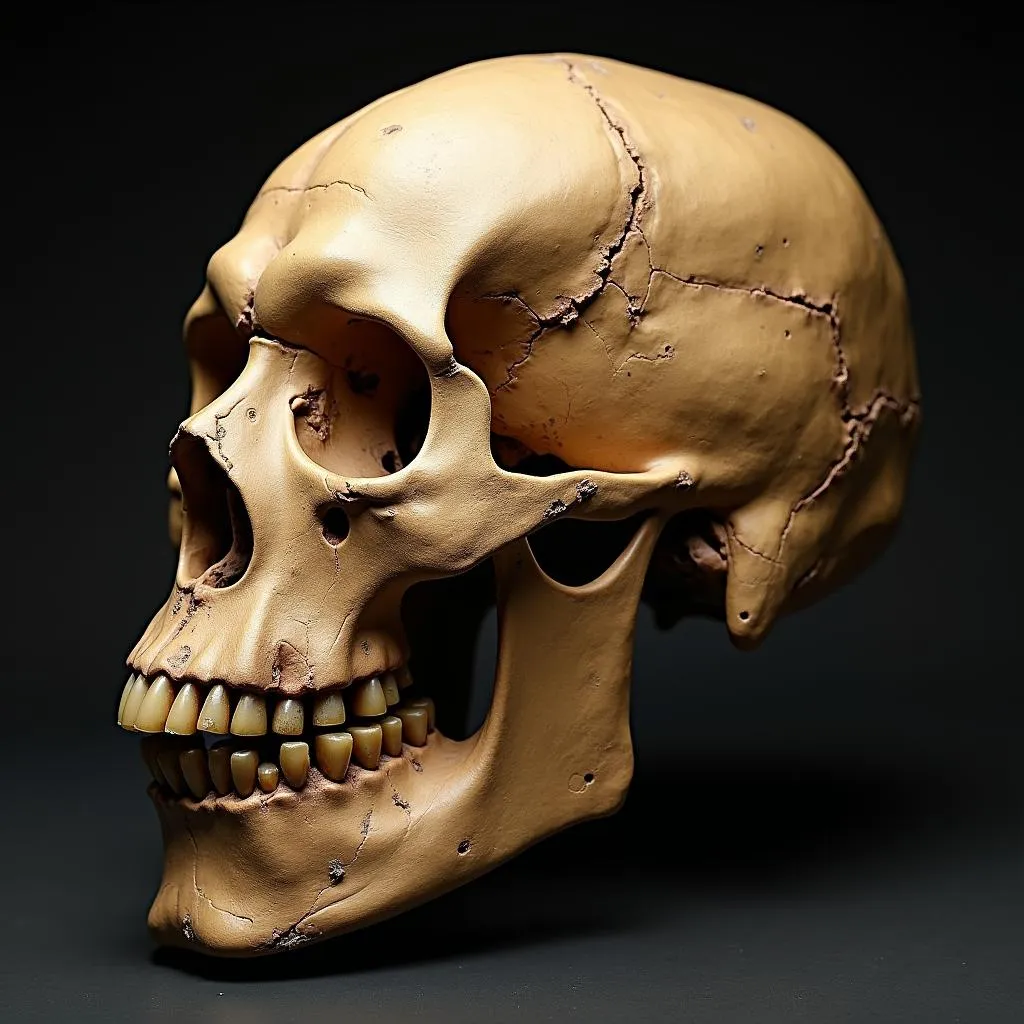 Bodo Skull, Ethiopia
Bodo Skull, Ethiopia
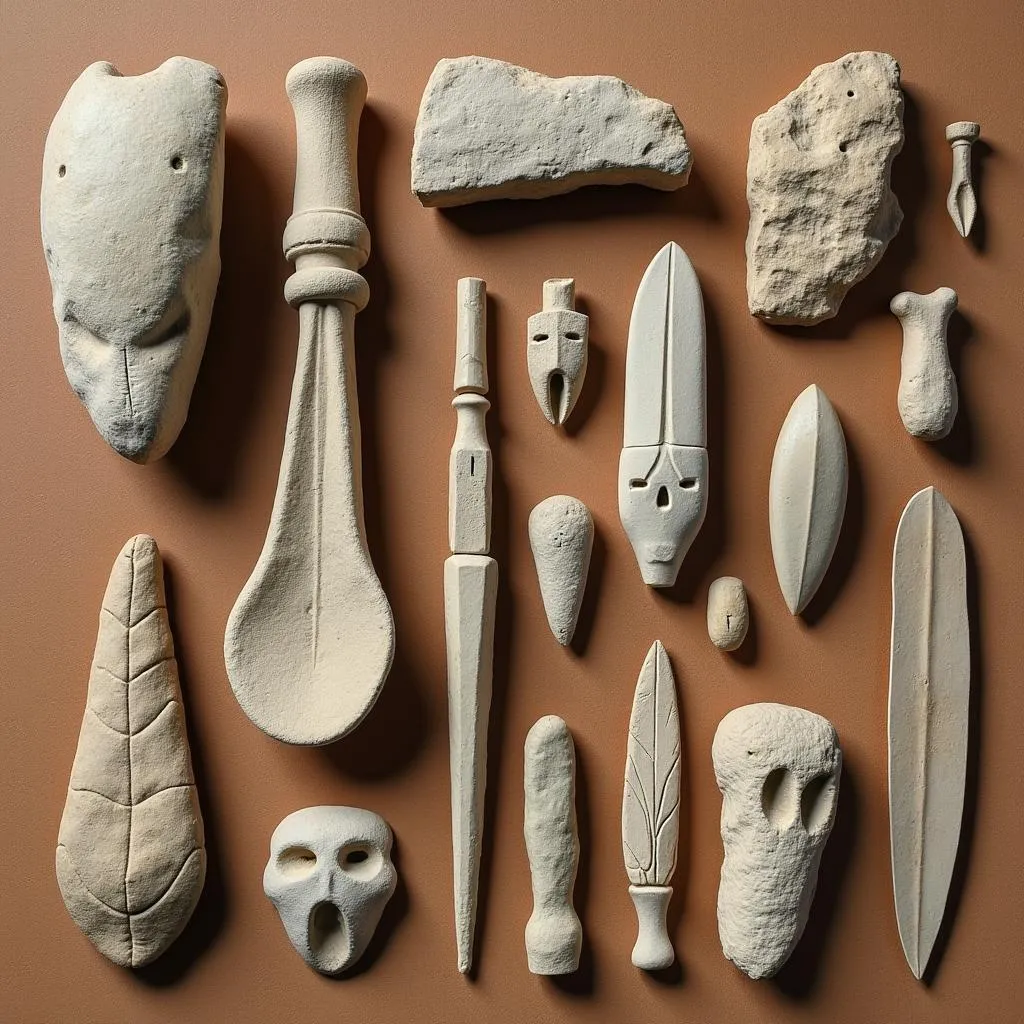 Stone Tools from Kabwe, Zambia
Stone Tools from Kabwe, Zambia
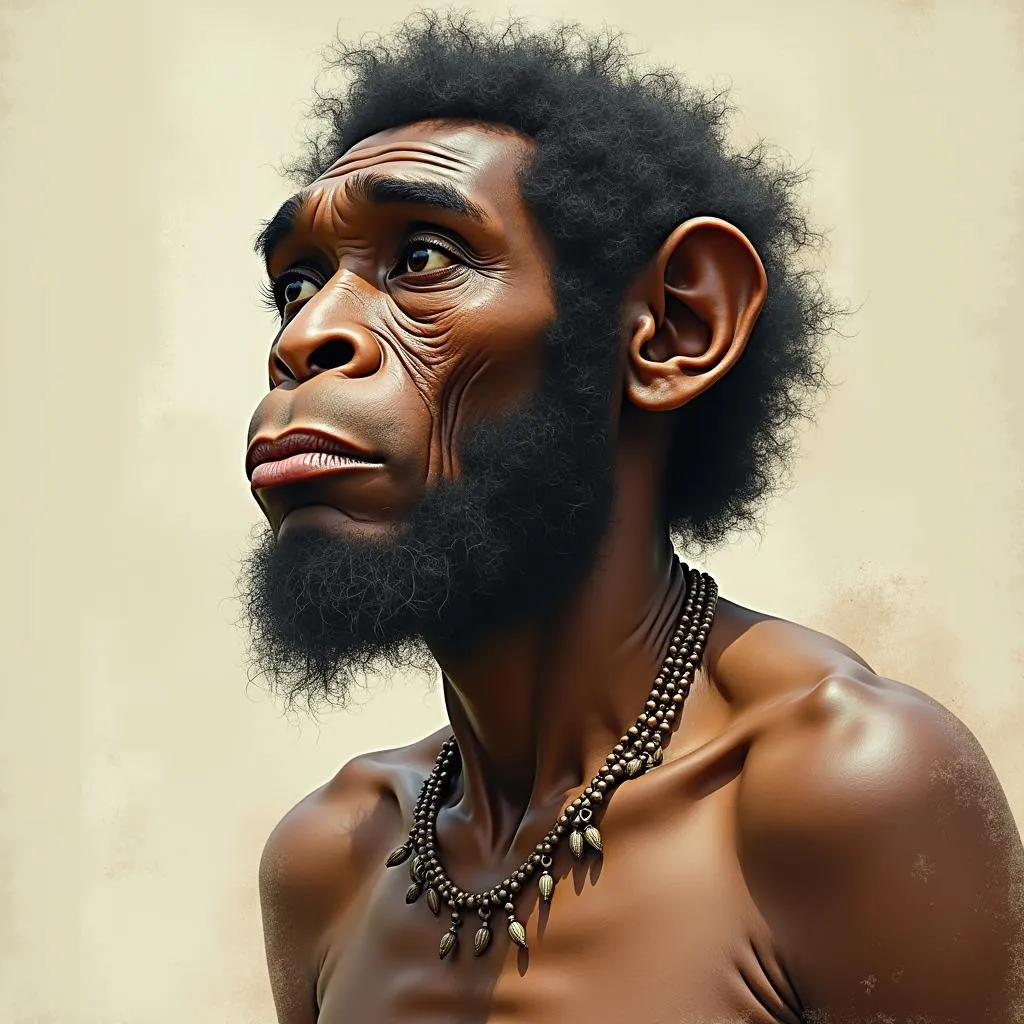 Reconstruction of African Homo heidelbergensis
Reconstruction of African Homo heidelbergensis
The study of African Homo heidelbergensis is a captivating and ongoing endeavor, offering valuable insights into the evolution of our species and the complex tapestry of human history. By continuing to explore the depths of Africa’s paleontological heritage, we can unlock more secrets about this enigmatic species and gain a deeper appreciation for our shared ancestry.