The Enigmatic African Horned Pit Viper: A Comprehensive Guide
The African Horned Pit Viper, a creature shrouded in both fascination and fear, embodies the enigmatic nature of the African wilderness. This venomous snake, scientifically known as Cerastes cerastes, is easily recognizable by its distinctive horn-like scales above each eye, making it a truly remarkable reptile.
Unveiling the Secrets of the Cerastes Cerastes
The Cerastes cerastes, also commonly referred to as the Sahara horned viper or desert horned viper, inhabits the arid regions of North Africa and parts of the Arabian Peninsula. Its unique adaptations to harsh desert environments have led to intriguing behavioral patterns and remarkable survival strategies. This snake exemplifies how nature’s ingenuity allows creatures to thrive in even the most challenging of habitats.
Physical Characteristics: A Master of Camouflage
The African horned pit viper’s most striking feature is, of course, the pair of supraocular “horns”. These modified scales can vary in size and shape between individuals, adding to the viper’s mystique. Their body coloration ranges from sandy yellow to reddish-brown, blending seamlessly with the surrounding desert landscape. This camouflage proves invaluable for ambushing prey and avoiding predators. The viper typically reaches a length of 30-60 cm, with females generally being larger than males.
Hunting Prowess: A Patient Predator
The African horned pit viper is a master of ambush, employing a unique hunting technique known as “sidewinding”. This allows it to move sideways across loose sand with surprising speed and efficiency. It patiently lies buried in the sand, patiently waiting for unsuspecting prey to wander within striking distance. Its diet primarily consists of small rodents, lizards, and birds.
Venom and Defense: A Potent Arsenal
The African horned pit viper possesses hemotoxic venom, which disrupts blood clotting and can cause significant tissue damage. While not generally considered life-threatening to humans, a bite from this viper requires immediate medical attention. The horns themselves play no role in venom delivery but may contribute to the snake’s cryptic appearance, breaking up its outline against the sand.
Conservation Status and Threats: Protecting the Desert Jewel
While the African horned pit viper is not currently considered endangered, habitat loss due to human encroachment and climate change poses a potential threat to its long-term survival. Understanding the role this fascinating creature plays in its ecosystem is crucial for implementing effective conservation measures.
Adapting to the Desert: A Story of Resilience
The African horned pit viper has evolved a suite of remarkable adaptations to thrive in the harsh desert environment. Its efficient sidewinding locomotion, cryptic coloration, and ambush hunting strategy all contribute to its success in this challenging ecosystem. Furthermore, its ability to tolerate extreme temperatures and conserve water allows it to survive in regions where few other creatures can.
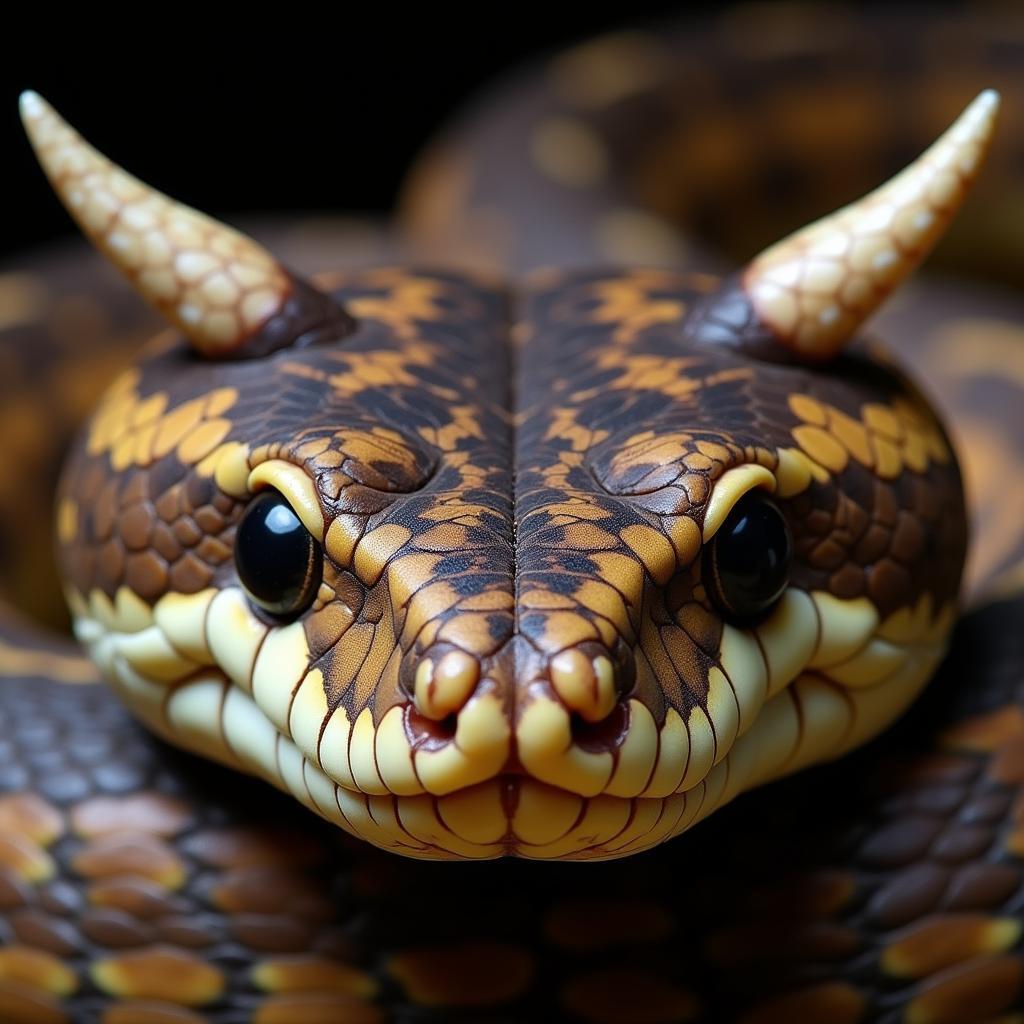 Close-up View of an African Horned Pit Viper
Close-up View of an African Horned Pit Viper
Conclusion: The Allure of the African Horned Pit Viper
The African horned pit viper, with its unique horns, captivating camouflage, and impressive adaptations, stands as a testament to the remarkable biodiversity of the African continent. Understanding and appreciating these fascinating creatures is essential for their continued survival and the preservation of their fragile desert habitats. Let’s protect this unique creature for generations to come. Learn more about other fascinating African wildlife by exploring other articles on our website.
FAQ
- Are African horned pit vipers dangerous to humans? While their venom is potent, bites are rarely fatal with prompt medical treatment.
- What do African horned pit vipers eat? Their diet primarily consists of small rodents, lizards, and birds.
- Where do African horned pit vipers live? They are found in the arid regions of North Africa and parts of the Arabian Peninsula.
- How do African horned pit vipers move? They utilize a specialized sidewinding motion for efficient travel across loose sand.
- What is the purpose of the horns on the African horned pit viper? While the exact function is debated, they are thought to aid in camouflage.
- How big do African horned pit vipers get? They typically grow to be 30-60 cm in length.
- Are African horned pit vipers endangered? They are not currently listed as endangered, but habitat loss is a growing concern.
When you need assistance, please contact us at Phone: +255768904061, Email: kaka.mag@gmail.com or visit us at Mbarali DC Mawindi, Kangaga, Tanzania. We have a 24/7 customer service team.