African Honey Badger Facts: The Fearless Creature of the Savanna
The African honey badger, often called the ratel, is a small but mighty creature that garners respect and even fear from animals many times its size. Don’t let their adorable name fool you; these animals are notorious for their ferocious attitude and incredible resilience. This article delves deep into fascinating African Honey Badger Facts, exploring their behavior, diet, habitat, and why they’ve earned the title of “world’s most fearless animal.”
The Honey Badger’s Fearless Reputation: More Than Just Hype
While small in stature, measuring around 2 feet long, African honey badgers possess an incredibly tough hide. This loose skin,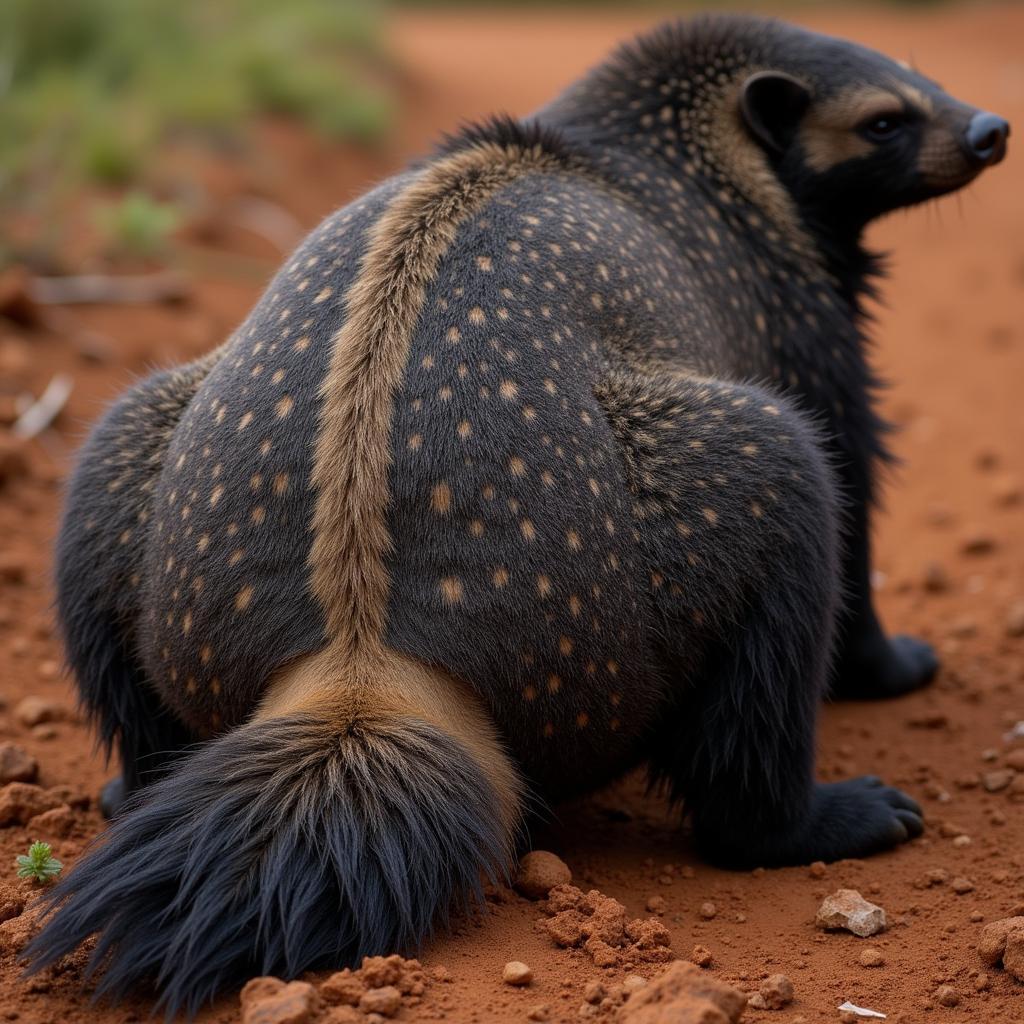  Honey badger with thick skin, is their secret weapon, allowing them to twist and turn with incredible flexibility even when caught in the jaws of a predator. This, combined with their powerful claws and sharp teeth, makes them a formidable opponent for any attacker, from lions and leopards to hyenas and pythons.
Honey badger with thick skin, is their secret weapon, allowing them to twist and turn with incredible flexibility even when caught in the jaws of a predator. This, combined with their powerful claws and sharp teeth, makes them a formidable opponent for any attacker, from lions and leopards to hyenas and pythons.
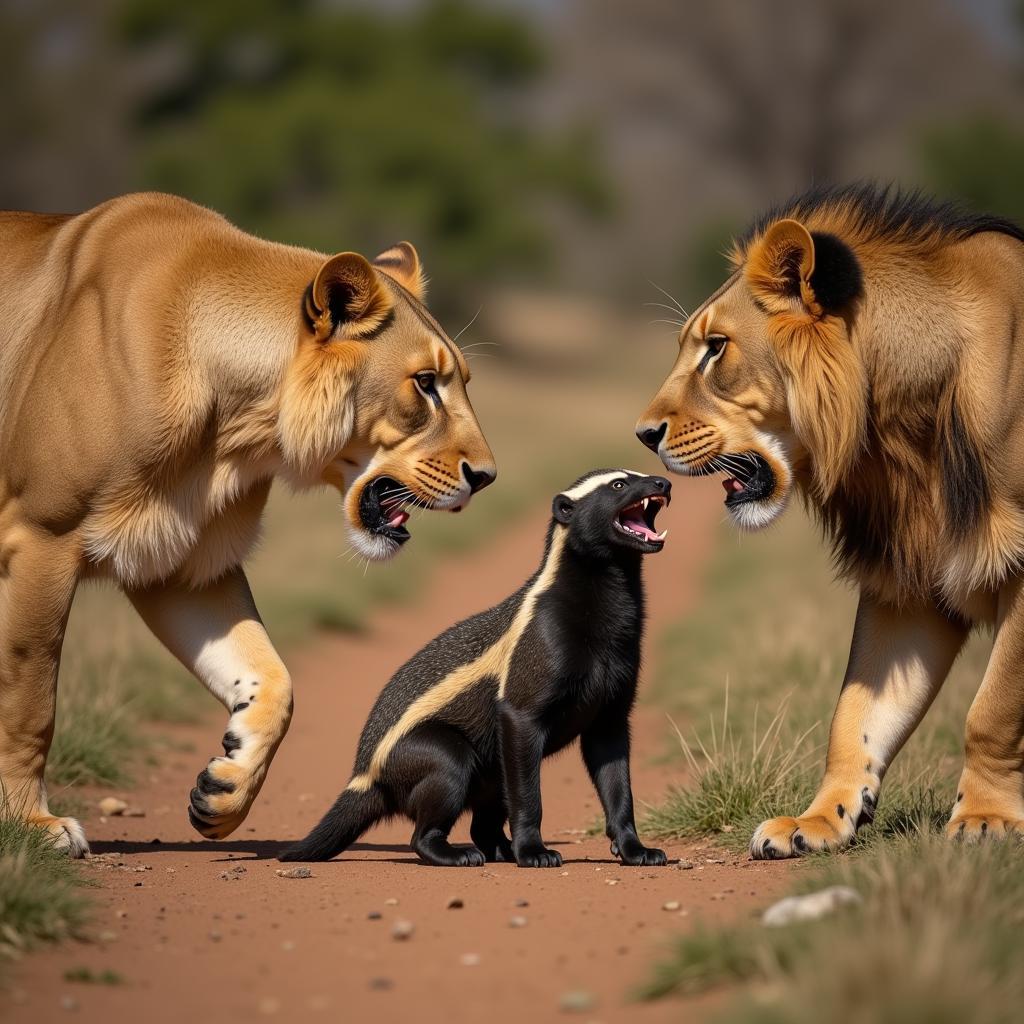 Honey badger facing off against lions
Honey badger facing off against lions
A Sweet Tooth and a Diverse Palate
The African honey badger’s love for honey is no secret, hence the name. But their diet extends far beyond this sweet treat. They are opportunistic omnivores, consuming a wide variety of food, including insects, snakes (even venomous ones!), birds, rodents, and carrion. Their strong sense of smell and powerful claws enable them to dig out burrows, uncovering hidden prey.
“Honey badgers are incredibly intelligent and resourceful when it comes to finding food,” says Dr. Sarah Njeri, a wildlife biologist specializing in African predators. “They’ve been known to use tools, like sticks, to reach honey in high places and even collaborate with honeyguides (birds) to locate beehives.”
Adaptable Survivors in Harsh Environments
African honey badgers inhabit a wide range of habitats across sub-Saharan Africa, from dry savannas and grasslands to dense forests. They are highly adaptable creatures, capable of thriving in diverse environments. Primarily solitary animals, they are most active at dusk and dawn, using their keen senses to navigate and hunt in low-light conditions.
Honey Badger Reproduction and Life Cycle
Honey badgers are generally solitary creatures, coming together primarily for mating. Females give birth to litters of 1-3 cubs in underground burrows. The young remain with their mothers for several months, learning essential survival skills before venturing out on their own. While the average lifespan in the wild is unknown, they can live up to 24 years in captivity.
Conservation Status: Least Concern, But Still Vulnerable
The African honey badger is currently listed as “Least Concern” by the IUCN, indicating that their populations are relatively stable. However, they still face threats from habitat loss, human-wildlife conflict, and the illegal wildlife trade. Conservation efforts focus on mitigating these threats and ensuring the long-term survival of this fascinating species.
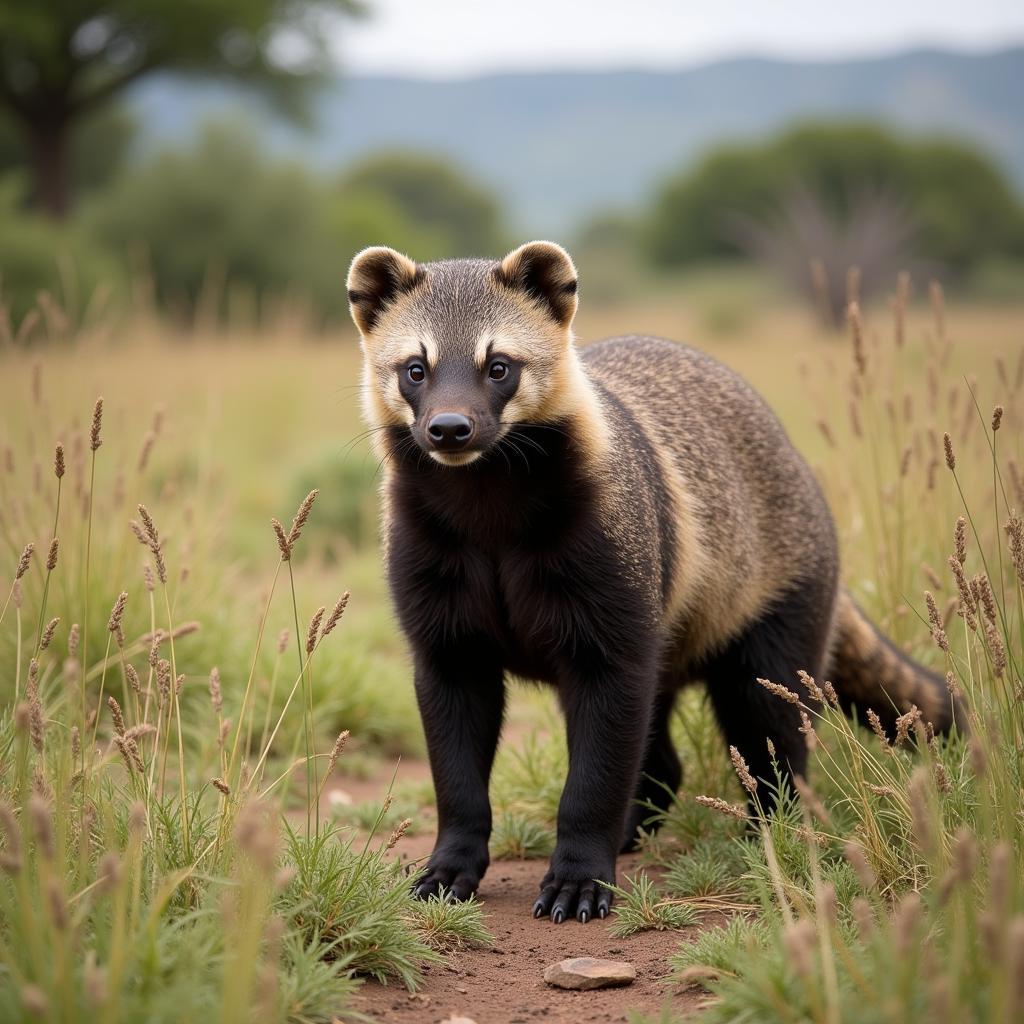 Honey badger in its natural habitat
Honey badger in its natural habitat
Conclusion: The Enduring Spirit of the African Honey Badger
The African honey badger’s reputation as a fearless and tenacious creature is well-deserved. From their incredibly tough hide and powerful defenses to their adaptability and resourcefulness, these animals are true survivors. Their story serves as a reminder of the incredible diversity and resilience of life on the African continent and the importance of protecting these creatures and their habitats for generations to come.