African Hemorrhagic Fever: Understanding a Deadly Disease
African Hemorrhagic Fever is a serious and often deadly disease that affects people and animals in various parts of Africa. This viral illness, known for its rapid progression and high fatality rates, can cause severe bleeding, organ failure, and shock. It is crucial to understand the causes, symptoms, prevention, and treatment of this disease to protect individuals and communities in endemic areas.
What is African Hemorrhagic Fever?
African hemorrhagic fever, also known as viral hemorrhagic fever, is a group of infectious diseases characterized by fever, bleeding, and multiple organ dysfunction. These diseases are caused by different viruses that are transmitted through contact with infected animals or humans. The most common types of hemorrhagic fever in Africa include Ebola virus disease, Marburg virus disease, and Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever.
Understanding the Different Types of African Hemorrhagic Fever
Each type of hemorrhagic fever is caused by a specific virus and has its own unique characteristics. Here’s a breakdown of the three most prevalent types in Africa:
- Ebola virus disease: Caused by the Ebola virus, it is highly contagious and has a high mortality rate. Transmission occurs through direct contact with infected bodily fluids or animals.
- Marburg virus disease: This disease, caused by the Marburg virus, is also highly contagious and has a high mortality rate. Transmission occurs through contact with infected bats or infected bodily fluids.
- Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever (CCHF): This disease is caused by the Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus and is transmitted through contact with infected ticks, animals, or human bodily fluids.
Symptoms of African Hemorrhagic Fever
The symptoms of African hemorrhagic fever vary depending on the specific virus involved. However, common symptoms include:
- High fever: A sudden onset of high fever is often the first sign of the disease.
- Headache: Severe headache is a common symptom across different hemorrhagic fevers.
- Muscle aches: Pain and tenderness in the muscles, particularly in the back and legs, are frequently reported.
- Fatigue: Extreme tiredness and weakness are common, making even simple tasks difficult.
- Nausea and vomiting: These symptoms often accompany the other signs of illness.
- Diarrhea: Loose stools can also occur.
- Rash: A rash may appear on the skin.
- Bleeding: This is a hallmark symptom of hemorrhagic fever and can manifest in various ways, including nosebleeds, gum bleeding, internal bleeding, and even blood in vomit or stool.
What to Do if You Suspect African Hemorrhagic Fever
It’s crucial to seek immediate medical attention if you experience any of these symptoms, especially if you have traveled to or lived in areas where hemorrhagic fevers are endemic. Early diagnosis and treatment can significantly improve the chances of survival.
Causes and Transmission of African Hemorrhagic Fever
African hemorrhagic fevers are caused by various viruses that primarily reside in animals, particularly wild animals like bats, rodents, and primates. Transmission occurs through contact with infected animals or their bodily fluids.
- Animal to Human Transmission: Humans can contract the virus through direct contact with infected animals, such as bats, monkeys, or rodents. This typically happens when people hunt, butcher, or handle infected animals.
- Human to Human Transmission: The viruses that cause hemorrhagic fevers can also be transmitted from person to person through direct contact with infected bodily fluids, such as blood, vomit, urine, feces, and saliva.
- Other Modes of Transmission: Transmission through contaminated needles, contaminated medical equipment, and contact with contaminated surfaces can also occur.
Risk Factors for African Hemorrhagic Fever
Individuals who are exposed to the viruses that cause hemorrhagic fever are at a higher risk of contracting the disease. Some of the key risk factors include:
- Living in or traveling to endemic areas: Areas of Africa where hemorrhagic fevers are common pose a greater risk of exposure.
- Working with animals: People who work with animals, particularly wild animals, are more likely to encounter the viruses.
- Healthcare workers: Medical professionals treating patients with hemorrhagic fever are at increased risk of contracting the disease.
- Contact with infected individuals: Close contact with individuals infected with hemorrhagic fever can facilitate transmission.
- Exposure to infected bodily fluids: Contact with contaminated blood, vomit, urine, or feces from infected individuals can lead to infection.
Prevention of African Hemorrhagic Fever
Several preventative measures can reduce the risk of contracting African hemorrhagic fever. These include:
- Avoid contact with wild animals: Don’t touch or handle wild animals, especially if they appear sick or injured.
- Practice good hygiene: Always wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water after handling animals, especially after cleaning up after animals or handling animal carcasses.
- Use protective gear: Wear protective clothing, including gloves and masks, when handling animals or working in areas with a high risk of exposure.
- Avoid contact with infected individuals: Avoid close contact with individuals who may be infected, especially those showing symptoms of hemorrhagic fever.
- Properly handle medical waste: Healthcare workers must carefully dispose of medical waste from patients with hemorrhagic fever to prevent contamination.
Treatment of African Hemorrhagic Fever
There is no specific cure for African hemorrhagic fever, but supportive treatment can significantly improve survival rates. Treatment involves addressing the symptoms and providing supportive care, such as:
- Fluid therapy: Replacing fluids and electrolytes lost through vomiting and diarrhea is crucial to prevent dehydration.
- Blood transfusion: Blood transfusions may be necessary to replenish blood volume in cases of severe bleeding.
- Antiviral medications: While there is no specific antiviral drug for all types of hemorrhagic fever, some medications may be helpful in certain cases.
- Symptom management: Pain relievers, anti-fever medications, and other treatments can help manage symptoms and improve patient comfort.
The Importance of Early Diagnosis and Treatment
Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for improving survival rates in hemorrhagic fever. Prompt medical attention and supportive care can significantly reduce the risk of complications and death.
Public Health Concerns: Outbreaks and Control
Outbreaks of African hemorrhagic fever are a serious public health concern, especially in endemic areas. Effective control measures are essential to prevent the spread of these deadly diseases.
- Surveillance and Monitoring: Continuous surveillance and monitoring of potential cases in endemic areas is crucial for detecting and responding to outbreaks.
- Rapid Response Teams: Trained medical professionals and public health specialists are essential for quickly responding to outbreaks, containing the spread, and providing effective treatment.
- Isolation and Quarantine: Isolating infected individuals and quarantining individuals who have been in contact with them are essential strategies to prevent further transmission.
- Public Awareness Campaigns: Educating the public about hemorrhagic fever, its symptoms, prevention measures, and treatment options is critical for reducing the risk of infection and facilitating early intervention.
“African Hemorrhagic Fever is a Serious Threat, But We Have the Tools to Fight It”
Dr. Amani Kabiru, Public Health Expert
“We must remember that African hemorrhagic fever is not just a medical concern, but a social and economic one. Outbreaks can have devastating impacts on communities, healthcare systems, and economies. We need to work together to raise awareness, strengthen public health infrastructure, and invest in research and development to combat this deadly disease.”
African Hemorrhagic Fever: A Complex Challenge, a Collective Responsibility
African hemorrhagic fever represents a significant health challenge for individuals, communities, and nations across the continent. Understanding the disease, implementing prevention strategies, and ensuring access to timely and effective treatment are essential steps in mitigating the threat of these deadly viruses. By combining global collaboration, scientific advancements, and robust public health interventions, we can work towards a future where the burden of hemorrhagic fever is significantly reduced.
FAQ:
Q: How can I protect myself from African hemorrhagic fever?
A: Practice good hygiene, avoid contact with wild animals, wear protective gear when working with animals, and avoid contact with infected individuals.
Q: What should I do if I develop symptoms of African hemorrhagic fever?
A: Seek immediate medical attention. Inform your doctor about any recent travel history or animal contact.
Q: Is there a vaccine for African hemorrhagic fever?
A: Vaccines are available for some types of hemorrhagic fever, such as yellow fever, but there is no vaccine currently available for all types, including Ebola, Marburg, and CCHF.
Q: What is the prognosis for African hemorrhagic fever?
A: Prognosis depends on the type of virus, the severity of symptoms, and the availability of supportive treatment. Early diagnosis and treatment significantly improve survival rates.
Q: What organizations are working to combat African hemorrhagic fever?
A: The World Health Organization (WHO), the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), and various national and international health organizations are actively involved in research, surveillance, and response efforts to combat African hemorrhagic fever.
Q: Can I get African hemorrhagic fever from a mosquito bite?
A: No, hemorrhagic fever is not transmitted by mosquitoes.
Q: What are some of the latest developments in research and treatment for African hemorrhagic fever?
A: Researchers are actively working on developing vaccines, antivirals, and other treatments for hemorrhagic fever.
Q: What are the social and economic impacts of African hemorrhagic fever outbreaks?
A: Outbreaks can lead to economic losses, disruption of trade, and healthcare system strain. They can also cause social instability and fear within communities.
Q: Where can I get more information about African hemorrhagic fever?
A: You can find additional information and resources from the World Health Organization (WHO), the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), and other reputable health organizations.
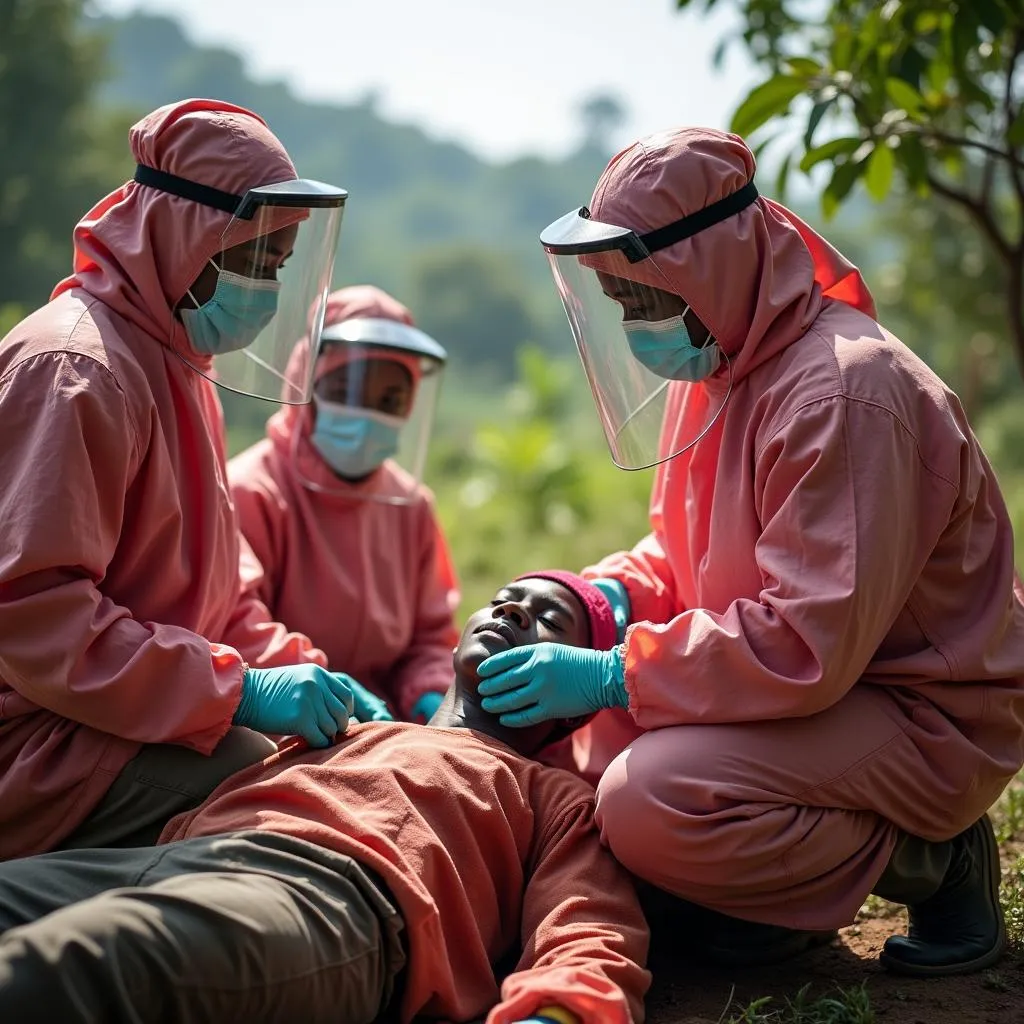 A medical team responds to an outbreak of African hemorrhagic fever in a remote village
A medical team responds to an outbreak of African hemorrhagic fever in a remote village
 A person washing their hands thoroughly with soap and water
A person washing their hands thoroughly with soap and water
 Scientists working in a laboratory on research related to African hemorrhagic fever
Scientists working in a laboratory on research related to African hemorrhagic fever
For further information, please contact us via phone at +255768904061, email at kaka.mag@gmail.com or visit us at Mbarali DC Mawindi, Kangaga, Tanzania. We have a 24/7 customer support team ready to assist you with any questions or concerns you may have.